This article introduces you to the STDEV.P function - one of the statistical functions highly favored in Excel.

Description: The function returns the population standard deviation, excluding logical and text values. Standard deviation measures the spread of values around the mean. Supported from Excel 2010 onwards.
Syntax: STDEV.P(number1,[number2],...)
Regarding:
- number1,[number2],...: These are the values you want to calculate the standard deviation for. number1 is mandatory, while the rest are optional and can contain up to 254 number parameters.
Note:
- The STDEV.P function assumes its arguments to be the entire population.
- For large sample sizes -> STDEV.S, STDEV.P yield similar values.
- Standard deviation is computed using the “n” method.
- The argument can be a number, a name, or an array reference containing numbers.
- When directly entering logical values and presenting text-formatted numbers as function arguments -> these values are still calculated.
- The function encounters errors when arguments are text or non-convertible error values.
- If you want to compute both logical and text values -> use the STDEVPA function.
- The STDEV.P equation uses:
Regarding:
+ x represents the sample mean AVERAGE(number1,number2,…)
+ n stands for sample size.
Example:
Calculate the population standard deviation based on the values in the data table below:
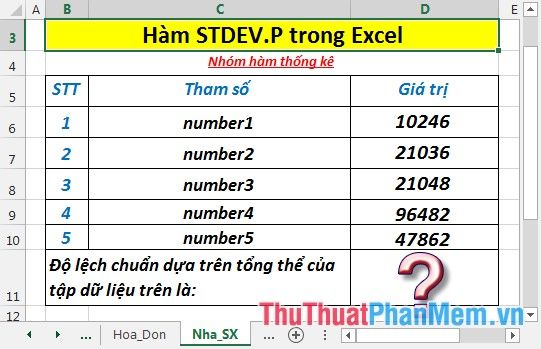
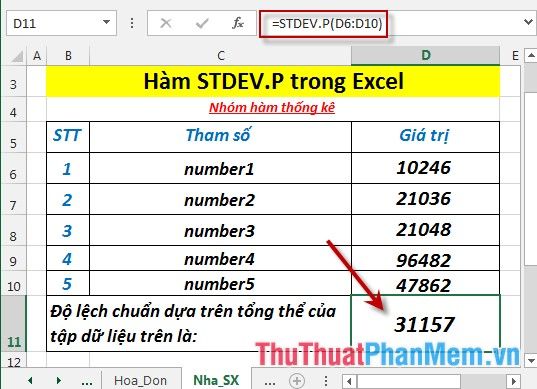
- In the cell where you want to calculate, enter the formula : =STDEV.P(D6:D10)

- Press Enter -> the population standard deviation is:
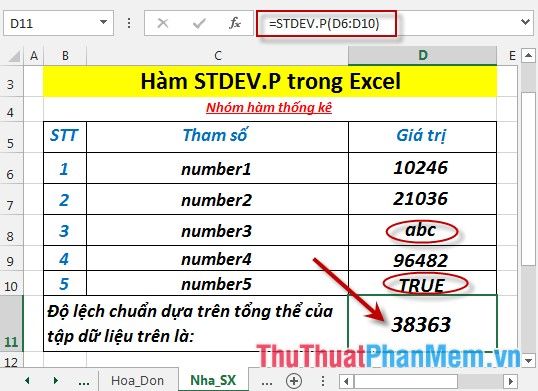
- In cases where the elements in the set are text or logical values -> they are ignored:
Here is a guide and some specific examples when using the STDEV.P function in Excel.
Wishing you all success!
