Nvidia cards are often praised for their performance, low temperature, and compatibility with top games. If you're using an Nvidia card, these small tricks can help you tweak its graphics performance, giving you a smoother and more stable gaming experience.

1. Optimizing NVIDIA Graphics Card in NVIDIA Control Panel
The Nvidia Control Panel is Nvidia's default driver that allows us to interact with the graphics card and adjust various parameters provided by the manufacturer, such as effects, screen resolution, and performance levels. Note that performance is inversely proportional to quality. If you want the best quality in your games and images, the 'Quality' option in the Nvidia Control Panel will give you the clearest and most beautiful visual effects. However, the 'Performance' mode will sacrifice graphics quality for a higher frame rate (FPS), resulting in a significantly smoother gaming experience.
Step 1: Right-click on your Desktop and select NVIDIA Control Panel.
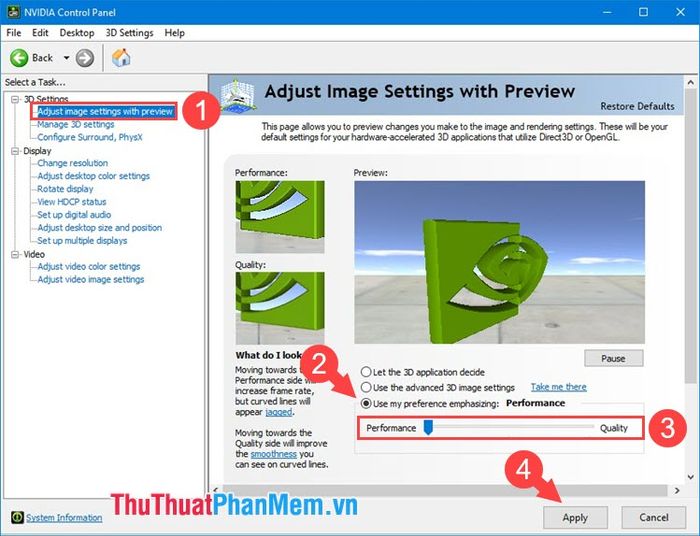
Step 2: Choose Adjust image settings with preview (1) => Use my Preference Emphasizing (2). Then, adjust the slider to either Performance or Quality based on your needs and computer configuration. To save the settings, click on Save (4).
2. Advanced Settings Adjustment in NVIDIA Control Panel
If the default settings don't satisfy you, you can optimize your NVIDIA card manually. However, you need to understand image processing terminologies to set it up properly and efficiently for your card.
Step 1: Right-click on your Desktop => select NVIDIA Control Panel.
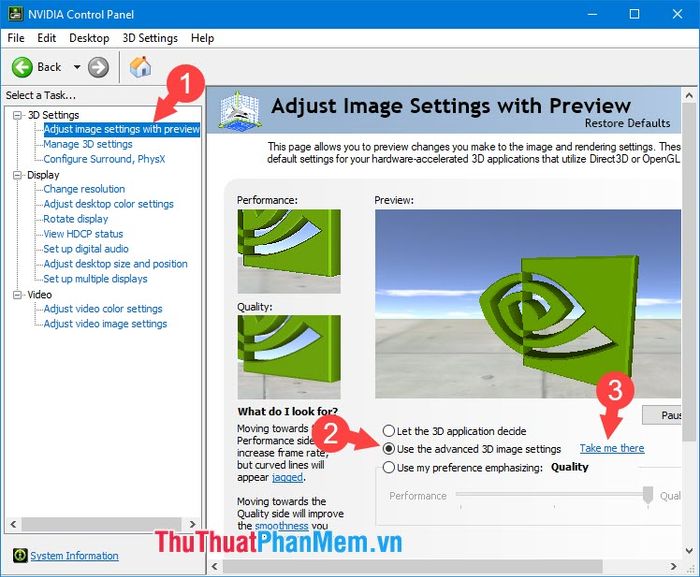
Step 2: Choose Adjust Image Setting With Preview (1) => Use the advanced 3D image settings (2) => Take me there (3).
Step 3: Next, navigate to the Global Settings section to fine-tune your NVIDIA card.
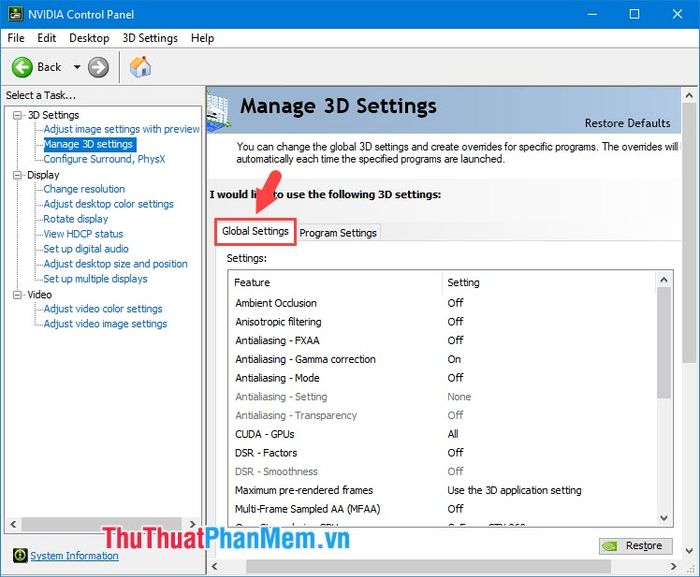
2.1. Ambient Occlusion
Ambient Occlusion is known for its light shading effect, providing you with realistic game scenes with light shining on objects. This technology is the precursor to Ray Tracing technology equipped on NVIDIA's RTX cards. However, Ambient Occlusion is still a basic feature on all cards, and we have three main options to adjust in the NVIDIA Control Panel: Off, Performance, Quality. Your task is to choose the settings according to your usage needs and based on your card. If you own high-end Nvidia cards with a powerful PC setup, Quality will give you the best gaming experience. However, if you only have a mid-range Nvidia card with an average PC setup, choosing Off or Performance will provide you with higher frame rates and smoother gameplay when tackling heavy games.
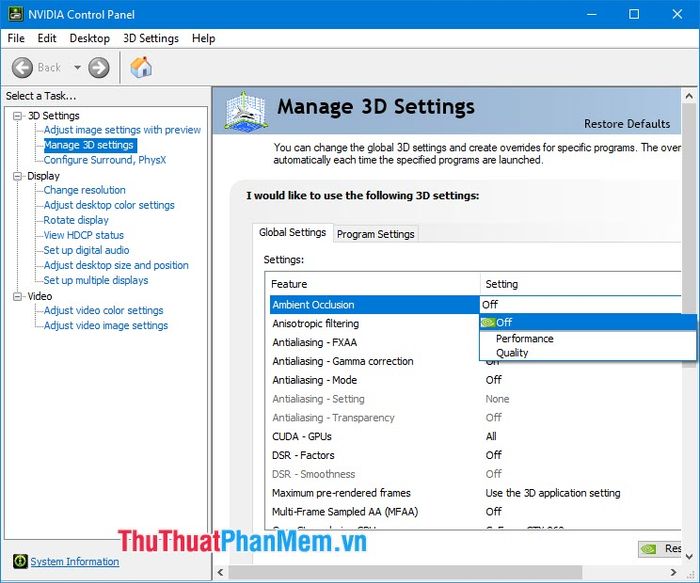
2.2. Anisotropic Filtering
This feature enhances image clarity, especially for objects in the distance. Anisotropic filtering is like being equipped with a very powerful zoom lens camera where you can see objects clearly. However, this feature consumes a lot of computer resources as it processes distant objects, and you should not set it to 16x if you own a high-end card with a powerful hardware setup.

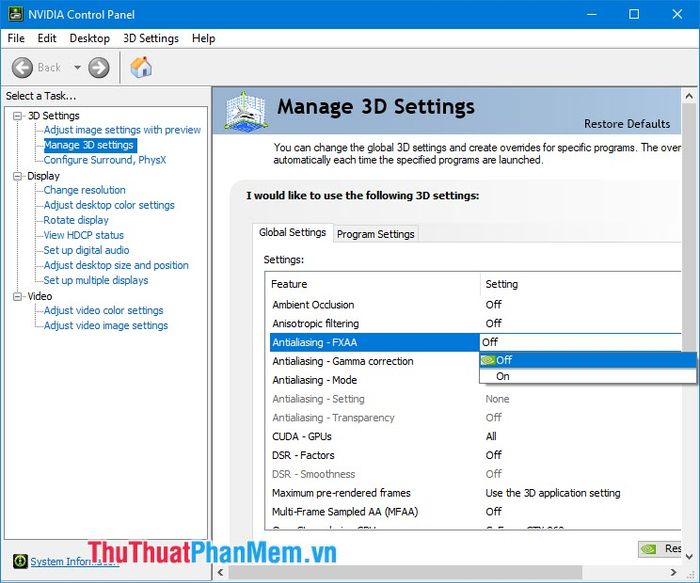
2.3. Antialiasing – FXAA/Gamma Correction
FXAA – Fast approximate anti-aliasing is responsible for smoothing out jagged edges, making the image much smoother. After the initial anti-aliasing process, FXAA acts as the second layer to blur the remaining jagged details of the image, making it look beautiful and more realistic. You can choose Off to disable it, which slightly improves performance during gaming.
Gamma correction adjusts brightness in the Antialiasing technique. This feature should be enabled along with FXAA to enhance the image realism. Otherwise, it's better to turn off both features rather than enabling just one.

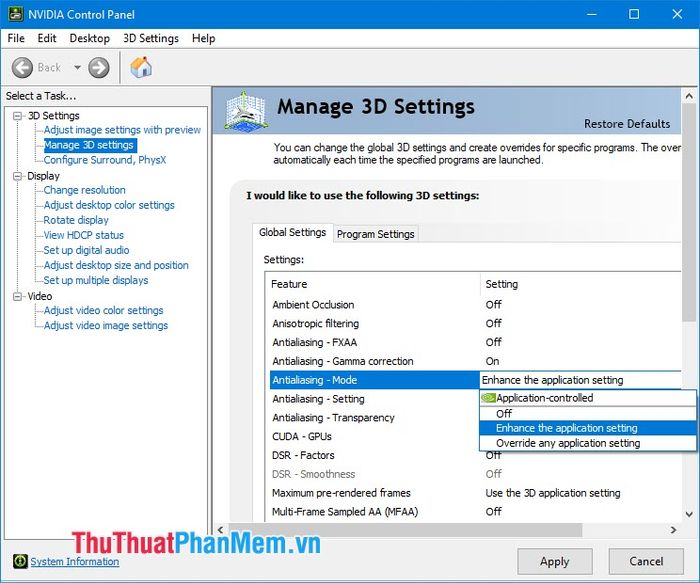
2.4. Antialiasing – Mode/Settings/Transparency
Next in the Antialiasing section, we have additional settings to make the antialiasing process more realistic. If you set Mode to Off, you won't be able to configure Settings and Transparency. Choosing Enhance the Application setting will enhance antialiasing along with the game. For example, if you set Enhance 2X and the in-game antialiasing to 2X, you'll have a total of 4X antialiasing. However, for games that don't allow antialiasing adjustments, this feature is useless, and you need to select Override any Application setting to override the game settings and customize the antialiasing as desired.
The Settings section allows you to adjust antialiasing from 2x to 8x. Set the configuration according to the game you want to customize, and avoid setting it to 8x if your system isn't powerful enough.
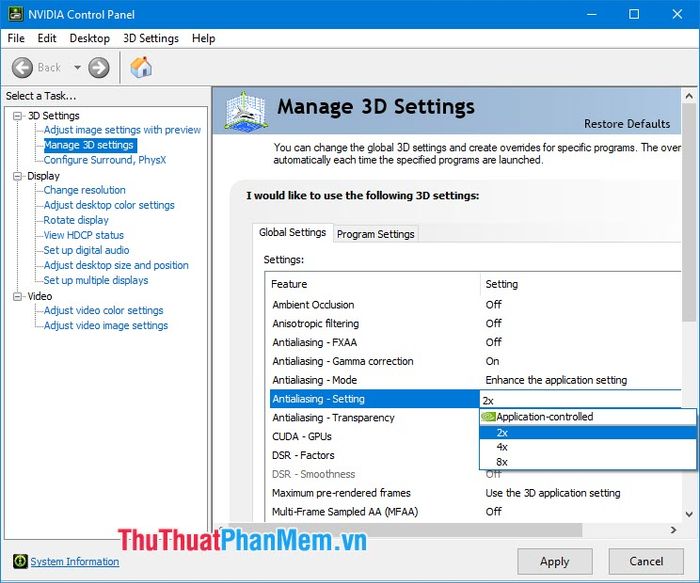
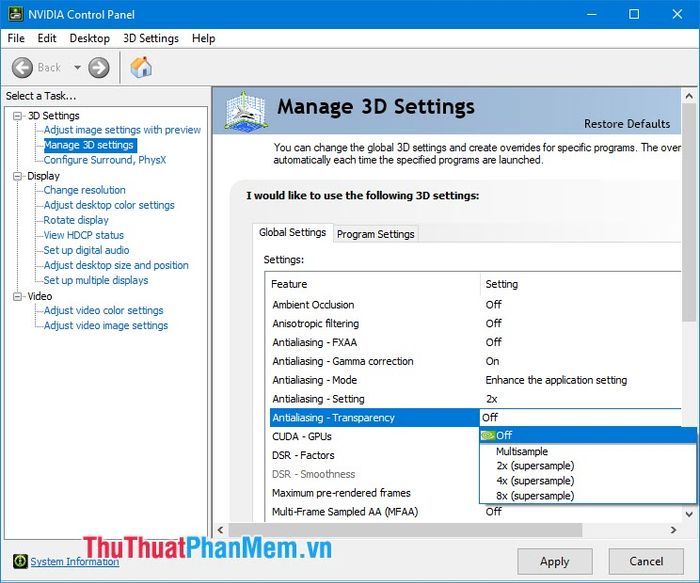
The Transparency part blurs jagged edges, making the image more realistic and less 'mechanical' looking. Set the option to match the setting in the Settings section for synchronized and best processing quality.
2.5. CUDA – GPUs
CUDA is considered the heart of graphics processing, similar to the cores in a CPU. However, CUDA cores here are quite numerous, with up to thousands of CUDA cores in a single card. Of course, the more cores, the better, and you should set CUDA – GPUs to All for high performance.

2.6. DSR – Factors/Smoothness
DSR or Dynamic Super Resolution is a feature that allows you to experience 4K resolution on a Full HD monitor. It's advisable to turn this option off as it consumes considerable resources on your PC due to the need for higher resolution. This feature is only useful when you have a powerful PC and want the image to be displayed on a large screen like a projector. DSR Smoothness complements DSR Factor in smoothing out the image when you upscale the resolution to 'super large'.

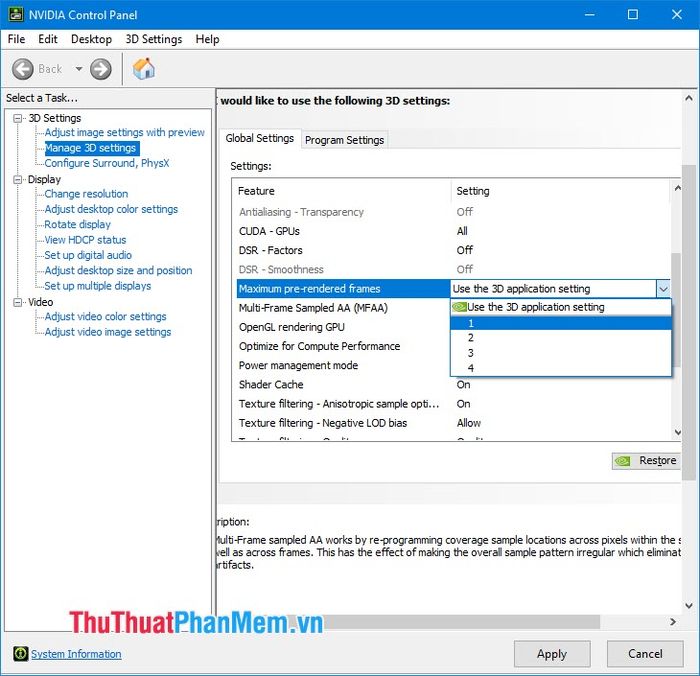
2.7. Maximum pre-rendered frames
This feature essentially means that the graphics card will process frames in advance to provide smooth gaming experience. It's recommended to leave it at default or set it to 1 to ensure the graphics card processes just enough frames, avoiding overloading.
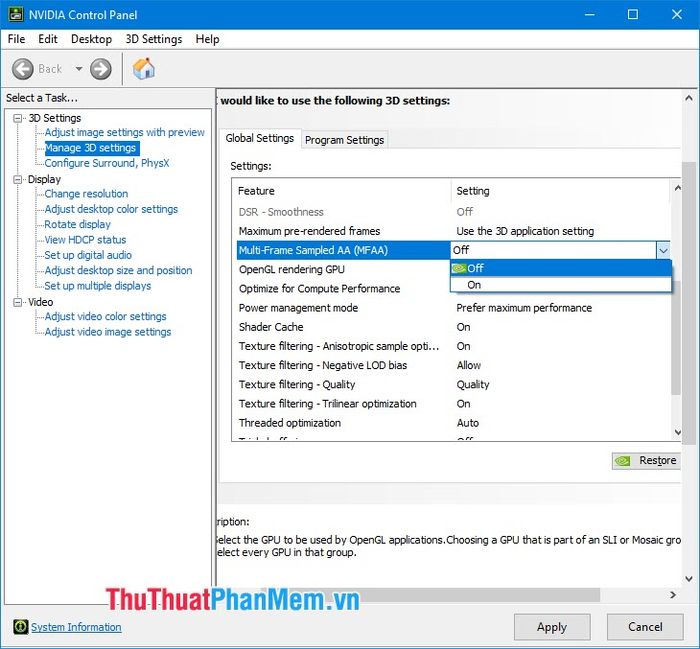
2.8. Multi-Frame Sampled AA (MFAA)
This is Nvidia's new anti-aliasing technology that accelerates the anti-aliasing process by preloading a graphics sample programmed in the processing software.
2.9. OpenGL rendering GPU
This option allows you to prioritize using the onboard graphics card or the Nvidia card. If your machine has two parallel cards (on a laptop), then naturally you should select the Nvidia card for primary graphics processing.

2.10. Optimize for Compute Performance
This feature serves image and video processing programs like Adobe Premiere, Adobe Encoder, enabling Nvidia cards to optimize computational capacity and allocate suitable performance for the software and workload. You can disable it if you're not using an Nvidia card for work purposes.

2.12. Power management mode
The power management mode helps you control power consumption. If you're using a laptop with an Nvidia card, the Optimal power option will provide impressive battery life, while if you're plugged in or using a desktop, it's advisable to set it to Prefer maximum performance for the best performance.
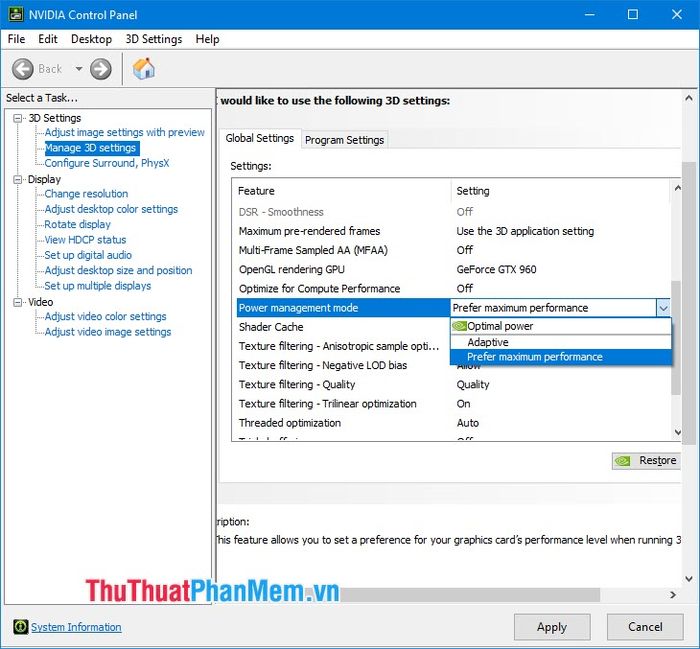
2.13. Shader Cache
When processing shaders, a data amount is stored in your computer's memory to accelerate processing. If your computer is equipped with an SSD, this feature is truly useful and helps your graphics card process faster. However, if your card is already powerful enough, this feature is not very necessary, and disabling it will help free up some memory capacity.
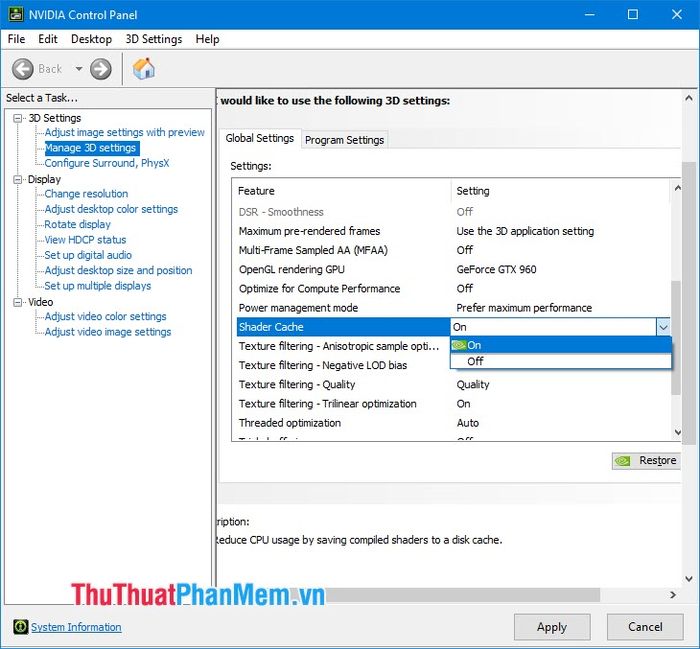
2.14. Texture filtering – Anisotropic sample optimization/Negative LOD Bias/Quality/Trilinear optimization
This setting is to increase detail for images and games, and we often see texture settings in games ranging from Low to Ultra.
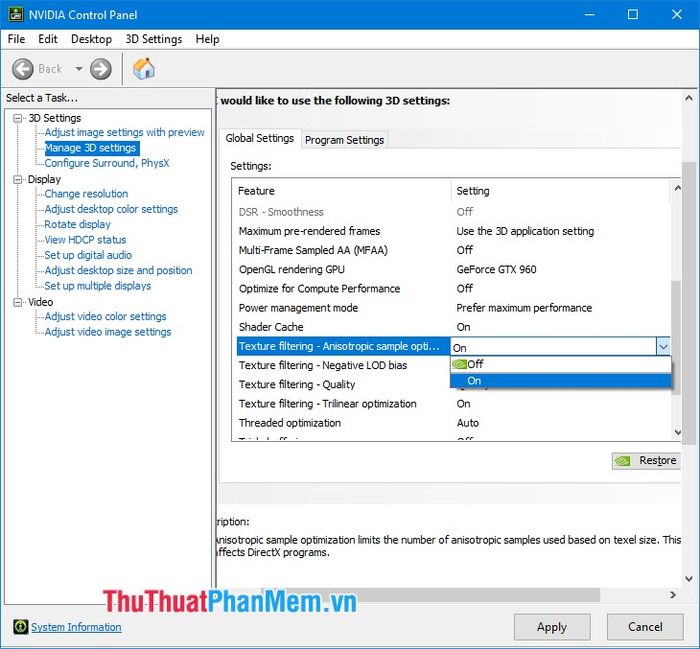
Anisotropic sample optimization: Optimize for graphic detail. Set this option to Off to avoid limiting your card's processing capability.
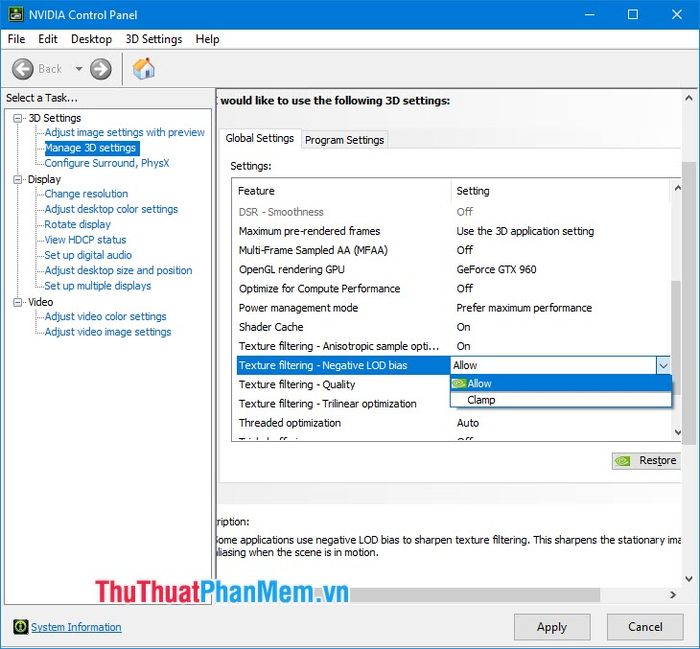
Negative LOD bias: This option adjusts the level of detail, and you should set it to Allow if you disable the Anisotropic sample optimization option, and vice versa, set it to Clamp if you enable Anisotropic sample optimization.
Quality: If you want the best performance when gaming, the High performance option will give you slightly higher FPS, while the High Quality option will provide beautiful, realistic images but trade off some performance decrease.
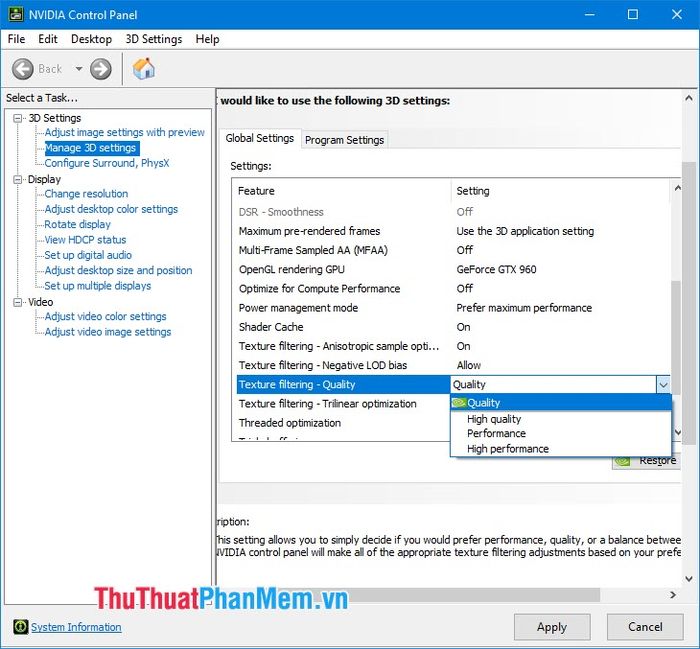
Trilinear optimization: helps blend two color gradients for realistic color representation. You can turn it on or off depending on your machine's configuration and the game you intend to play.
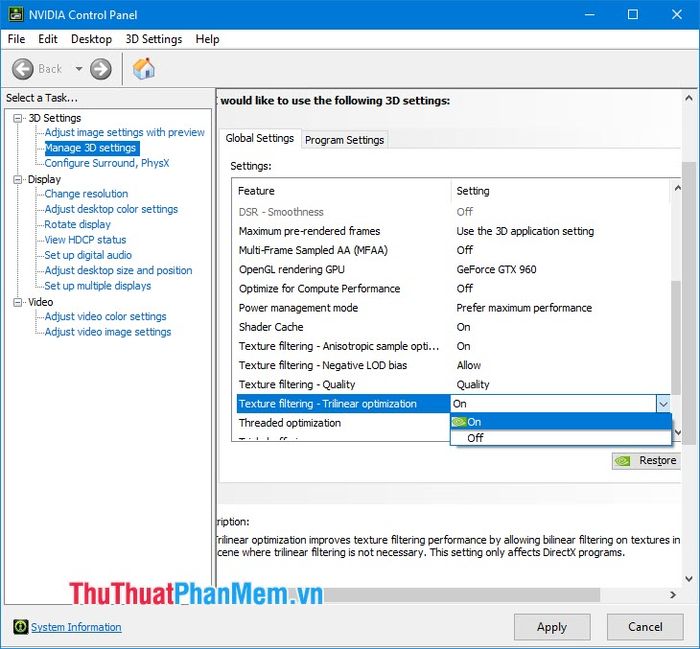
2.15. Threaded optimization
This feature optimizes the number of threads used on the CPU, especially on CPUs that support Hyper Threading. Enabling this feature will slightly increase FPS when the CPU automatically boosts clock speed, but sometimes it may decrease FPS depending on the CPU's performance at that time.
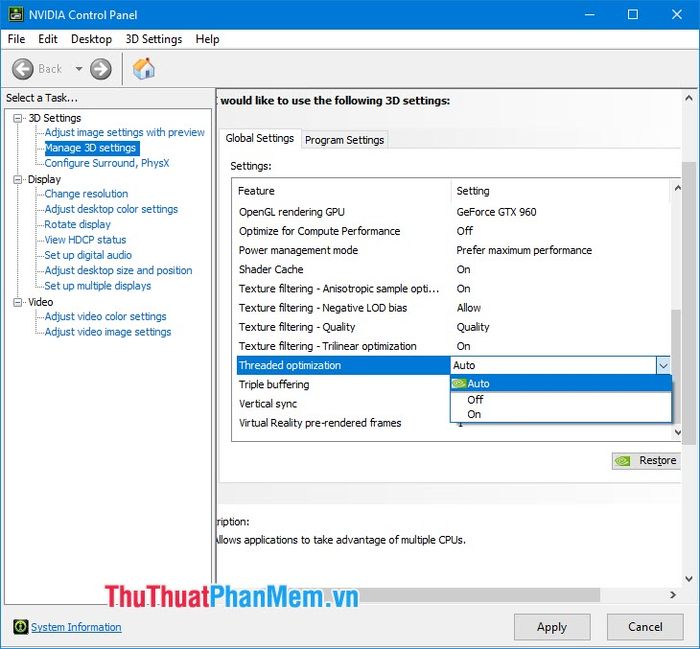
2.15. Triple buffering
Triple buffering handles the frame smoothing process to prevent FPS from dropping below half. You should enable this option when you turn on V-Sync.
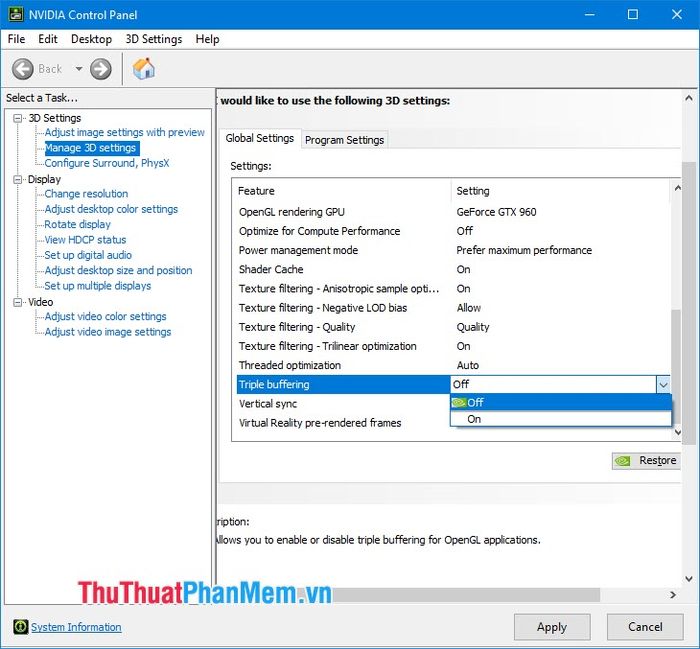
2.16. Vertical sync
V-sync, also known as vertical synchronization. This feature helps maintain FPS at a stable level and prevents it from dropping too low.
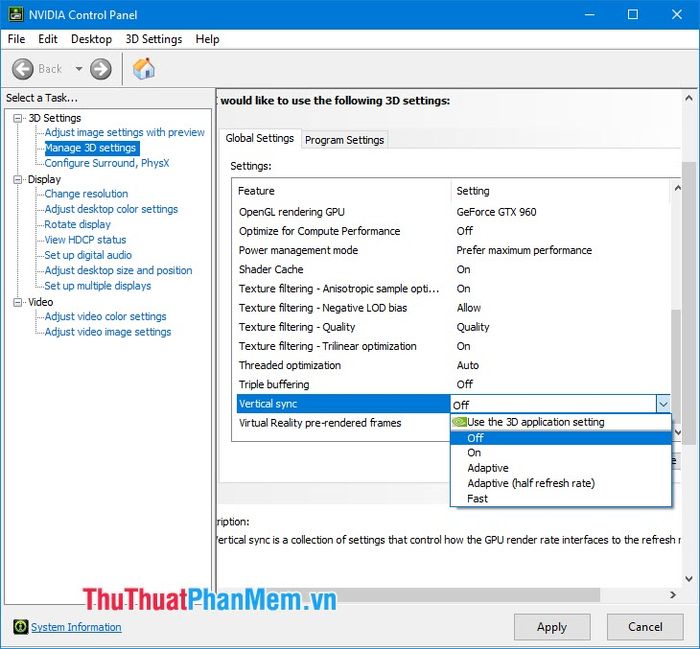
2.17. Virtual Reality pre-rendered frames
The Virtual Reality pre-rendered frames feature, similar to Maximum pre-rendered frames, creates pre-rendered frame samples to improve image performance and smoothness. However, this feature is for games that support virtual reality (VR) headsets, and you should leave it at the default setting of 1 to optimize between performance and computer resources.
3. Utilize Geforce Experience for optimization
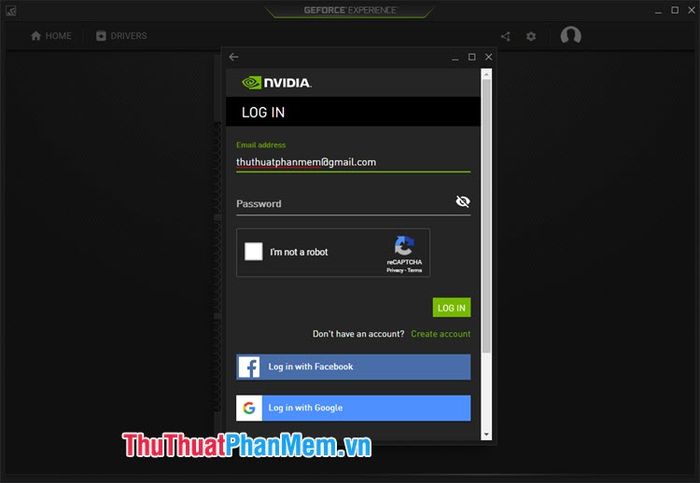
Firstly, download and install Geforce Experience from https://www.nvidia.com/vi-vn/geforce/geforce-experience/
Geforce Experience is Nvidia's tool for optimizing and enhancing gaming performance. Begin by downloading and installing Geforce Experience. Next, create an account to log into the Geforce Experience service. You can use a Gmail or Facebook account to quickly create a Geforce Experience account.
Once successfully logged in, open any game to play. Afterward, the list of games you've played will appear within the Geforce Experience interface. To optimize, simply click on the desired game and run it within Geforce Experience for automatic optimization.

With the insights shared in the article, you can enhance your gaming experience to a whole new level with your Nvidia card. Wishing you all success!
