In this guide, we'll show you how to check XMP functionality, verify RAM speeds, and troubleshoot if necessary.
What is XMP?XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) is a feature that allows RAM modules to operate at their advertised speeds, bypassing the default limitations set by the system.

XMP là gì?
Demystifying XMP: Unleashing RAM Performance Across Platforms
So, what exactly is a 'memory profile'? Put simply, it's a set of pre-defined frequency, voltage, and timing parameters that a
RAMmodule can use to operate at speeds higher than its default specifications. Think of it as overclocking RAM, but with meticulously tested timings, voltages, and frequencies for optimal stability, minimizing the risks associated with traditional overclocking, and enabling PC builders to easily achieve maximum speeds.
How to Check RAM's XMP?
Checking current RAM speed is straightforward: simply open Windows Task Manager (Ctrl + Alt + Del or Ctrl + Shift + Esc), then select the Performance tab. Click on Memory and you'll see all the necessary details, as shown in the image below.
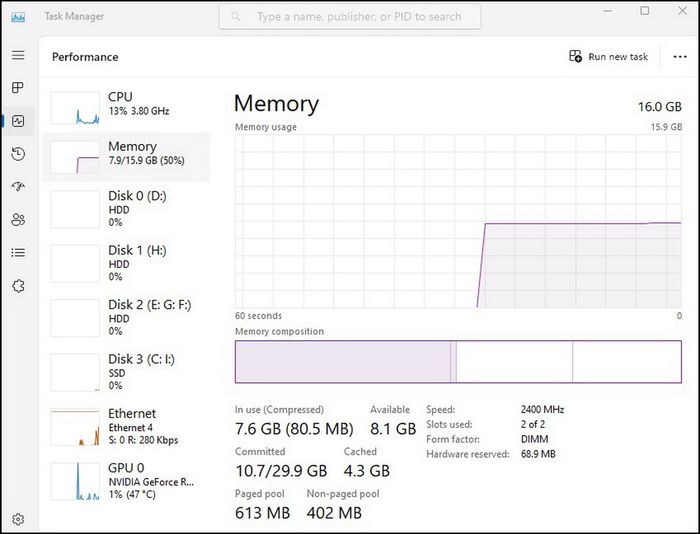
Unveiling RAM Speeds: Troubleshooting and Activating XMP
If you're confident in your motherboard and CPU compatibility, yet your RAM isn't hitting the right speeds, the only solution is to delve into the BIOS and tweak a few settings to boost your RAM's performance. Despite sounding a bit 'high tech,' it's actually a straightforward process, and Mytour will guide you through the steps at the end of the article.
Why Isn't RAM Operating at the Right Speed?
You might wonder why RAM doesn't operate at its intended speed out of the box, requiring XMP activation. The reasons behind this issue are quite complex, as RAM speed depends on various factors like power supply, motherboard, memory controller on the CPU, etc.

Hence, the JEDEC organization has set a standard for the minimum speed that a RAM module must achieve. This is the speed at which your RAM modules will operate when plugged into the system, ensuring normal operation with any combination of motherboard, CPU, and existing RAM. Afterwards, you can activate XMP in the BIOS to unleash your RAM's advertised speeds.
How to Activate XMP in BIOS
As mentioned by Mytour above, XMP can be referred to as A-XMP or DOCP depending on the motherboard manufacturer you choose for your PC build. However, the activation process remains the same: you need to access the BIOS of your motherboard to find this feature. Below is a list of keys you can use to enter the BIOS with some well-known computer brands and motherboards:
- Acer, Asus: F2 or DEL.
- Dell: F2 or F12.
- HP: ESC or F10.
- Lenovo: F2 or Fn + F2.
- MSI: DEL.
- Microsoft Surface Tablet: Press and hold the volume up button.
- Samsung, Toshiba: F2.
- Sony: F1, F2, or F3.
Once in the BIOS, you need to search for one of the names mentioned by Mytour above, and switch 'disable' to 'enable' or 'off' to 'on'. Below is how to activate XMP on an Asus motherboard.
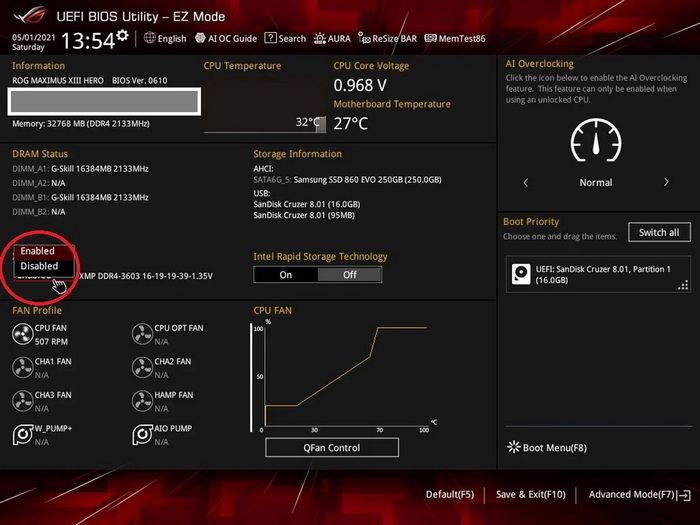
Additionally, you may need to select a suitable profile. Currently, there are two main versions of XMP: 2.0 and 3.0. XMP 2.0 has 2 common profiles for DDR4 RAM, and XMP 3.0 has 3 profiles (plus 2 user-defined) introduced alongside DDR5 RAM. To activate XMP, simply choose one of these profiles, save the changes, and restart your computer.
Is it Okay Not to Activate XMP?
All high-performance RAM modules utilize XMP because they run at speeds higher than the normal DDR standard. Without XMP enabled, they will operate at speeds dictated by your CPU, potentially not utilizing the designed higher frequencies. In most cases, this doesn't affect stability but simply prevents your built PC from reaching its maximum speed potential.
