Foam padding serves various purposes, such as replacing cushions on furniture or crafting customized mattresses for outdoor adventures. However, adjusting its size often becomes necessary. Although foam is pliable, achieving precise cuts can be challenging. Fortunately, employing different tools and working methodically ensures clean and accurate cuts.
Key Steps
Choosing the Right Blade

Utilize a lengthy serrated blade for effortless cutting through dense foam. Foam develops small air pockets upon heating, akin to those in baked bread, which contribute to its lightweight texture and make cutting difficult. Opting for a serrated knife, typically used for slicing bread, significantly eases the process.
- This method is most effective for foam exceeding 2 inches (5.1 cm) in thickness. Ideally, the blade should surpass the foam's thickness, facilitating complete cuts.
- A longer knife may offer better maneuverability, making it suitable for intricate cuts.

Achieve swift cuts through dense foam using an electric kitchen knife. An electric knife, commonly used for carving turkey, proves invaluable for efficiently trimming foam to size. Particularly beneficial for large-scale projects or angled cuts.
- Position the foam off the work table edge when using an electric knife to prevent contact between the knife's edge and the surface.
- For foam under approximately 2 inches (5.1 cm), a rotary cutter or craft knife may offer easier handling.
- Electric kitchen knives are readily available at most department stores and are typically budget-friendly, making them a practical investment for substantial projects.

Utilize a rotary cutter for slicing thin foam pieces. A large (60mm) rotary cutter simplifies cutting tasks for foam pads measuring 1⁄2 inch (1.3 cm) or less. Mark the desired cutting line and roll the blade over it.
- Rotary cutters excel at cutting curved lines but may not be suitable for intricate detailing.
- Alternative tools for thin foam include box cutters with appropriately sized blades or sharp scissors, although these are less effective for thicker foam.
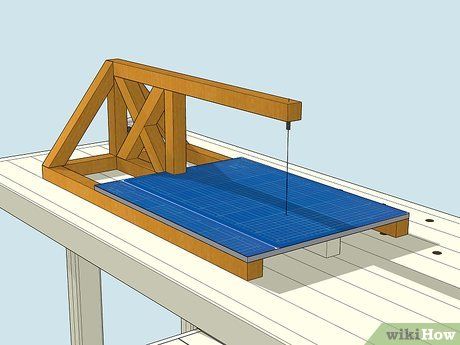
Experiment with a hot wire cutter for horizontal cuts, exercising caution. Hot wire cutters effortlessly slice through foam, making them ideal for cutting large foam pads horizontally. These devices utilize an electrical current to heat a taut wire held within a frame, requiring the wire to be pushed through the foam.
- Work in a well-ventilated area when using hot wire cutters to mitigate potential exposure to toxic fumes produced by heating the foam.
- Prolonged or paused cutting may result in foam melting and hardening, leading to misshapen cuts.
- Only suitable for foam composed of polystyrene and polyethylene; avoid use with polyurethane foam due to the production of highly toxic fumes.
- Exercise caution to prevent burns when handling the wire.

Consider investing in a foam cutter for extensive projects. Foam cutters feature an electric blade similar to an electric kitchen knife but mounted on a stationary flat plate that slides beneath the foam. This design facilitates precise cuts and allows for curved lines and detailed work by rotating the foam during cutting.
- Foam cutters are a significant investment; therefore, they are more suitable for projects requiring prolonged use rather than one-off tasks.
Executing the Cuts

Prepare a stable surface for foam cutting. Choose a spacious area such as a large worktable and cover it with a protective layer like a tarp or blanket. This setup ensures easy cleanup by containing foam debris.
- Select a surface resistant to blade damage or heat, especially for hot wire cutter use, such as a wooden or metal table.
- If a suitable table is unavailable, lay down plywood or flattened cardboard sheets to safeguard the floor while catching foam remnants. Ensure the foam remains supported to prevent shifting during cutting.
- Consider wearing cut-resistant gloves for hand protection during the project.

Outline cuts with a permanent marker. Use a marker to trace desired foam pad shapes lightly, employing a straight edge for straight lines or templates for intricate patterns. Ensure thorough marking, especially for thicker foam pieces, covering top, sides, and bottom.
- Opt for larger cut dimensions to allow for adjustments, as foam can compress into place or be further trimmed if necessary.
- Avoid adjoining shapes to prevent errors; maintain a gap between cuts for flexibility.

Score foam along marked lines using appropriate tools. Maintain a vertical blade orientation for knives, rotary cutters, or box cutters, exerting steady pressure away from the body along the marked line. Employ a gentle sawing motion for serrated knives, ensuring even edges.
- Exercise caution with hot wire cutters, maintaining continuous motion to prevent foam melting or misshaping.
- For curved cuts, adjust blade angles accordingly for optimal results.

Proceed with smooth cutting motions until foam is fully sliced. Follow scored lines with controlled blade movements, allowing the weight of the blade to guide each pass. Avoid exerting excessive pressure to prevent uneven cuts.
- Make multiple passes if needed to ensure complete foam penetration.
- Avoid compressing foam during cutting; maintain consistent blade pressure for uniform results.
- Employ gentle sawing motions for serrated knives without applying excessive force.
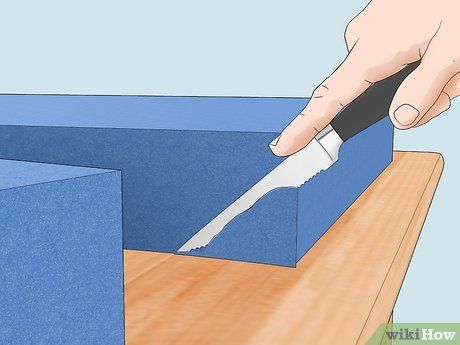
Rectify any uneven cuts as desired. Trim away any irregularities or protrusions along the foam edge with a straight knife if necessary, ensuring a clean finish.
- Minimal unevenness may be acceptable, particularly if covering foam with fabric.
Necessary Items
- Foam padding
- Protective material (cardboard, blanket, or towel)
- Permanent marker
- Blade or cutting tool
- Straight edge or template (optional)
Helpful Tips
-
If you're dealing with intricate cuts, begin with rough outlines before tackling finer details with a craft knife.
-
Remember, it's better to cut conservatively; you can always remove more material, but you can't add it back once it's cut.
Cautionary Notes
- Prioritize knife safety at all times. Ensure there are no individuals or animals in close proximity while cutting, and be vigilant to keep your fingers and other body parts away from the blade's path.
