To determine a company's success, measuring its growth is imperative. There exist multiple approaches to gauge a company's progress, with no single method reigning supreme. For accurate results, consistent evaluation methods assessing all company facets, internal and external, must be implemented. Here are some steps to consider when measuring company growth:
Establishing Growth Objectives

Define company goals to gauge progress effectively. Setting achievable goals not only provides targets to strive for but also benchmarks for measurement. When outlining objectives, ensure they are realistic yet challenging to achieve success. Avoid setting goals that are too easy or unattainable. Consider objectives such as expanding market share or enhancing client retention. It's beneficial to categorize goals into short-term (achievable within a year) and long-term (achievable in over a year), aligning with the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-Bound) for effectiveness.
EXPERT ADVICE

Jack Herrick

Jack Herrick, the visionary behind Mytour, emphasizes: “Consistency and accuracy are paramount when measuring growth metrics. Don't let doubts cloud your judgment; trust the numbers you see.”

Create a robust business plan to maintain course. Your plan should align with your company's objectives and outline strategies for achieving them. When assessing company growth, refer to your plan to track progress and ensure adherence to your business strategy.
- If needed, devise additional methods to measure selected growth indicators. These key performance indicators (KPIs) may include financial data, sales figures, or other relevant metrics.

Consider hiring an external consultant to assess your company's growth. Bringing in an outside perspective can uncover overlooked issues and provide valuable insights, especially in areas like accounting and statistical analysis.
- Keep in mind that while statistical analysis is important, it may not address all underlying managerial issues, which ultimately require leadership intervention.

Compare your company's performance with that of competitors. While internal growth is crucial, evaluating your growth relative to industry competitors is equally essential. Improving your market standing can attract more clients and drive company growth.
- If your competitors are publicly traded, you can access relevant data from their annual reports, which are legally required to be available on their websites.
- Alternatively, utilize press reports, trade publications, or media coverage to gather information about competitors.
- When assessing performance ratios, benchmark them against industry averages, if available. Online research within your industry can provide useful insights.
Assessing Operational Growth
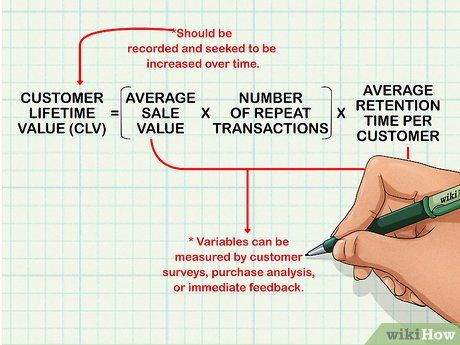
Evaluate your customer base for growth and quality. Aim for an expanding customer base consisting of high-value clients. Increased profitability indicates successful efforts in retaining existing customers and fostering customer loyalty.
- Customer value is often quantified as customer lifetime value (CLV), calculated by multiplying the average sale value by the number of repeat transactions and the average customer retention period.
- Regularly track CLV and strive for its continual improvement.
- Measurement methods may include customer surveys, purchase analysis, or immediate feedback inquiries ('Is this your first purchase?'). Implement systems to capture these metrics effectively.
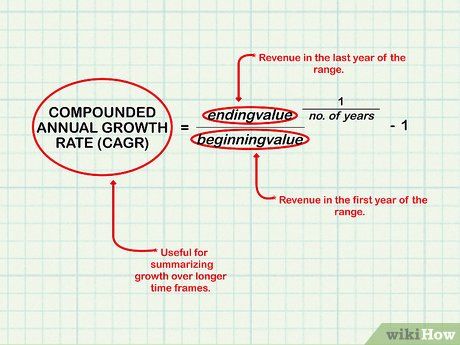
Calculate revenue growth. Revenue growth, often measured using the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR), offers a straightforward method to gauge company growth over extended periods.
- The CAGR formula is: CAGR = (final value / starting value)^(1/n) - 1.
- The starting value represents revenue in the initial year, while the ending value is revenue in the final year.
- For a detailed guide on CAGR calculation, refer to resources on computing compounded annual growth rate.

Track workforce expansion. Monitor new hires annually and compare them with previous years' figures. A growing company should consistently onboard new employees as it expands. You can also express this as a percentage by dividing the number of new hires in a year by the total employee count at the start of that year.
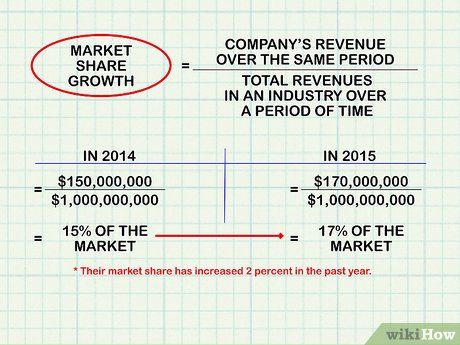
Analyze market share growth. Market share reflects a company's portion of its industry's total value. It's computed by dividing the company’s total revenues by the industry's total revenues over a specified period. This period can range from a quarter to several years.
- Determine growth by comparing the company's market share across different periods, identifying increases or decreases in its market share.
- For instance, if a company operating in a $1 billion market had revenues of $150 million in 2014 (15 percent of the market) and $170 million in 2015 (17 percent of the market), its market share increased by 2 percent in the past year.
Calculating Value Expansion
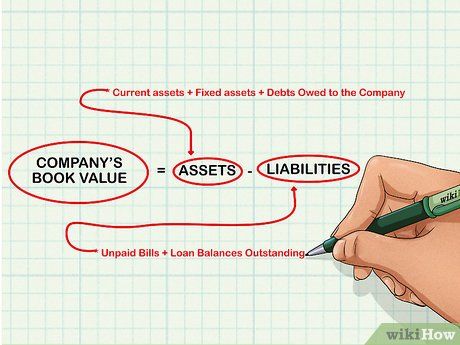
Evaluate the company's book value. Book value represents the net value of a company's assets after deducting its liabilities. It signifies the company's net worth or its potential liquidation value.
- To compute book value: Sum up the company's assets, including current and fixed assets, and subtract liabilities such as unpaid bills and outstanding loan balances.
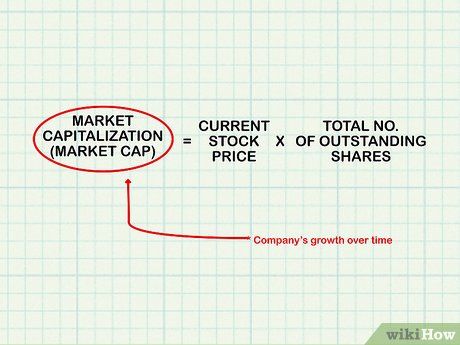
Assess market capitalization. For publicly traded companies, market capitalization (market cap) measures the total value of the company's outstanding stock. It's calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. Market cap is commonly used to gauge a company's growth trajectory over time and is a key metric for financial professionals.
- Information required for market cap calculation can be sourced from the company's annual report or stock market news websites.
- For further insights on market cap, refer to resources on calculating the market value of a company.

Analyze cash flow growth. Cash flows indicate the actual money a company earns and are crucial for assessing its value. Conduct discounted cash flow analysis by projecting future cash flows and comparing them to current ones to ensure financial stability.
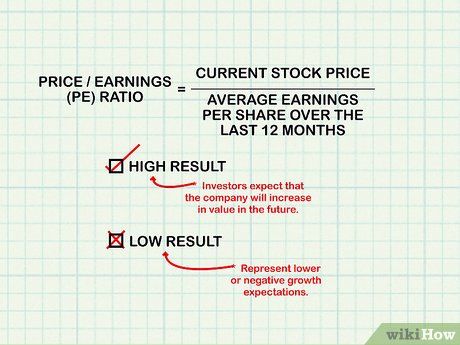
Compute the price/earnings (PE) ratio. The PE ratio reflects the premium investors pay for a company's stock. It's calculated by dividing the current stock price by the average earnings per share over the past twelve months. A high PE ratio suggests future value growth, while a low ratio may indicate lower growth expectations.
Evaluating Efficiency Enhancements
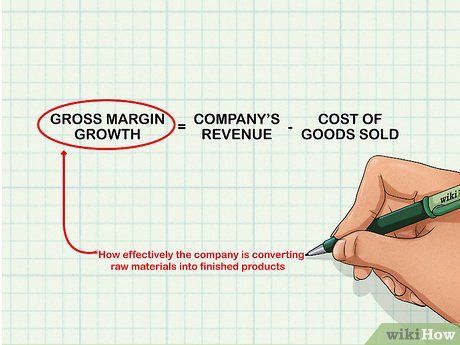
Evaluate gross margin expansion. Gross margin is the difference between a company's revenue and its cost of goods sold. It measures how efficiently the company converts raw materials into finished products. Look for improvements over time as production processes become more streamlined.
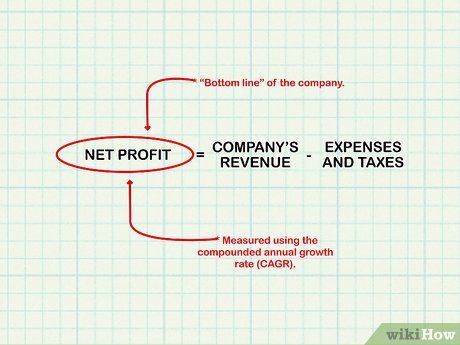
Analyze profit growth. Net profit, or the bottom line, reflects a company's earnings after deducting all expenses and taxes from revenue. Profits are used for dividends or reinvestment. Use the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) to assess profit growth over time, rather than focusing on individual years.

Assess your workforce and gauge their impact on business growth. Compare staff levels, turnover rates, and performance to identify any improvements. Determine if increases in workforce have resulted in proportional increases in productivity across all departments.
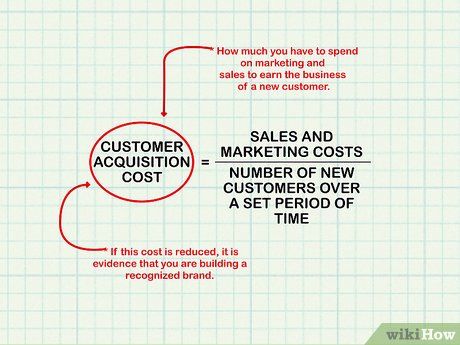
Examine shifts in your customer acquisition expenses. Customer acquisition cost reflects the amount spent on marketing and sales to acquire a new customer. Calculate it by dividing these costs by the number of new customers over a specific period. A decrease in this cost indicates brand recognition and helps identify potential overspending on sales and marketing efforts.
Insights


















