
The REPLACE() function and REPLACEB() function both serve to substitute a portion of the input text string.
REPLACE() Function: It allows you to replace a part of the input text string with another text string, based on the specified number of characters. This function is used in single-byte character set (SBCS) languages. REPLACE() counts each character as 1, whether it's a single byte or a double byte character, regardless of the default language.
REPLACEB() Function: It helps replace a portion of the input text string with another string, based on the specified number of bytes. This function is used in double-byte character set (DBCS) languages. REPLACEB() counts each double-byte character as 2 when you're using the default language as DBCS; otherwise, it counts each character as 1.
Syntax
=REPLACE(old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text)
=REPLACEB(old_text, start_num, num_bytes, new_text)
In which:
- old_text: the text string you need to replace a number of characters.
- start_num: the position of the character in the text string to be replaced, starting from the left.
- num_chars: the number of characters in old_text that you want to replace with the new string.
- num_bytes: the number of bytes in the old_text string that you want to replace with the new string.
- new_text: is the new text string that you want to replace for the characters in the old_text string.
Example
- Replace 6 characters starting from the 16th character in the string at cell B5 with the new string '.vn'.
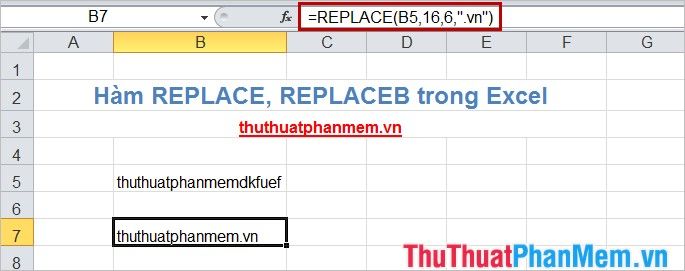
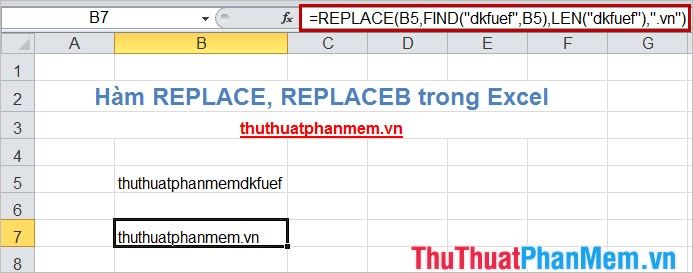
- Alternatively, instead of counting characters or specifying the number of characters to replace, you can use the FIND() or SEARCH() function to determine the start position (start_num) and use the LEN() function to determine the number of characters in the string to be replaced (num_chars).
=REPLACE(B5,FIND('dkfuef',B5),LEN('dkfuef'),'.vn')
Now you have learned how to use the REPLACE() and REPLACEB() functions in Excel. You should combine them with other functions to achieve the best results. Wishing you success!
