Managing CPU power is crucial for determining laptop battery life or the amount of electricity consumed by a PC. Incorrect power usage can lead to direct hardware consequences. In this article, we will discuss how to optimize CPU performance to accurately manage power consumption.
I. CPU States
CPU states are determined by its current function, including:
- P State
- C State
1. P State
The processor is in P state when it's operating with normal functionality. It's a way to scale the processor's operating frequency against the voltage at which it consumes minimum power.
Before moving forward, it's crucial to understand the concepts of processor frequency and voltage.

We've all heard about CPU frequencies, such as 2.2 GHz or 2.4 GHz,… These are the clock frequencies at which the CPU performs its functions. For example, a 2.4GHz CPU completes a task fastest in 1 second. By logic, when the frequency is halved, that CPU will take 2 seconds to process.
This is the case for older CPU systems. However, newer CPUs do not adhere to this rule. Instead, they adjust the input voltage to efficiently carry out tasks.
Therefore, each CPU has its own P states, which are states that adjust both frequency and input voltage to optimize performance and complete tasks as quickly as possible.
2. C State
C State is not as intricate as P State. CPU achieves C state when it's running idle. C state depends on the functions that the processor cuts off to save power. The more functions and tasks it halts, the more power it saves.
II. What are CPU Minimum and Maximum States?
CPU Minimum State defines the minimum frequency at which a processor runs when idle. By default, Windows 10 sets the CPU minimum state to 5%, which can be adjusted to as low as 0%.

CPU Maximum State is the percentage at which the CPU operates at maximum workload. The CPU will queue tasks and process them sequentially upon reaching the maximum operating threshold. By default, the CPU Maximum State is set to 100%, but you can also lower it to maintain CPU temperature.
III. Adjusting CPU Power in Windows 10
Adjusting CPU power depends on user experience. For instance, if you're engaging in heavy tasks and pushing the CPU to operate at 90%, causing the computer to overheat, then set the maximum CPU state to 70% to prevent overheating. However, processing time will decrease slightly.
Experiment to find out how to adjust CPU power consumption to suit your computer.
Step 1: Press Windows + X and select Power options from the displayed menu.
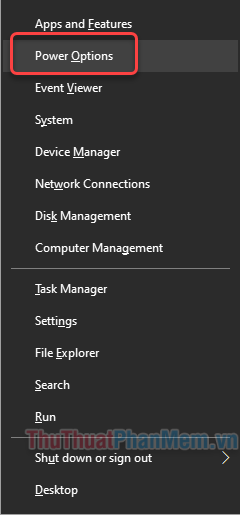
Step 2: The Settings window will appear. Click on Additional power settings.

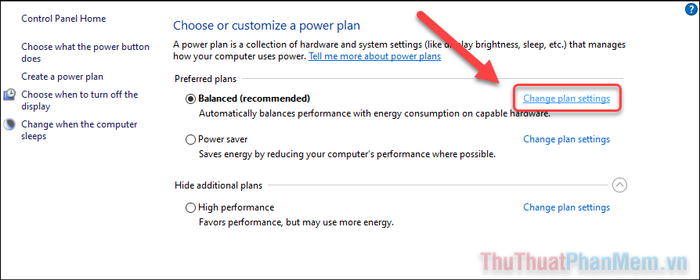
Step 3: Press Change plan settings next to the power plan you're currently using (usually Balanced).
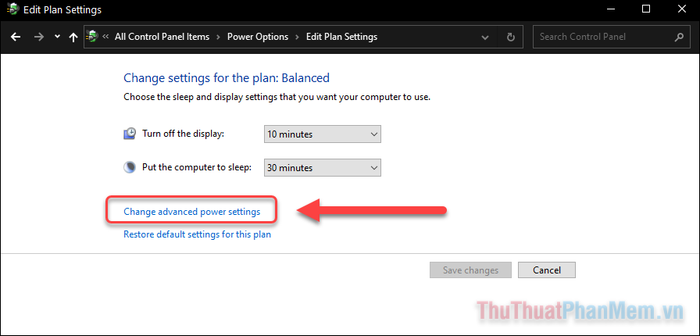
Step 4: Now, click on Change advanced power settings.
Step 5: In the Power Options window, expand Processor power management.
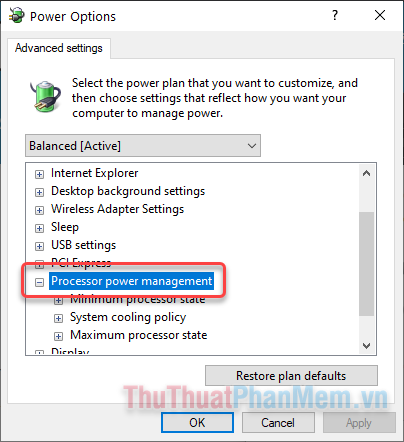
Step 6: Set the Minimum and Maximum processor states according to your usage needs.
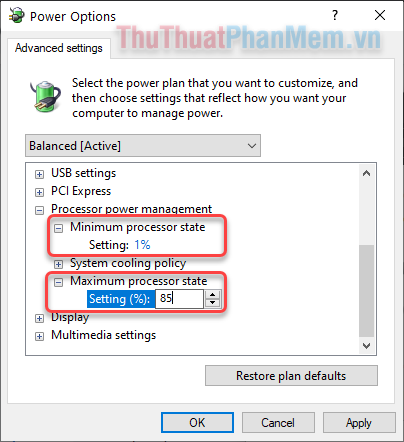
Step 7: Once completed, click on Apply and OK.
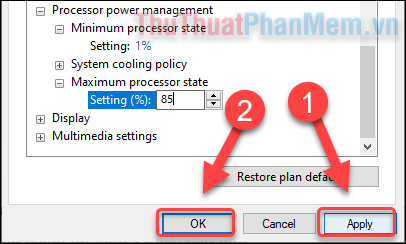
Your CPU power management settings will be applied immediately. If you wish to revert to the default settings, simply return to the Power Options window and select Restore plan defaults.
Conclusion
As previously mentioned, adjusting CPU power depends on your computer usage experience. However, it's advisable not to set the CPU's Maximum state too high, especially if you notice the computer overheating and the fan running excessively. High temperatures can damage your computer.
