 Within the Raptor Lake-S Refresh lineup for desktop computers currently available on the market, most are similar to the 13th generation, with only minor upgrades in clock speeds. However, the Intel Core i7-14700K stands out the most and is also the most worthy 14th generation CPU choice if you're considering building a new machine or upgrading from an older one.Raptor Lake-S Refresh can essentially be seen as elite silicon dies from the corresponding 13th generation, capable of operating at higher clock speeds. For example, the Core i9-13900K with 24 cores and 32 threads running at a maximum speed of 5.8 GHz, then the special edition Core i9-13900KS with speeds up to 6 GHz. However, the Core i9-14900K Refresh can already run at 6 GHz, simultaneously being the standard version. If the Core i9-14900KS indeed exists, I speculate it will be the selected dies of the 'new season,' possibly achieving speeds around 6.2 GHz. As you can see, the regular version of the new generation will match the special edition of the old generation, thanks to Intel's mature manufacturing process, which they've optimized to produce more high-quality dies (high yield rate). But these upgrades from generation to generation are only like this, except for the Core i7-14700K.
Within the Raptor Lake-S Refresh lineup for desktop computers currently available on the market, most are similar to the 13th generation, with only minor upgrades in clock speeds. However, the Intel Core i7-14700K stands out the most and is also the most worthy 14th generation CPU choice if you're considering building a new machine or upgrading from an older one.Raptor Lake-S Refresh can essentially be seen as elite silicon dies from the corresponding 13th generation, capable of operating at higher clock speeds. For example, the Core i9-13900K with 24 cores and 32 threads running at a maximum speed of 5.8 GHz, then the special edition Core i9-13900KS with speeds up to 6 GHz. However, the Core i9-14900K Refresh can already run at 6 GHz, simultaneously being the standard version. If the Core i9-14900KS indeed exists, I speculate it will be the selected dies of the 'new season,' possibly achieving speeds around 6.2 GHz. As you can see, the regular version of the new generation will match the special edition of the old generation, thanks to Intel's mature manufacturing process, which they've optimized to produce more high-quality dies (high yield rate). But these upgrades from generation to generation are only like this, except for the Core i7-14700K.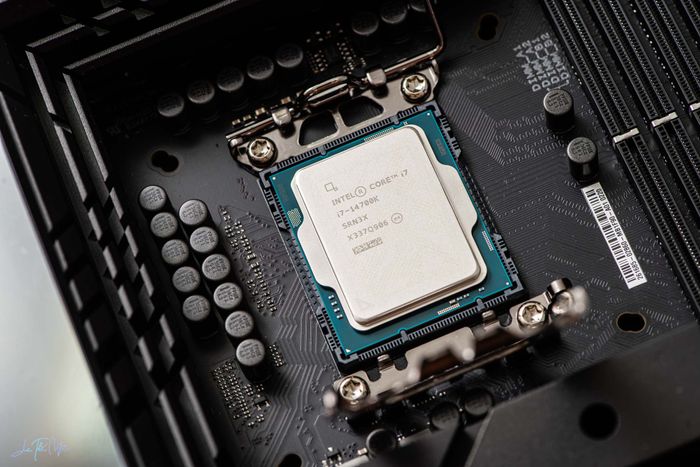 When comparing directly with the corresponding previous generation - Core i7-13700K - the Core i7-14700K undergoes significant changes. The number of Efficient cores increases by 50% (from 8 to 12), resulting in a higher total processing thread count. While the base clock remains the same, the boost clock sees a 200 MHz increase, going from 5.4 GHz to 5.6 GHz. Additionally, the L3 cache size grows by 10% (33 MB compared to 30 MB). Inside the chip, the memory controller or memory management is also updated, now supporting faster DDR5 RAM, even with 12 GB or 24 GB modules.Inside the 14th generation chip, the Performance cores known as “Raptor Cove” have a maximum count of 8, while the Efficient cores named “Gracemont” amount to 16. The E-cores are grouped into clusters of 4, with the highest L3 cache size being 36 MB shared between P-core and E-core. Each Performance core possesses 2 MB of L2 cache, whereas the cluster of 4 Efficient cores shares 4 MB of L2 cache. Hence, the Core i7-14700K stands as a special variant, missing one E-core cluster compared to the flagship choice, i9-14900K. In comparison to Alder Lake, both the 13th and 14th generation Core i7 K Series have a Maximum Turbo Power (MTP) threshold of 253 W, equivalent to Core i9 K Series. Despite the identical MTP space, having fewer E-core clusters to feed results in the i7-14700K exhibiting improved turbo acceleration across all cores.
When comparing directly with the corresponding previous generation - Core i7-13700K - the Core i7-14700K undergoes significant changes. The number of Efficient cores increases by 50% (from 8 to 12), resulting in a higher total processing thread count. While the base clock remains the same, the boost clock sees a 200 MHz increase, going from 5.4 GHz to 5.6 GHz. Additionally, the L3 cache size grows by 10% (33 MB compared to 30 MB). Inside the chip, the memory controller or memory management is also updated, now supporting faster DDR5 RAM, even with 12 GB or 24 GB modules.Inside the 14th generation chip, the Performance cores known as “Raptor Cove” have a maximum count of 8, while the Efficient cores named “Gracemont” amount to 16. The E-cores are grouped into clusters of 4, with the highest L3 cache size being 36 MB shared between P-core and E-core. Each Performance core possesses 2 MB of L2 cache, whereas the cluster of 4 Efficient cores shares 4 MB of L2 cache. Hence, the Core i7-14700K stands as a special variant, missing one E-core cluster compared to the flagship choice, i9-14900K. In comparison to Alder Lake, both the 13th and 14th generation Core i7 K Series have a Maximum Turbo Power (MTP) threshold of 253 W, equivalent to Core i9 K Series. Despite the identical MTP space, having fewer E-core clusters to feed results in the i7-14700K exhibiting improved turbo acceleration across all cores. The Intel 7 process used to manufacture Raptor Lake-S Refresh is upgraded with 3rd generation SuperFin transistors, aimed at enhancing performance and energy efficiency, at both high clock speeds and low voltages. The V-F Curve indicates that the new processor can operate at over 200 MHz higher clocks while maintaining the same voltage, or reduce by 50 mV while keeping the clock constant. According to Intel, Raptor Cove is the fastest core the company has ever produced.Intel Thread Director emerges as one of the most impressive and innovative features brought by the 12th generation Core processors, alongside the hybrid architecture. Naturally, it's been integrated across Alder Lake-S, Raptor Lake-S, and now Raptor Lake-S Refresh. This technology is directly built into the hardware, providing specialized instructions to ensure proper workload distribution to the correct processing cores at the right time. Performance cores focus on active, intensive, and critical tasks such as gaming, graphics rendering, and video editing, while Efficient cores handle background tasks requiring less power and processing capacity. When necessary, the Thread Director dynamically switches roles between P-core and E-core to meet workload demands, consistently optimizing energy efficiency for the most efficient performance. Since the 13th generation Raptor Lake-S, the Thread Director has become smarter and more advanced, designed for upgradability and fine-tuning to evolve over time. Intel updates tools to classify workloads using ML algorithms, further enhancing foreground and background task processing.Test Configuration
The Intel 7 process used to manufacture Raptor Lake-S Refresh is upgraded with 3rd generation SuperFin transistors, aimed at enhancing performance and energy efficiency, at both high clock speeds and low voltages. The V-F Curve indicates that the new processor can operate at over 200 MHz higher clocks while maintaining the same voltage, or reduce by 50 mV while keeping the clock constant. According to Intel, Raptor Cove is the fastest core the company has ever produced.Intel Thread Director emerges as one of the most impressive and innovative features brought by the 12th generation Core processors, alongside the hybrid architecture. Naturally, it's been integrated across Alder Lake-S, Raptor Lake-S, and now Raptor Lake-S Refresh. This technology is directly built into the hardware, providing specialized instructions to ensure proper workload distribution to the correct processing cores at the right time. Performance cores focus on active, intensive, and critical tasks such as gaming, graphics rendering, and video editing, while Efficient cores handle background tasks requiring less power and processing capacity. When necessary, the Thread Director dynamically switches roles between P-core and E-core to meet workload demands, consistently optimizing energy efficiency for the most efficient performance. Since the 13th generation Raptor Lake-S, the Thread Director has become smarter and more advanced, designed for upgradability and fine-tuning to evolve over time. Intel updates tools to classify workloads using ML algorithms, further enhancing foreground and background task processing.Test Configuration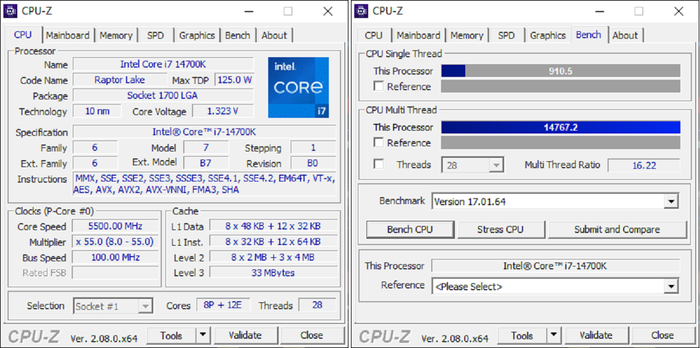
- CPU: Intel Core i7-14700K
- Mainboard: ASUS ROG Strix Z790-A Gaming Wi-Fi II
- RAM: Kingston FURY Renegade DDR5-7200 32 GB (16 GB x 2)
- VGA: ASUS ROG Strix GeForce RTX 4060
- SSD: ADATA LEGEND 960 MAX 1 TB
- Cooler: Cooler Master MasterLiquid 360 ATMOS
- PSU: ASUS ROG THOR 1600 W Titanium
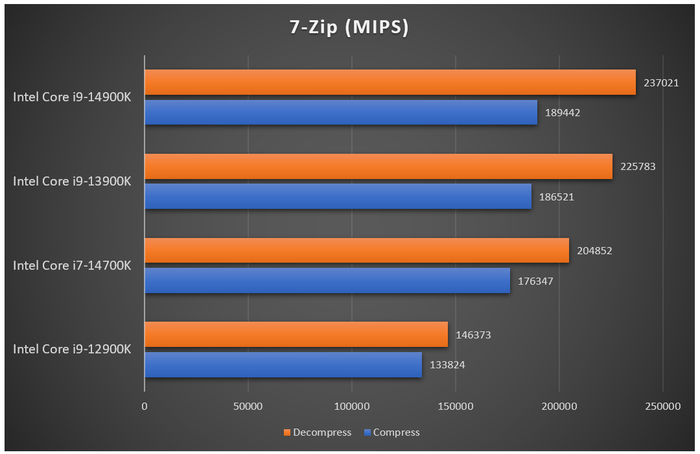
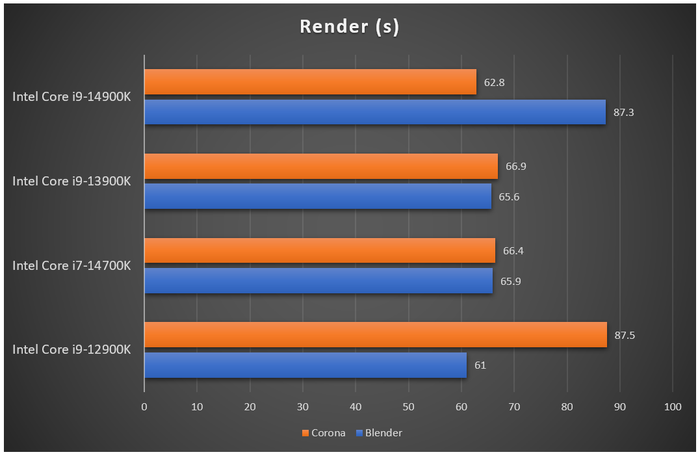
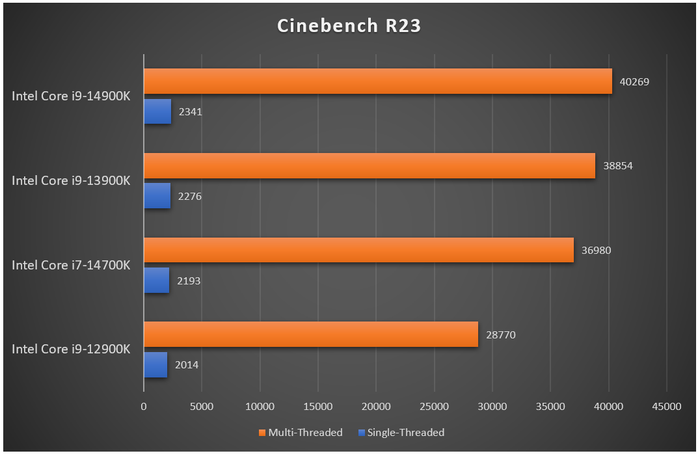 When it comes to rendering tasks, leveraging the processing power of each core within the chip, the Core i7-14700K performs exceptionally well, surpassing even the higher-tier Core i9-12900K and coming close to the Core i9-13900K. With the additional E-cores, the Core i7-13700K also proves no match for the corresponding Raptor Lake-S Refresh. Compression and decompression tests using 7-zip yield similar results, with the Core i7-14700K outperforming its predecessor, the Core i7-13700K, and trailing only slightly behind the Core i9-13900K. Gaming with the Core i7-14700K at the same system settings shows frame rates only marginally lower than the Core i9-13900K across Full HD, 1440p, and 4K resolutions.
When it comes to rendering tasks, leveraging the processing power of each core within the chip, the Core i7-14700K performs exceptionally well, surpassing even the higher-tier Core i9-12900K and coming close to the Core i9-13900K. With the additional E-cores, the Core i7-13700K also proves no match for the corresponding Raptor Lake-S Refresh. Compression and decompression tests using 7-zip yield similar results, with the Core i7-14700K outperforming its predecessor, the Core i7-13700K, and trailing only slightly behind the Core i9-13900K. Gaming with the Core i7-14700K at the same system settings shows frame rates only marginally lower than the Core i9-13900K across Full HD, 1440p, and 4K resolutions.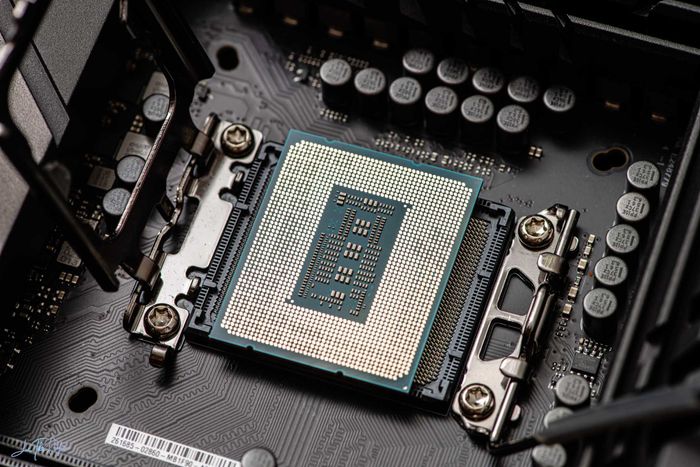 Within the 14th generation of processors - Raptor Lake-S Refresh - the Core i7-14700K stands out as the most prominent and distinctive model. The addition of extra E-cores, increased L3 cache, and improved boost clocks are the highlights of the i7-14700K compared to its predecessor. The chip's performance in tasks like rendering, data compression, encoding, and gaming all surpasses its older generation, even approaching that of the Core i9-13900K. For those using Intel 600 Series or 700 Series chipsets with older CPUs, upgrading to the Core i7-14700K is worthwhile. In Vietnam, the retail price of the Intel Core i7-14700K is around 11.5 million dong, while the non-integrated graphics option - Core i7-14700KF - is cheaper by about 600,000 to 700,000 dong.
Within the 14th generation of processors - Raptor Lake-S Refresh - the Core i7-14700K stands out as the most prominent and distinctive model. The addition of extra E-cores, increased L3 cache, and improved boost clocks are the highlights of the i7-14700K compared to its predecessor. The chip's performance in tasks like rendering, data compression, encoding, and gaming all surpasses its older generation, even approaching that of the Core i9-13900K. For those using Intel 600 Series or 700 Series chipsets with older CPUs, upgrading to the Core i7-14700K is worthwhile. In Vietnam, the retail price of the Intel Core i7-14700K is around 11.5 million dong, while the non-integrated graphics option - Core i7-14700KF - is cheaper by about 600,000 to 700,000 dong.