1. Eating Boogers is Good for Your Health
It may sound bizarre and even disgusting, but some doctors and scientists have actually proven the health benefits of eating boogers. Professor Scott Napper (from Canada) conducted research that revealed an interesting result: while boogers don’t contain many nutrients, when digested, they can boost your immune system.
Surveys have also shown that most people who eat boogers tend to lead more energetic lives and experience less stress. However, don’t rush to start eating your boogers just because of this information—doing so could increase your risk of nosebleeds!


2. The Small Intestine is as Long as a Truck
The human small intestine isn’t straight—it has a twisted, coiled shape that helps save space. It stretches an impressive 5 to 9 meters in length, which is roughly the same length as a truck.
Even more astonishing is the total surface area of the small intestine, which covers 400 to 500 square meters. Looking at it from the outside, it’s hard to believe it could be so long and expansive.
3. The Average Person Can Produce 2 Swimming Pools of Saliva
Saliva is a crucial secretion for the human body. It keeps your mouth moist and ensures that your internal organs stay well-lubricated.
Every day, our bodies constantly produce saliva. Interestingly, it increases significantly when triggered by our senses, especially smell and sight. For instance, when you hear about a delicious meal or see it, your salivary glands kick into overdrive, making you salivate more as a response to hunger.
Scientific studies show that, over the course of a lifetime, a person can produce as much as 28,500 liters of saliva—about the equivalent of two swimming pools' worth!

4. We Breathe Through Only One Nostril at a Time
This means that when we breathe through the left nostril, the right nostril gets a break, and vice versa. In fact, about 85% of people breathe through just one nostril at a time.
Every four hours or so, your body alternates the airflow between nostrils to ensure continuous breathing. Interestingly, the activity of your nose is also connected to brain function: when breathing through the right nostril, the left side of your brain is stimulated more, and the opposite happens when breathing through the left nostril.


5. Humans Shed Skin Every Day
Every minute, around one million skin cells die and are replaced. This process is visible when you occasionally notice small flakes of white skin falling off—these are dead skin cells being shed, much like a process of ‘skin peeling’.
Each hour, approximately 600,000 skin flakes are replaced. If you live to the age of 70, you will have shed nearly 50 kilograms of skin—an impressive figure indeed!


6. As We Grow, the Number of Our Bones Decreases
You might have thought that children start with fewer bones and their number increases as they grow, but that's not true! As we mature, smaller bones fuse together to create stronger, more stable ones.
While babies are born with around 350 bones, adults typically have just 206. The bones don’t disappear; instead, they combine to form a more robust skeletal system that supports the body better.

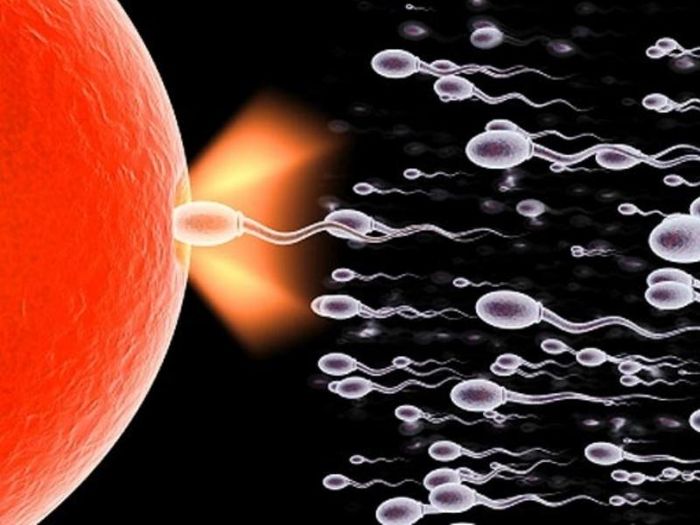
7. The Secrets of Sperm
The male body produces an average of 10 million sperm cells every day. During each ejaculation, around 180 million sperm are released. Each sperm carries 37.5 megabytes of DNA information from the male, the exact amount needed to create a child. Therefore, every ejaculation from an adult man transmits information equivalent to 1,500 terabytes. However, studies show that up to 90% of the sperm in a single ejaculation are deformed, as reported by Healthday. Sperm also contains calcium, potassium, sodium, vitamin C, citric acid, fructose, nitrogen, chlorine, and other substances.
Sperm cells are the male reproductive cells, crucial for human reproduction. A man has around 1,500 billion sperm, or approximately 17 liters of semen over the course of his life.
However, not every sperm cell that is produced can fertilize an egg. They must undergo a fierce race, and only the strongest and healthiest sperm reach the egg for fertilization.
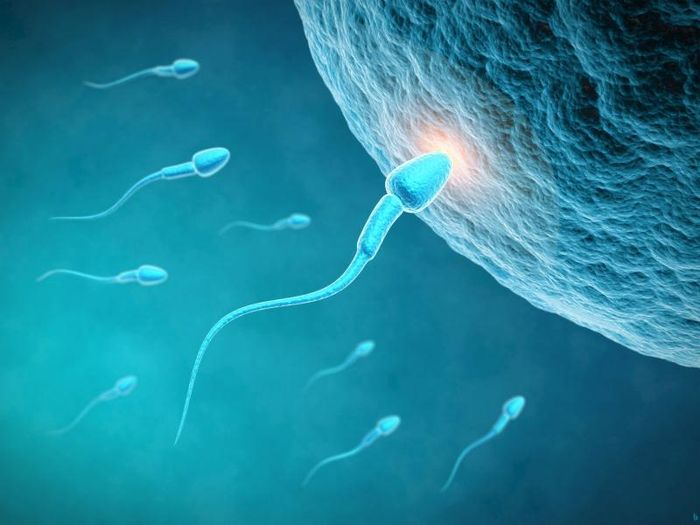
8. Humans Cannot Breathe and Swallow at the Same Time
You might think that breathing and swallowing have nothing to do with each other. Try breathing and swallowing simultaneously, and you’ll see that it’s impossible. This happens because, whether you breathe or swallow (or even eat something), both air and saliva (or food) must travel through the esophagus. When this happens, food heads to the stomach while air goes to the lungs. To prevent food from entering the lungs and air from entering the stomach, a valve automatically closes off one path while you breathe or swallow.
Humans are the only mammals that can’t breathe and swallow at the same time. When we’re born, we all have this ability. This is why newborns can breathe and nurse simultaneously. However, we lose this ability by around 9 months of age, as the larynx in the throat descends. According to Discover magazine, while this drop in the larynx allows us to produce a wider range of sounds, it also means we lose the ability to breathe while eating or drinking.

9. The Length of Your Nose Equals Your Thumb
Ever wondered how long your nose is? Well, it turns out the length of your nose is about the same as your thumb!
If you're reading this and checking your thumb to compare, you're probably surprised at how closely the two measurements match, right? The length of your thumb and your nose is almost identical, which is a fascinating coincidence.


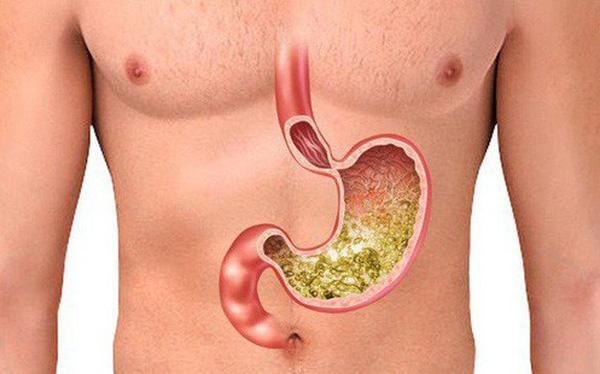
10. The Stomach Can Destroy Steel
To digest food, the stomach secretes a unique acid. Once food enters, your stomach continuously contracts and releases acid to break down food into beneficial nutrients, while also helping to expel waste.
What's remarkable is that the surface of the stomach has a lining that regenerates every 3 to 4 days. If this lining fails to renew, the stomach acid will begin to erode the stomach itself, mistakenly thinking it’s food. The acid is so potent that it can even break down a razor blade.