
Air conditioners and refrigerators are familiar devices to everyone. However, not everyone understands the structure and operating principles of these cooling appliances.
1. Structure and Operating Principles of Air Conditioners and Refrigerators
Air conditioners and refrigerators are familiar devices to everyone. However, not everyone understands the structure and operating principles of these cooling appliances.
What is an Air Conditioner?
An air conditioner is a household appliance that uses electrical energy to change the temperature in a room according to the user's needs. In the market, air conditioners are divided into two types: one-way air conditioners and two-way air conditioners. One-way air conditioners only have the ability to cool, so they are often called air conditioners. Meanwhile, two-way air conditioners have both cooling (used in summer) and heating functions (used in winter).

Air conditioning - a device capable of regulating air temperature
Structure and operating principles of air conditioners, air coolers
1. Structure of air conditioners, air coolers
The structure of an air conditioner, air cooler typically consists of the following components:
Cooling coil: Functions to absorb heat in the room for the refrigerant to take outside. The air conditioner's cooling coil has parallel copper tubes wrapped in aluminum fins for heat dissipation.
Heat exchanger unit: Responsible for releasing heat into the environment after the refrigerant has absorbed heat at the cooling coil and moved to the heat exchanger. The structure of the air conditioner's heat exchanger is similar to the cooling coil.
Air conditioner compressor: Also known as the air conditioner compressor, it functions to create a vacuum at the cooling coil, compressing gas into liquid at the condenser to enhance the heat dissipation process most efficiently.
Evaporator fan: Generates a continuous airflow through the evaporator coil for better heat absorption. If the evaporator fan runs weak or does not operate, the air conditioner will not be able to cool the entire room.
Condenser fan: Blows air through the condenser coil, facilitating efficient heat dissipation into the external environment.
Expansion valve: A component that reduces the pressure of gas after it passes through the condenser to dissipate heat. Gas passing through the expansion valve will be converted into a low-pressure, low-temperature gas.
Refrigerant lines: Responsible for conveying gas from the evaporator to the condenser. Refrigerant lines are typically made of copper, capable of withstanding high pressure and temperature, and are resistant to oxidation.
Control panel: Mounted on the indoor unit, it is the operational and control unit for the entire air conditioning system.
Capacitor: Functions to assist the electric motor of the compressor during startup.
In addition to the main components mentioned above, the structure of air conditioners and air coolers also includes various other parts such as the temperature sensor in the evaporator coil, frame casing, water tray, safety components, etc.
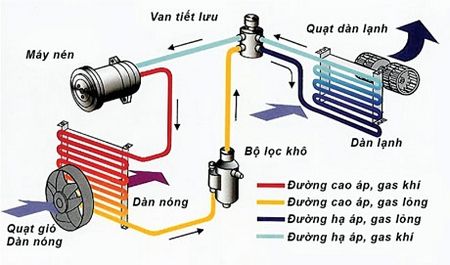
Air conditioner structure diagram
2. Operating principles of air conditioners and coolers
We have briefly explored the structure of air conditioners and coolers. So how does the air conditioner mechanism work?
Step 1: After passing through the expansion valve, the gas (refrigerant) will have low pressure and low temperature.
Step 2: The refrigerant passing through the evaporator coil will absorb heat from the surrounding environment. The fan inside the indoor unit draws air from the room, passes it through the evaporator to cool it, and then returns it to the room.
Step 3: The heat-carrying refrigerant is sent to the compressor. Here, the gas will be compressed to a higher pressure.
Step 4: The high-temperature, high-pressure gas is sent through the condenser coil to cool down with the help of the fan and aluminum fins for heat dissipation. As it passes through the condenser, the refrigerant will have a lower temperature.
Step 5: The gas continues to be sent to the expansion valve to reduce pressure, decrease temperature, and start a new cycle.
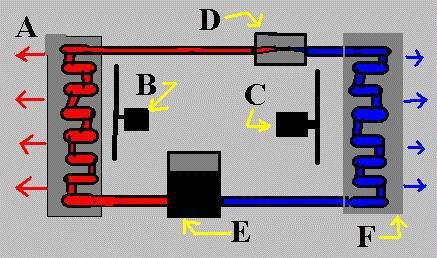
Air conditioner operating principle diagram
We hope our insights will help you better understand the structure and operating principles of air conditioners and coolers.
Source: quantrimang.com
