Learning how to measure a room accurately is essential for various home improvement undertakings, such as flooring installation and painting. Depending on your project, you'll need to take different measurements. For instance, if you're installing flooring, you'll need to determine the floor area. If you're painting, you'll need measurements for the walls and ceiling. This task might seem daunting if you're unfamiliar with it, especially when dealing with features like slanted ceilings, alcoves, and bay windows.
Steps
Measuring Floor Space
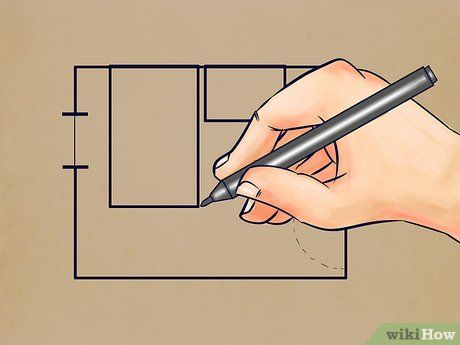
Create a floor plan sketch of the room you're measuring. Use this sketch to jot down your measurements. While it doesn't have to be perfectly to scale, the more accurate it is, the more helpful it will be.
- Since you're focusing on floor measurements, details like windows and doors are not crucial.
- Include all relevant areas in your project. For instance, if you're installing flooring and also working on a walk-in closet, make sure to include the closet in your sketch.
- In the example sketch, there's a bathroom to the right (considered a separate room, hence not included in the drawing) and a bay window to the left (represented by a semicircle).
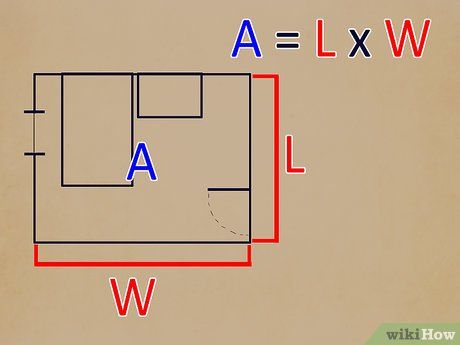
Determine the length and width of the main area of the room. Use the standard formula (Length) x (Width) = Area to find the room's area. Measure the widest points for both length and width. This ensures accuracy in your measurements.
- Clear any obstacles or furniture blocking your measuring tape.
- Having a friend assist by holding one end of the tape may be helpful.
- Focus solely on measuring the main area, disregarding features like bay windows and separate rooms.
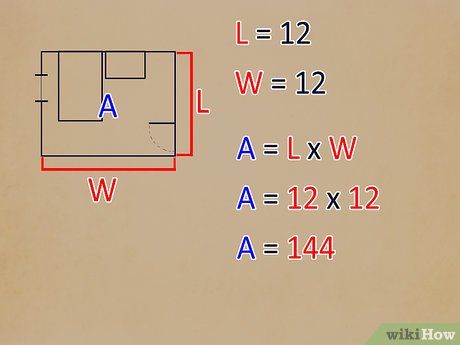
Calculate the main area by multiplying the length and width. Utilize a calculator for precision. For example, if the room measures 12 feet in width and 12 feet in length, the floor area is 144 square feet. Record this value on your sketch.
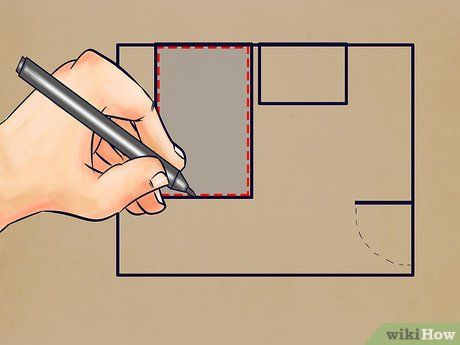
Measure any square or rectangular recesses. These typically include closets or bathrooms involved in flooring or tiling projects. Measuring these recesses follows the same process as the main area: measure width and length, then calculate the area by multiplying these dimensions.
- Note down the results in the recessed area of your sketch.
- Repeat for multiple recesses, if applicable.

Determine the area of circular recesses. Measure the longest length (often through the center) and width without extending beyond the main area already measured. Divide the length by two, then multiply by the width. Multiply this total by pi (3.14) and divide by two.
- Record the result in the recessed area of your sketch.
- This provides the area of the U-shaped protrusion within the room.
- Include the bay window area in the room's total only if it has a floor (not just a seat) and the ceiling is at least seven feet (2.13 meters) high.
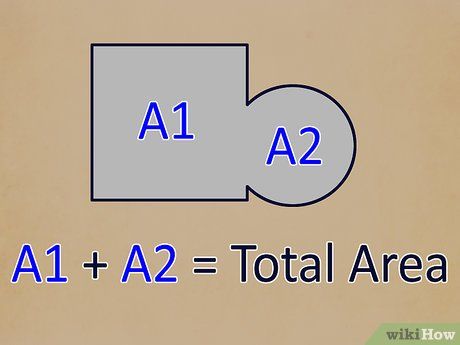
Combine all areas to find the total floor area. Sum up the areas of all recesses with the main floor area. Now, you have the total square footage of your floor, allowing you to purchase carpet, flooring, or other materials accordingly.
Measuring Walls

Create a sketch of all walls requiring measurement. Include doors and windows in your illustration. Leave space on the drawing to note down measurements.
Determine the width and height of the wall. To find the wall area, use the formula (Width) x (Height) = Area. With a measuring tape, measure the wall's width and height. As walls can be tall, consider seeking assistance from a friend or neighbor to hold the tape measure steady. Record the measurements on your sketch.
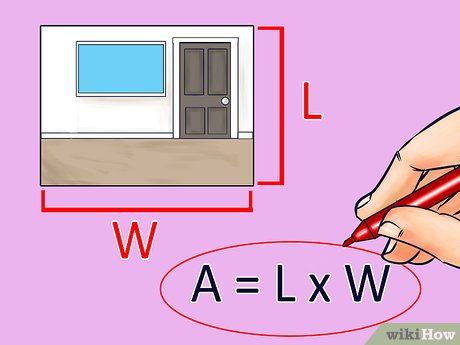
Multiply the length and width. Utilize a calculator to multiply the length and width, yielding the total square footage of the wall. Jot down this figure.
Measure the dimensions of any doors, fixtures, or windows. Record the dimensions of doors or windows on your sketch.

Calculate the area of any doors, fixtures, or windows by multiplying their length and width. Use a calculator to find the product of each door's or window's length and width. Record each total separately. These measurements represent the square footage of each door, window, or fixture.
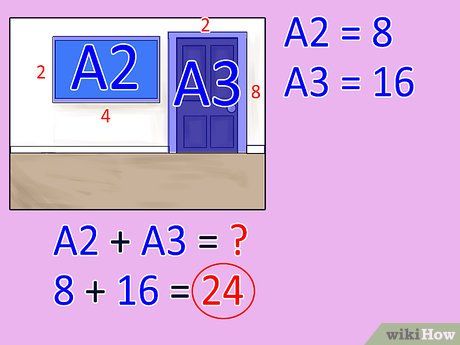
Sum up the total areas of all doors, fixtures, or windows. This step is relevant only for walls featuring multiple doors, fixtures, or windows. Note down this sum.
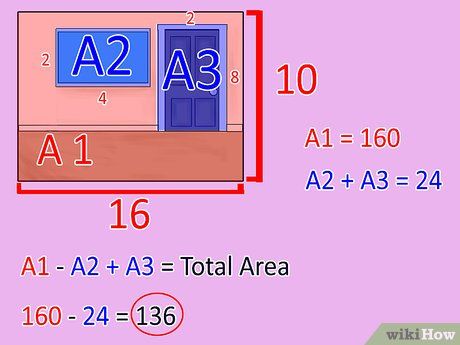
Subtract the sum from step six from the total wall square footage. Use a calculator for this computation as well. This resulting number represents the wall's square footage, which you can utilize when purchasing paint or wallpaper.
Measuring the Perimeter of a Room
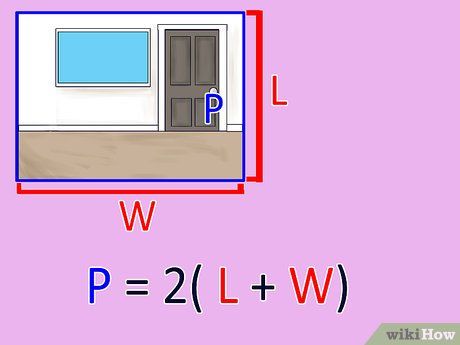
Determine the length and width of a square or rectangular room. Utilize the standard 2(Length + Width) = Perimeter formula to determine the perimeter of a room. With a measuring tape, ascertain the room's length and width.
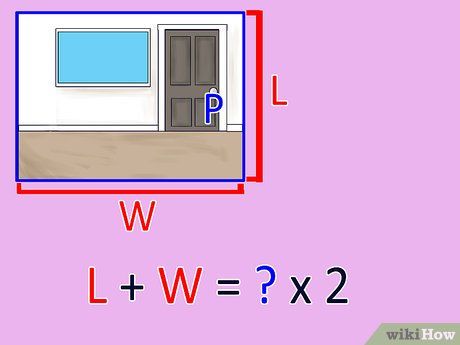
Combine the length and width, then multiply the result by two. Utilize a calculator to ensure accuracy in your addition and multiplication. After adding the length and width, double the total. This yields the perimeter of the room.

Measure a uniquely shaped room manually. If the room you're measuring isn't square or rectangular, you must measure each side of the room's perimeter individually. Traverse around the room's perimeter with a measuring tape, noting down the length of each side.
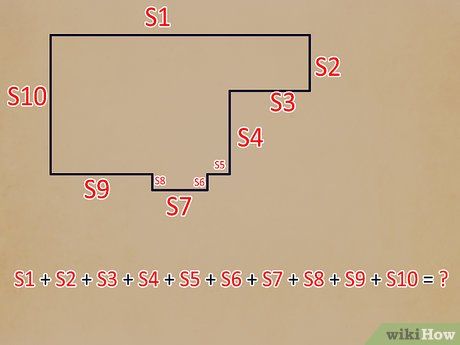
Total all the measurements. Use a calculator to sum up all measurements taken of the irregularly shaped room. The resulting sum represents the perimeter length of the room.
Measuring Room Ceilings
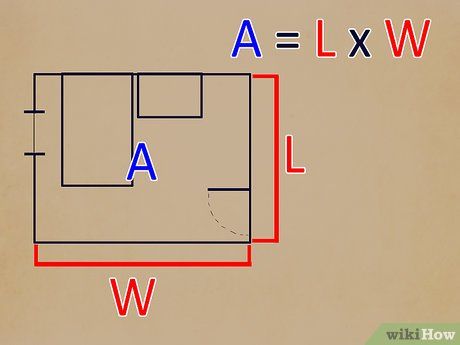
Determine the floor area. This method is outlined in step one. If the ceiling is flat, calculating the floor area automatically provides the ceiling area. For square or rectangular rooms with flat ceilings, the floor area equals the ceiling area. If there are any protrusions or recesses in the ceiling, proceed to step two.
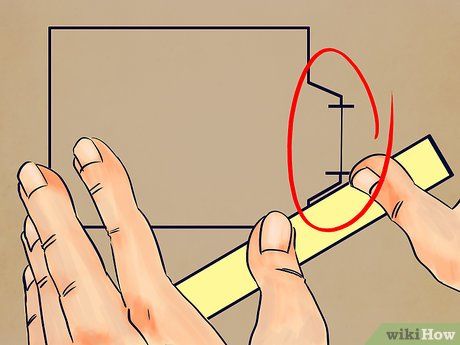
Measure any extensions to the ceiling area separately. This pertains to ceilings with non-flat surfaces. Many ceilings feature alcoves and window bays that protrude; measure the width and depth of these alcoves or window bays. Record all measurements.
- Ceilings with slopes, recesses, or irregularities will have a larger surface area than the floor, so consider this when purchasing materials (e.g., buy a little extra).
- Accessing ceilings can be challenging. If you're measuring a ceiling, enlist the help of a friend.
- You may need a ladder to reach the ceiling for measurement purposes.
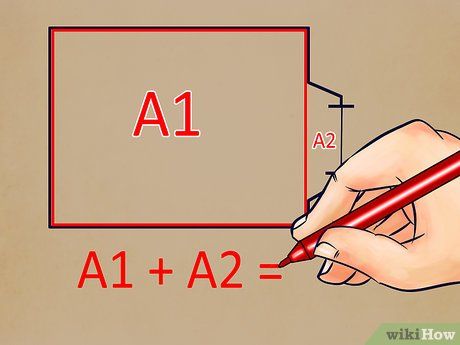
Incorporate additional ceiling measurements into the room's area. Add all supplementary measurements to the figure calculated in step one. Document the total.
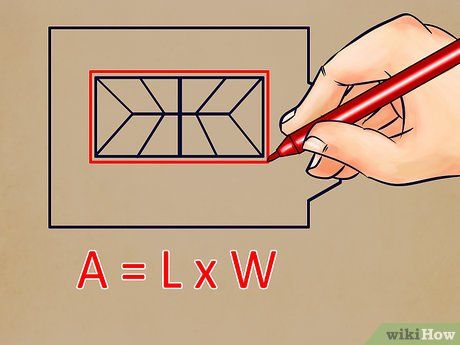
Determine the area of any skylights. If your ceiling lacks skylights, skip this step. Skylights are sometimes present in ceilings, and their area must be deducted from the total ceiling area calculated in step three. Measure the length and width of a skylight to obtain its area. Then, multiply the length by the width to find the skylight's area.
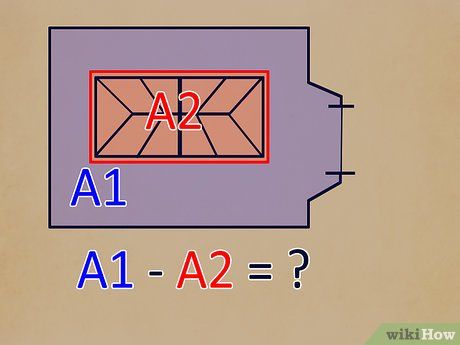
Subtract the skylight area from the ceiling area. Deduct the figure calculated in step four from the total ceiling area. This calculation yields the square footage of your ceiling.
Useful Tips
-
Make use of a calculator for each measurement.
-
When measuring for wood, tile, or laminate flooring, calculate the floor area as described above. However, ensure to order extra material to accommodate the waste generated during cutting. The industry standard is 10% waste.
-
Enlisting a friend's assistance can simplify the process. One of you can record the measurements while the other performs the measuring.
Essential Items
- Measuring tape
- Pencil
- Paper
- Calculator
- Ladder
