A garage serves multifunctional purposes, from housing vehicles to accommodating storage or serving as a workshop. Given its versatility, meticulous planning is imperative. Commence by drafting a blueprint, essential for securing a building permit. Adherence to local building codes is mandatory; however, construction and inspection can proceed post-permit acquisition.
Necessary Steps
Picking the Right Garage Design

Identify Property Boundaries Using Deed Details. Property demarcations dictate garage placement. Refer to your property deed to ascertain these boundaries. Upon obtaining the deed, verify the boundaries by physically surveying the premises and using property landmarks for estimation.
- If the deed is unavailable, consult your local zoning department for property maps.

Select an Ideal Location for Your Garage. Deliberate on your garage's purpose to determine its placement. Opt for proximity to your home for convenience or consider a separate location for a distinct aesthetic. Allocate additional funds as needed to align with your preferences and local regulations.
- Property dimensions and zoning laws are pivotal in deciding the garage's location.

Determine Available Space for Your Garage. Venture outdoors armed with a tape measure. After outlining property boundaries, gauge your available space. Document both maximum and desired dimensions, facilitating discussions with architects and contractors.
- Recording measurements is advisable for consultations with professionals.

Opt for an Attached Garage for Seamless Access. Contemporary garages often attach directly to homes, enhancing accessibility. While construction costs may be higher due to the required door installation, the convenience of indoor access outweighs the expenses.
- Considerations include space allocation for the garage and the integration of roofing with the house.

Construct a Detached Garage for Additional Flexibility. Position a detached garage anywhere on your property to accommodate spatial constraints. This cost-effective option allows for greater design freedom and independence from the main dwelling.
- Detached garages offer versatility in design without mirroring the home's aesthetics.
- Placement adjacent to the house is feasible, creating a standalone structure.

Envision a Second Story for Enhanced Storage. Expanding vertically can compensate for limited width in the garage. While local building codes may pose restrictions, alternative solutions such as attics, lofts, or modified framing can maximize storage potential.
- Consider incorporating dormers or separate rooms above the garage, necessitating stair or ladder installations.
- For those averse to second floors, explore wall and overhead storage options.
EXPERT INSIGHT

Ashley Moon, MA

Maximize Garage Wall Storage Efficiency. Utilize shelving racks and tall cabinets along garage walls to organize small items and seasonal gear effectively, ensuring easy access while preventing clutter.
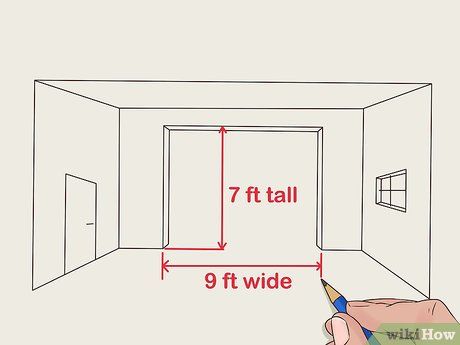
Select Optimal Door Size and Quantity. Tailor garage door dimensions to accommodate intended usage, considering vehicles' dimensions and additional access requirements. Electronic door openers offer convenience, albeit at an extra cost, which can be retrofitted later if needed.
- Assess the necessity of multiple doors versus a single large one, keeping in mind parking arrangements.
- Features like electronic door openers may incur additional expenses but offer long-term benefits.
Drafting and Refining the Blueprint

Set a Budget to Avoid Overspending on Garage Construction. Initiate budget planning as a priority to mitigate project costs. Expenses encompass blueprint creation, additional features, material selections, and contractor fees. Researching costs beforehand and engaging in dialogue with contractors can offer cost-effective solutions.
- Online resources provide insights into feature and service costs prior to contractor consultations.
- Contractors can propose budget-friendly alternatives if expenses exceed initial estimations.
- For example, incorporating a storage loft may incur an additional $1,000 USD, necessitating supplementary expenses for a pull-down ladder installation.

Determine Optimal Garage Size. Define the garage dimensions based on parking and storage requirements. Considerations include accommodating large or multiple vehicles with wider and deeper layouts. Zoning regulations and property size influence available space, crucial for blueprint development and contractor discussions.
- A workshop necessitates a smaller garage layout devoid of parking spaces.
- Available space is contingent upon local zoning regulations and property dimensions.

Integrate Windows for Enhanced Illumination and Ventilation. Incorporate multiple windows into garage design for improved lighting and ventilation, particularly advantageous for workshop conversions. Strategic placement within the blueprint enhances functionality and aesthetic appeal.
- Position freestanding windows away from garage doors and adjoining walls.
- Consider integrating windows into garage doors to optimize natural lighting.

Ensure Accessibility of Wall Outlets. Collaborate with professionals such as architects or electricians to optimize outlet placement. Seamless electrical wiring distribution facilitates access to outlets and lighting fixtures without obstructing functionality. Additional wiring and outlet installations may be necessary for workspace utilization.
- Installation of a sub-panel may be warranted for air conditioning or power tool usage, serving as a supplementary circuit breaker.

Incorporate Heating, Air Conditioning, and Specialized Features. Despite escalating construction costs, consider installing heating, air conditioning, and other amenities if you anticipate spending significant time in the garage. Pre-installation is imperative before laying the foundation, ensuring seamless integration.
- Features like radiant in-floor heating or drainage systems require pre-floor completion installation.

Erect a Retaining Wall for Hillside Dwellings. Prevent soil erosion by constructing retaining walls, vital for garages situated near slopes. Engage professional construction services if DIY construction seems daunting.
- Similar to foundation setup, constructing retaining walls entails ground leveling, cutting, and assembling wall materials.
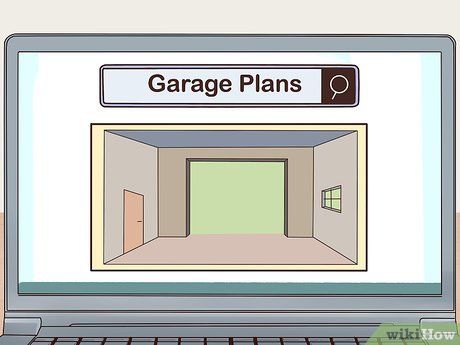
Acquire Garage Plans Online. Explore online resources by searching for 'garage plans.' Free and purchasable plans are readily available, serving as blueprints for construction endeavors. Paid plans typically range from $100 to $200.
- Seek plans aligning with your garage vision for optimal customization.
- Modifications to plans are feasible, accommodating preferences for increased size or additional features.

Engage Architectural Professionals for Tailored Plans. Invest in architectural services to procure customized plans. While this incurs a substantial budget allocation, architects ensure compliance with local building codes while fulfilling client specifications.
- Architects and drafters can harmonize garage designs with existing architectural aesthetics or introduce bespoke elements.
- Alternatively, customize existing plans through drafters, often at a fraction of the cost.

Design Plans Independently to Minimize Costs. Utilize pencil and graph paper to sketch garage blueprints, ensuring accuracy through meticulous measurements. Collaborate with architects if necessary for regulatory compliance and professional blueprint reproduction.
- Architectural approval may still be necessary depending on local regulations, with architects often able to replicate personal sketches.
- For non-artists, photographic references can aid in conveying preferences to architectural professionals.
Navigating Legal Permits and Inspection Procedures

Initiate Permit Application Submission to Local Building Authority. Familiarize yourself with local building regulations and application procedures. Present a detailed project sketch outlining the proposed garage structure to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Approval likelihood hinges on garage location and dimensions.
- Professional assistance from architects or contractors can facilitate application approval.

Settle Building Application Fees. Allocate funds for administration fees, which vary by jurisdiction, upon application submission. Payment methods typically include check or electronic payment. Additional inspection fees may apply, often managed by contractors and billed accordingly.
- Payment methods typically include check or electronic payment.
- Contractors commonly handle inspection fees, incorporating costs into the final bill.

Await Permit Approval for 6 to 8 Weeks. Allow for review and deliberation by the building authority. Public objections may prompt adjustments to the proposal. Once approved, you receive a notification from the local council, signaling commencement of garage construction.
- Community objections typically pertain to adherence to local building regulations, necessitating proposal modifications.
- Expedite the process by contacting the building authority if delays occur.

Facilitate On-Site Inspections During Construction. Adhere to scheduled inspections as stipulated by local building regulations. Inspection intervals typically include foundation laying and frame construction stages. Inspectors ensure compliance with building codes throughout the construction process.
- Contractors often coordinate inspector visits on your behalf.
- Additional inspections may be required for electrical wiring installation and post-construction assessments.
Establishing the Foundation

Contact Utility Companies to Identify Underground Utilities. Prevent damage to underground utility lines by arranging for their marking before construction commences. Obtain necessary permissions to build over these lines if required.
- Coordination with utility companies is essential for relocation of utility lines if necessary.

Mark Out Construction Site Boundaries. Position wooden stakes around the construction area periphery according to blueprint specifications. Connect stakes with twine to demarcate the construction area and ensure accurate execution of construction tasks.
- Prioritize confirmation of absence of utility lines within the construction zone.
Level the Construction Site. Commence construction by leveling the designated area. Employ heavy construction equipment or professional excavators to excavate the site, forming the groundwork for the garage foundation.
- The foundation serves as the base for the garage structure, with surrounding soil graded to facilitate proper drainage.

Excavate Footings for Structural Stability. Dig trenches surrounding the foundation to create footings. Fill these trenches with concrete to stabilize the garage structure, particularly in soft soil conditions. Professional excavator services are advisable for this task.
- Given the technical nature of foundation construction, hiring professional excavators is recommended for optimal results.
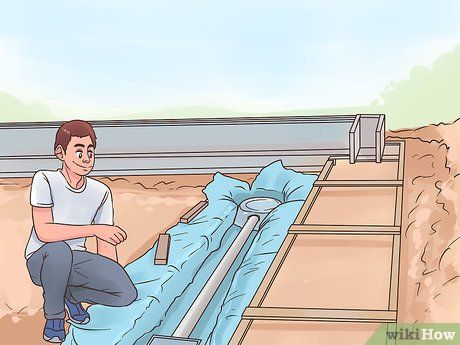
Install In-Ground Drains or Heating Elements. Pre-installation of these features is imperative before completing the foundation. Failure to do so may necessitate breaking the garage floor for installation post-concrete pouring. Coordinate with contractors to ensure inclusion of these features during construction.
- Clear communication with contractors regarding desired features is essential.

Proceed to Pour Concrete for the Foundation. Upon settling of the soil, commence foundation creation by filling footings with concrete. Extensive concrete mixing and pouring are required, followed by smoothing the surface. Opt for professional assistance if lacking experience in foundation construction to ensure structural stability.
- Engage reputable building companies for reliable foundation construction, a fundamental aspect of garage stability.
Useful Tips
-
Delegate complex planning or construction tasks to experienced contractors.
-
Consult your local homeowner’s association for any applicable design regulations.
-
Optimal installation of new features is achievable prior to garage completion, particularly for in-ground amenities like radiant heating systems and drains.
Important Warnings
Constructing a garage without proper permits can lead to significant legal ramifications.
Building a new garage can incur substantial costs, thus prudent budgeting is crucial.
Essential Supplies
-
Property deed, survey, or map
-
Tape measure
-
Blueprint
-
Pencil
The content is developed by the Mytour team with the aim of customer care and solely to inspire travel experiences. We do not take responsibility for or provide advice for other purposes.
If you find this article inappropriate or containing errors, please contact us via email at [email protected]




























