1. Hebrew (Jewish) Language
Hebrew is an ancient and unique language, often considered sacred (lashon hakodesh) – many Orthodox Jews only use it for prayer. Originally a Biblical language, Hebrew was revived after 2,000 years and is now spoken as a modern language by over 9 million people. In the Middle Ages, Hebrew was mainly used for writing religious texts. Today, it is widely spoken and is the official language of Israel. Modern Hebrew differs from the ancient or Classical Hebrew used in Jewish religious texts and prayers. After Israel, the United States has the second largest Hebrew-speaking population.


2. Aramaic Language
Aramaic is believed to have originated with the Arameans around the late 11th century BCE. By the 8th century BCE, it was adopted by the Assyrians as a second language.
Aramaic also served as a widespread language among the Jewish people. Though not as famous or sacred as Hebrew, it was widely spoken by Jews and other religious communities such as Christians and Muslims. It is one of the oldest languages in the region.


3. Chinese Language
The Chinese language originated around 3000 BCE and evolved significantly by 1200 BCE during the Zhou Dynasty. Following the fall of the Northern Song Dynasty (959–1126), Old Mandarin was widely spoken during the Jin (1115–1234) and Yuan (Mongol) Dynasties in northern China. The development of Classical Chinese started at this point.
Studies show that there are hundreds of modern Chinese dialects derived from various forms of Classical Chinese, with Mandarin now the most widely spoken language in the world. It spread rapidly across China and to neighboring regions, including Vietnam.


4. Greek Language
The Greek language has been spoken on the Balkan Peninsula since around the 3rd millennium BCE, or even earlier. The earliest known written evidence of Greek is a clay tablet in Linear B found in Messenia, dating back to approximately 1450–1350 BCE, making Greek one of the oldest languages still in existence.
Greek is primarily spoken in Greece, Albania, and Cyprus by around 13 million people. The Greek language holds a significant place in the history of Western civilization and Christianity. Ancient Greek literature, including works like the Iliad and the Odyssey, has profoundly influenced Western literature. Greek also serves as the language of many foundational texts in science, particularly in astronomy, mathematics, logic, and Western philosophy, including the works of Aristotle. Along with Latin, Greek is a major source of international scientific vocabulary.

5. Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language is a Northern Afro-Asiatic language closely related to Berber and Semitic languages. It is one of the oldest languages in history, second only to Sumerian, and was written from around 3200 BCE through the Middle Ages, continuing as a spoken language long after. The stages of Ancient Egyptian include Old Egyptian, Middle Egyptian (Classical Egyptian), Late Egyptian, Demotic, and Coptic.
Egyptian is considered one of the most historically significant languages in the world. Its simplified hieroglyphic script provides insight into daily life and culture in ancient Egypt. However, Egyptian writing is no longer widely used due to its difficulty in learning and transcription.


6. Sanskrit Language
Sanskrit is an ancient language of India with a history spanning over 3,500 years. It is the primary liturgical language of Hinduism and serves as the main language for many key philosophical works of Hinduism, as well as important texts in Buddhism and Jainism.
As one of the oldest documented members of the Indo-European language family, Sanskrit holds a prominent place in Indo-European studies. It is related to Greek and Latin, as well as extinct languages like Hittite, Luwian, Old Avestan, and many others that hold historical significance in Europe, West Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. Today, Sanskrit can be found in various Indian scriptures and in famous temples across the region.


7. Tamil Language
Tamil is the official language of Tamil Nadu and the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. It is also used in education in Malaysia, alongside English, Malay, and Mandarin. The earliest phase of Tamil literature, known as Sangam literature, began around 300 BCE.
In 2004, Tamil was recognized as a classical language of India. It met three criteria: its ancient origin, an independent tradition, and a rich body of ancient literature. By the early 21st century, over 66 million people spoke Tamil.


8. Latin Language
Latin is a classical language from the Indo-European family, originally spoken in the region around the city of Rome. As the Roman Empire expanded, Latin became the dominant language across vast territories. During its peak, it was considered the language of power, the official language for international communication, academic texts, and scientific research.
The Latin alphabet is derived from the Etruscan and Greek alphabets. Five Romance languages—French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and Romanian—are all descended from Latin, with much of their vocabulary and grammar rooted in it. In addition, approximately 50% of English vocabulary and grammar traces its origins back to Latin.


9. Armenian Language
Along with Latin, Armenian is another significant language within the Indo-European family. It is widely believed that the Armenian alphabet was created around 450 BCE, with the Bible translation being one of the oldest artifacts proving its existence.
Today, more than 5 million people speak Armenian worldwide. The modern language has two main branches: Eastern Armenian, which is the official language of Armenia, and Western Armenian, spoken by many in the Armenian diaspora. A unique feature of Armenian is its distinct alphabet, which is celebrated with a monument in Armenia where all 39 characters are carved into massive stones.


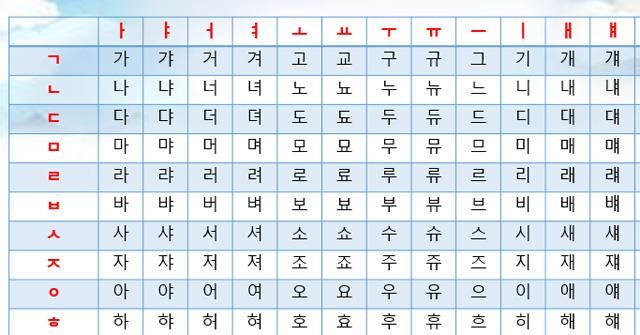
10. Korean Language
The Korean language traces its origins back to around 300 BCE. It is believed that Korean evolved through a combination of ancient languages, developing into its modern form through the medieval language of Goryeo in the north and the language of Gaya Silla in the south.
Korean is the official language of both the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and the Republic of Korea. Various dialects of Korean are spoken throughout both countries, and it is also one of the two official languages in the autonomous Korean region of the People's Republic of China in Yanbian. Over 80 million people around the world speak Korean.