Are you aiming to enhance your home audio experience? Perhaps you're considering the installation of a home theater system. Incorporating a surround sound setup can significantly elevate your enjoyment of movies and gaming. Unlike a standard stereo system, which typically comprises two speaker channels positioned in front to the left and right, a surround sound system introduces an additional speaker in the center and at least two more speakers behind, effectively creating a multi-directional audio environment. Moreover, surround sound systems are equipped with a subwoofer to deliver powerful bass. While the concept of surround sound might appear complex, setting it up is actually quite straightforward. This Mytour guide walks you through the process of setting up a surround sound system.
Key Considerations
- Surround sound speakers can be connected via an audio receiver, soundbar, or a surround sound Blu-ray/DVD player.
- Surround sound systems come in various configurations, including a 2-speaker (2.1) setup, a 5-speaker (5.1) setup, or a 7-speaker (7.1) setup.
- Consider concealing wires under carpets or within walls, or opt for a wireless Bluetooth receiver to connect the rear speakers.
Step-by-Step Guide
Preparing Your Surround Sound Equipment
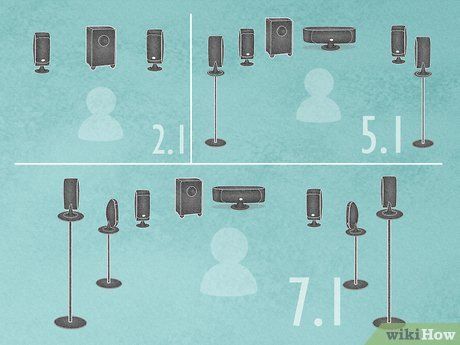
- 2.1 — Basic stereo setup with two front speakers and a subwoofer.
- 5.1 — Standard surround sound setup featuring front, center, and rear speakers, along with a subwoofer.
- 7.1 — Advanced configuration with additional side speakers added to the 5.1 setup.

- Most surround sound kits include a receiver, but second-hand sets may require a separate purchase.
- Some systems utilize a soundbar or DVD/Blu-ray player instead of a receiver, but the setup remains similar.
- Connect speakers to the receiver using AV cables or speaker wires, ensuring compatibility with your TV's audio output.

- AV — Single circular inputs, often color-coded, suitable for soundbars or subwoofers.
- Spring Clips — Dual inputs for each speaker, accommodating positive and negative wires with a lever mechanism.
- Binding Posts — Two inputs per speaker, featuring color-coded knobs for connection, and support for banana plugs.
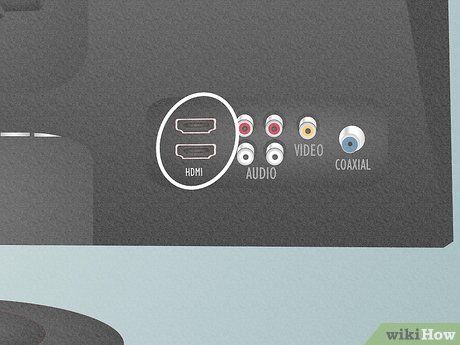
- Optical — Small square-shaped port providing clear audio, compatible with modern receivers.
- HDMI — Thin rectangle port transmitting audio and video, widely supported for connectivity.
- AV — Circular red and white ports for basic audio, universally supported by receivers.

- If you lack the appropriate cables, they're readily available online or at tech department stores. Online purchases are often more cost-effective.

Speaker Placement


- Although omnidirectional, avoid corner placements to prevent excessive bass amplification.
- Ensure proper ventilation and avoid placing subwoofers on unstable surfaces or near vibrating objects to minimize sound vibration.
- Consider neighbors; subwoofer frequencies can travel through walls, potentially disturbing adjacent residents. Opt for locations away from shared walls or floors.
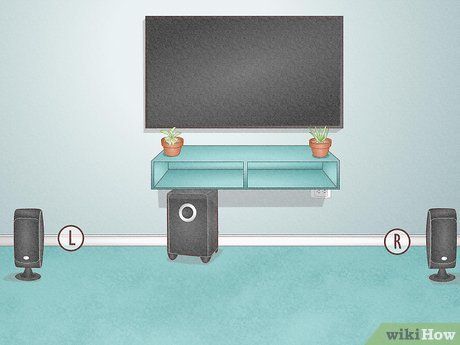
- Front speakers should maintain equal distance from the TV's sides (e.g., three feet on each side), with flexibility in width for optimal setup.
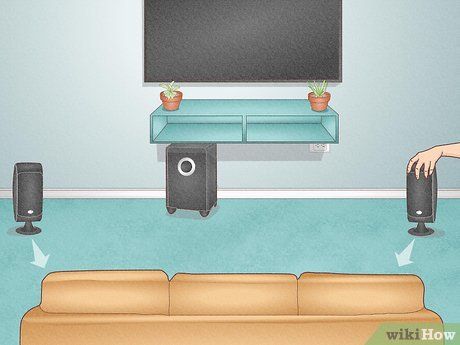
- Angle adjustment should create a symmetrical triangle encompassing both speakers and the seating area's center.
- Elevating front speakers to ear level significantly enhances sound quality.

- Angle the center channel to align with the audience's position.
- Avoid placing the center channel behind the TV to prevent muffled sound.
- Not applicable to 2.1 stereo systems, which lack a center speaker.

- Ensure rear channel speakers match the surround speakers' height.
- For 2.1 systems, rear speakers are not included.

- Side speakers enhance immersion by enveloping viewers in surrounding sound, complementing the action on-screen without overpowering front speakers.

- Speakers can be mounted on stands, shelves, or walls. Taller speakers can rest on the floor.
Linking the Speakers



- Hide wires under carpets or within walls where possible.
- Leave some slack at both ends to prevent wire strain.
- Modern systems may utilize wireless receivers for rear speaker connection. If applicable, plug the wireless receiver near the rear speakers and connect them accordingly.
- For extended reach, replace wires with longer ones for optimal sound quality instead of relying on extensions.
- For wires exceeding 100 ft (30 m), use thicker gauge wires to maintain sound quality.

- AV — If your speakers use AV cables, plug each cable into the corresponding labeled input on the receiver. Ensure color-coded wires match inputs. Rear speaker inputs may be on the subwoofer or wireless receiver for some systems.
- Spring Clips — With spring clips, connect two wires per speaker by inserting them into the red and black clips. Ensure bare wire is exposed for connection. Alternatively, use clear wires with writing for red terminals and wires without writing for black terminals.
- Binding Posts — Binding posts accept bare wire or banana plugs. Insert bare wire into the bottom opening and tighten the binding posts. Or, attach banana plugs to the speaker wire and insert them into the input holes. Connect red wires to red terminals and black wires to black terminals, or follow writing indications.

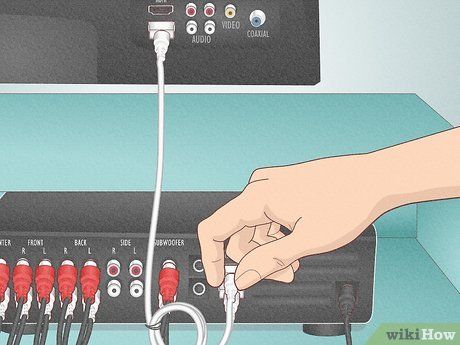
- Connect the subwoofer to the receiver's 'sub out' or 'sub pre-out' port.
- If the subwoofer has multiple inputs, use the one marked 'LFE in' or the far left input if unmarked.

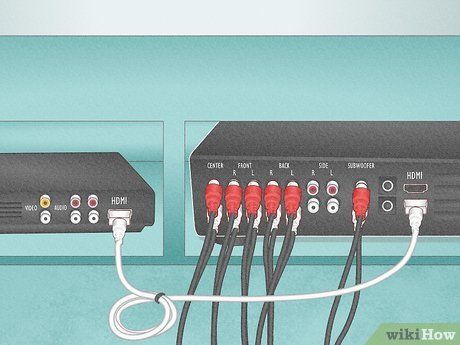
- Most receivers feature 'HDMI IN' and 'HDMI OUT' ports for connecting devices to the TV via HDMI cables.
- Older devices using AV or composite cables can also be connected similarly.
- Although older connectors like AV cables are viable, they offer significantly lower quality. HDMI is preferred for most modern TVs.
- If your TV supports ARC or eARC HDMI output, utilize this for controlling the receiver volume with the TV remote.

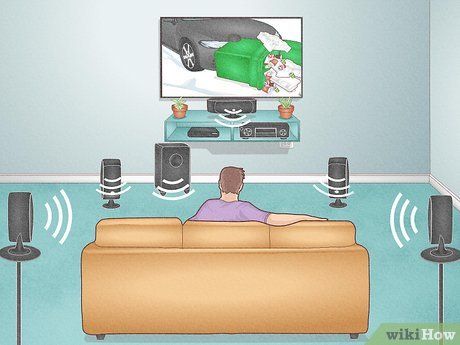
- YouTube offers various 'Surround Sound Test' videos to evaluate your system.
- If you've connected devices like game consoles, set your TV's Audio Out mode to 'PCM' for unaltered audio pass-through.
- Newer systems often feature automatic setup via a connected microphone, adjusting speaker distance from the viewer based on ambient sound levels. Alternatively, receivers may offer manual speaker distance adjustments in the Settings menu.
- To fine-tune your setup, adjust TV settings and connected device outputs before physically altering speaker positions. You can also balance speaker volumes for optimal performance.
- If you encounter audio delay, troubleshoot using available resources.
Pointers
-
Adjust individual device settings as needed for optimal surround sound setup. For instance, consoles may require different settings compared to DVD players.
Caution
- Exercise extreme caution when connecting bare speaker wire to a powered device to avoid potential shorts or electrical shocks.
