1. High Blood Pressure
According to recent statistics, high blood pressure is the leading cause of death worldwide, claiming the lives of 7 million people each year. In Vietnam, there are nearly 21 million people affected, with deaths outnumbering traffic accidents by 10 times.
Almost half of those with high blood pressure are unaware of their condition. Suddenly, you may experience a heart attack, stroke, or kidney disease. If lucky enough to survive, you'll realize this condition has silently damaged your blood vessels for a long time. Hence, for prevention, it's advised to check blood pressure at least once a year, even if you don't perceive any risks.
Limit alcohol consumption, manage weight for obese individuals, engage in physical activity daily like walking for 30 – 45 minutes, perform gentle exercise 4-5 days a week. Regular health check-ups every 6 months are essential to detect and treat any illness early (if present). For those already diagnosed, the utmost importance lies in controlling and stabilizing blood pressure promptly and consistently. To achieve this, regular and consistent medication usage is necessary.

2. High Cholesterol
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. It usually occurs in people over 40, although there is another form of glaucoma in newborns (congenital). Those with a family history of glaucoma are at high risk of developing the condition. Other risk factors include thinner corneas, chronic eye inflammation, and use of eye pressure-raising medications.
This is a condition that destroys vision by attacking the optic nerve. But visual decline occurs very slowly, so slowly that you may not realize your eyes have a problem until your condition has progressed to an advanced stage. Sometimes you may stumble on the sidewalk, miss a step on the stairs, or spill a cup because your vision is not wide-ranging. You also struggle to drive at night, as you can't see well if the lights are too bright or too dim.
To prevent this condition, you should undergo screening tests at age 40, then repeat screening every 2 - 4 years depending on your risk of developing the disease. After age 65, you should have annual check-ups.


3. Sleep Apnea
Research indicates that about half of women aged 20 to 70 often suffer from sleep apnea, a condition where your breathing stops while you sleep. This can increase the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Instead of loud snoring and daytime sleepiness, women with this condition often wake up with headaches, mood swings, and mild fatigue.
These symptoms are often overlooked. Another sign of this condition is insomnia. Women wake up in the middle of the night because their breathing stops, jolting them awake. To prevent this disease, you should see a doctor if you experience these symptoms. The doctor can measure your heart rate, breathing rate, and blood oxygen levels to diagnose the condition.
Sleep apnea can also affect children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly. Those at higher risk include overweight or obese individuals, those with metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases (with elevated blood pressure resistance, poorly controlled blood pressure), or patients with poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
In the short term, sleep apnea affects concentration in learning, work, labor, and can particularly cause hyperactivity in children and pose dangers when participating in traffic.

4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
About 10% of women of childbearing age suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This occurs when the body produces excess male hormones, disrupting the ovulation process and increasing the risk of heart disease or type 2 diabetes. Less than 50% of women with this condition are diagnosed early, most are unaware they have the condition, especially those who use contraceptive pills. Most patients only seek medical attention and discover the disease when they have trouble conceiving. If not properly diagnosed, they may only be prescribed ovulation-inducing drugs.
This is concerning because half of women with this condition will develop prediabetes or diabetes before age 40. They are also at risk of high blood pressure, sleep apnea, high cholesterol, and endometrial cancer. To detect the disease early, pay attention to common symptoms such as irregular menstruation (cycles lasting more than 35 days without birth control pills). Other signs include acne (not just teenage acne), excessive facial and body hair, and thinning hair. Some combination medications and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition.

5. Diabetes
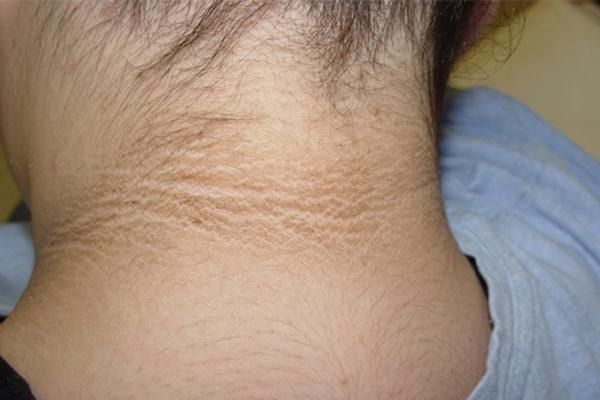
According to estimates by public health experts, about 8 million out of 29 million diabetes cases are diagnosed too late. The blood sugar level may already be abnormal, but you hardly have any symptoms. Minor signs like dry mouth, constant thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, etc., are easily overlooked. You might think you're just stressed or tired. For those who are overweight, you may develop acanthosis nigricans (meaning that areas of skin on the neck, underarms, groin, elbows, etc., become thickened and dark (or brown), looking dirty. At this point, you may not have diabetes yet but your body is producing excess insulin.
Therefore, to prevent diabetes, everyone aged 45 and older should undergo diabetes screening every 3 years. If you're overweight, have high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, then you should undergo screening more frequently.
6. Cerebrovascular accident
Cerebrovascular accident or stroke is a condition caused by the inability to supply blood and oxygen to the brain, leading to the sudden loss of brain function. The disease occurs within a 24-hour period, and severe strokes can lead to death during this time. According to some studies, this is the second leading cause of death worldwide and in Vietnam, second only to heart disease.
If in the past, cerebrovascular accidents mainly occurred in the elderly, nowadays, it is increasingly common in young people. The cause is due to imbalanced diet, excessive alcohol consumption, or stress and pressure.
Cerebrovascular accidents are extremely dangerous, and the likelihood of death is very high, so young people cannot take it lightly. The best way is to prevent it by adhering to a balanced diet, exercising regularly, working and resting properly, moderating stress, and not allowing the brain to function continuously for long periods of time.
7. Lung Cancer
In the early stages, this disease hardly shows any symptoms. But by the time it's detected, patients hardly have a chance of survival. More than half of the patients have never smoked, so they never suspect they have the disease. To prevent lung cancer, if you have been smoking for over 30 years (about 1 pack a day for 30 years, or 2 packs a day for 15 years) and are over 55 years old, you should get an annual lung CT scan.
This method can detect the disease early and reduce the mortality rate by up to 20%. For non-smokers, there's no need for screening because the results are rarely accurate. However, if you have a persistent cough for 2 weeks, wheezing, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, etc., you should visit a specialized hospital for examination.

8. Heart Disease
Cardiovascular diseases are often referred to as “silent killers”. Progressing silently is what makes the disease dangerous. Therefore, recognizing the early signs of heart disease is also protecting yourself and your family from potential complications. Heart failure is the ultimate consequence of most heart diseases, difficult to cure, but patients have many opportunities to alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, coughing, swelling, and slow down the progression of the disease.
In the early stages when cardiovascular diseases transition to heart failure, symptoms are very difficult to detect, so many patients lose the opportunity for early treatment. In the progressing stage, patients may experience typical symptoms of heart failure such as shortness of breath, fatigue. Patients always feel exhausted or tired even when performing daily and simple activities.
The prognosis of cardiovascular patients is difficult to predict, worsening or improving over time depending on the treatment method, early or late detection of the disease.
9. Leukemia
Leukemia occurs when white blood cells are produced excessively and rapidly in a short period of time. White blood cells are naturally produced to protect the body from external factors. However, excessive production of white blood cells leads to a condition where white blood cells attack red blood cells. Red blood cells will gradually be destroyed, and patients will show signs of anemia. If not treated promptly, it can lead to death in a short time. This is a malignant cancer that does not form tumors.
This disease often occurs in people exposed to radiation, or in highly polluted environments. Leukemia is acute and progresses rapidly. If not detected and treated promptly, it can pose a danger to health and lead to death.

10. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, also known as brittle bone disease or porous bone, is a condition where bones gradually thin out and the density of bone material decreases, making the bones more fragile and prone to fractures even with minor trauma. As people age, bone mass is lost faster than it is produced, leading to osteoporosis. Therefore, your risk of osteoporosis depends on the highest bone mass you achieved in youth. If your peak bone mass is high, it means you have 'stored' more bone and are less likely to develop osteoporosis as you age.
Osteoporosis is a silent disease that is only detected when a bone is fractured. Many people believe that osteoporosis is a natural and unavoidable part of aging. However, modern healthcare experts believe that osteoporosis can be prevented. Moreover, individuals who have osteoporosis can still take steps to prevent or slow down the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of fractures in the future.