
Comprehensive guide on how to recover data from an old or damaged USB that you need to be aware of.
1. Guide to Resolving USB Hardware Issues
Check if the USB is compatible with the port
This is one of the initial steps users should take when a USB faces issues. Ensure that the USB size matches the USB port on the computer. Incomplete contact points with the USB can lead to various problems, such as random disconnection, file loss, and slow data transfer speed.

Gently shake the USB to check if it fits snugly into the USB port. In some cases, you may need to hold the drive at a certain angle to ensure proper connection and easy data access.
Inspect the shell and intact pins
Examine both the external casing and USB pins to ensure they are intact. If the pins are corroded or the shell is bent, it may lead to connection issues, resulting in data loss within the USB drive.
Check inside the port for any debris or dirt that might hinder the connection. Gently clean them off without blowing, as it could worsen the situation.
Inspect the USB port
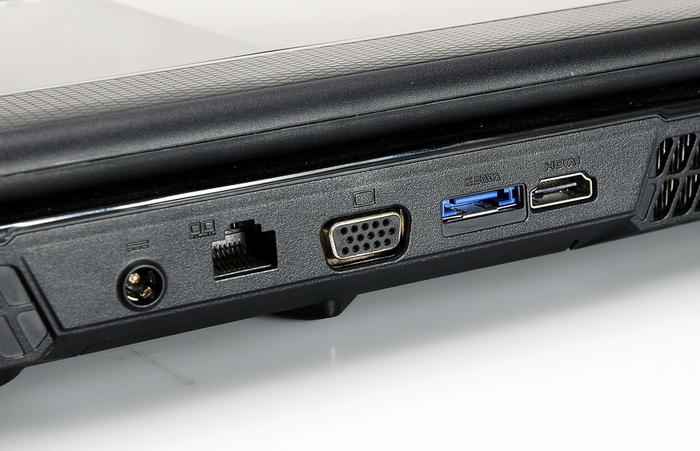

The USB port on your computer could also be a potential cause of the issue. Similar to the USB port on the drive, check if there is any debris or dust inside. Additionally, make sure none of the pins are bent, as it could render the port useless.
Check for damaged USB motherboard
Try opening the USB and carefully examine the internal circuit board for any signs of damage. If the USB motherboard is damaged, it means the issue may be irreparable. However, for crucial data, consider replacing the faulty component or reaching out to data recovery services.
2. Guide on how to troubleshoot USB software issues
Run a diagnostic scan
Scanning a corrupted USB can identify and address issues for potential repair.
Windows
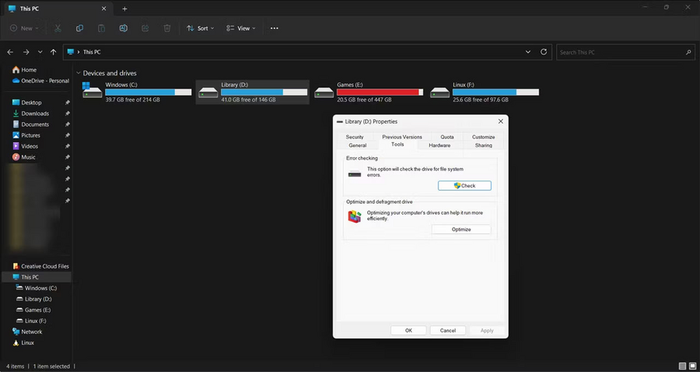
Step 1. Firstly, select your USB in the Windows File Explorer. Right-click on it and choose Properties from the appearing menu below.
Step 2. In the Tool tab, click on Check to initiate a scan on the drive and identify errors.
macOS
Step 1: Access Disk Utility by navigating to Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility.
Step 2: In Disk Utility, a list of drives will appear on the left side of the window. Select your USB from the list.
Step 3: At the top of the Disk Utility window, click on First Aid.
Step 4: A dialog box will appear, asking if you want to run First Aid on the selected drive. Click on Run. Disk Utility will then search for and fix errors on the drive.
Linux
Step 1. Insert the USB into the computer and access the Terminal. Type the command sudo fdisk -l and press Enter.
Step 2. The drives currently connected to the computer will be displayed. Locate your hard drive by name or partition.
Step 3. Disconnect the drive. Enter the command sudo umount /dev/sdb1 (replace '/dev/sdb1' with the ID of your drive) and press Enter.
Change Drive Letter
Changing the drive letter can sometimes force Windows to read a drive it couldn't read before.
Step 1. Press the Windows + R key combination to access Run. Enter the command diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
Step 2. Locate your drive, right-click on it, and choose Change Drive Letter and Path.
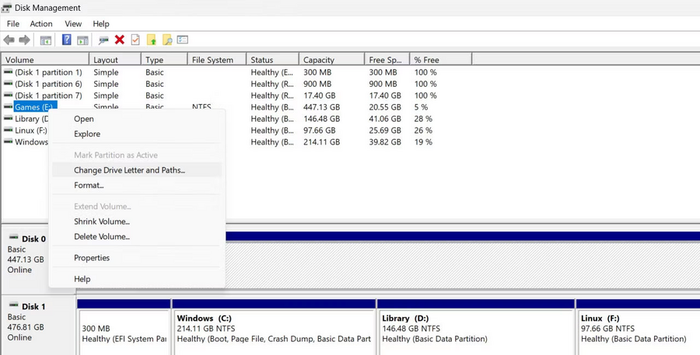
Step 3. Click on Change.
Step 4. From the drop-down list, choose the drive letter you want and click OK.
Check USB driver
Step 1. In the Start menu on the taskbar, click on Device Manager.
Step 2. Inside the drive, right-click on the USB and select Update driver.
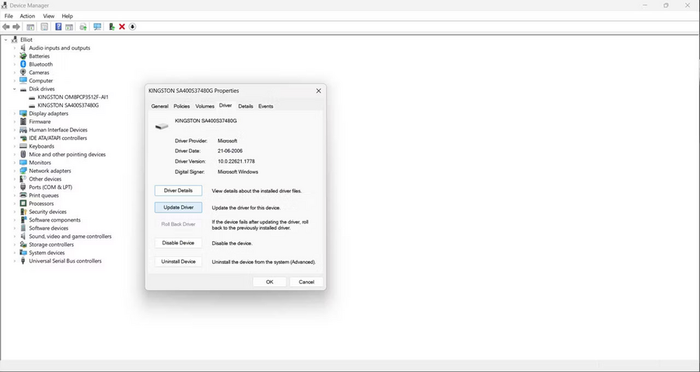
Step 3. Choose Search automatically for drivers, and Windows will install relevant updates.
Here are ways to retrieve data from a damaged or old USB that you need to be aware of. Save this for reference and application. Don't forget to follow Mytour for quickly updating the most useful information.
