The Vatican is the country with the smallest population in the world, with only about 1,000 people. In addition, The Vatican is also the smallest country in the world (about 44 hectares). This country was established in 1929 based on the Lateran Treaty as the successor to the Papal States. The Pope is the head of state and the leader of the government of Vatican City. At the same time, the Pope is the Bishop of the Diocese of Rome, and the leader of the Holy See and the Catholic Church. The current Pope is Pope Francis, born Jorge Mario Bergoglio and from Argentina. The Secretary of State is currently Pietro Parolin. The President is currently Fernando Vérgez Alzanga.
In Vatican City, there are many large structures such as St. Peter's Basilica, the Vatican Museums, the Sistine Chapel, etc. Despite its small size, Vatican City is a powerful and influential country with a significant impact on billions of Catholics worldwide (constituting about 1/6 of the world's population). The main budget of Vatican City comes from contributions from Catholic churches worldwide, through the issuance of publications and tourism.


2. Nauru
Nauru is essentially an island nation in the southern Pacific with an area of about 21 km2, ranking as the third smallest in the world after Vatican City and Monaco. The population of Nauru is only 13,005 people. Nauru is also the only country in the world without an official capital. The President of Nauru heads both the executive and the unicameral parliament consisting of 19 members. Nauru is a member of the United Nations, the Pacific Community, the Asian Development Bank, and the Pacific Islands Forum. Nauru also participates in the Commonwealth Games and the Olympics.
The people of Nauru use two languages, English and the native language (Nauruan). The country's main source of income comes from phosphate exports. Australia provides diplomatic and defense protection for Nauru. Remarkably, 90% of the population in Nauru is affected by obesity due to high alcohol consumption and fatty food.
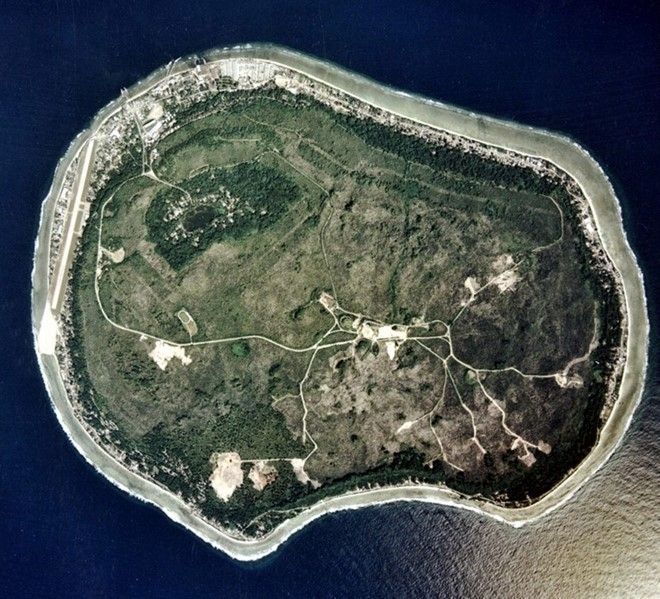


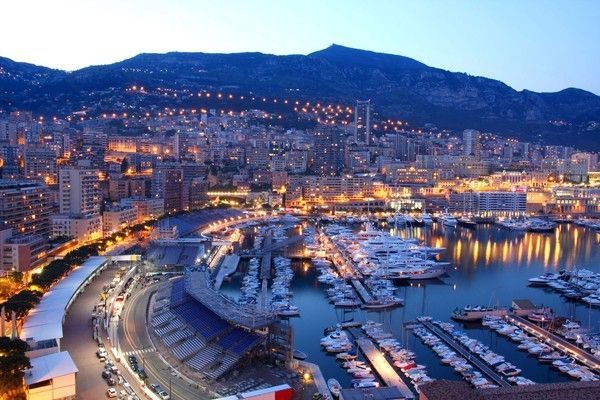
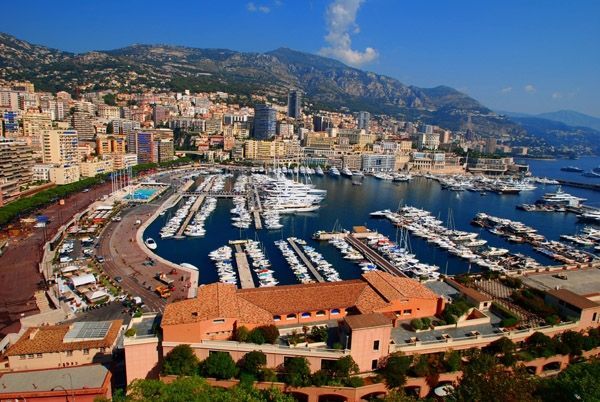
3. Principality of Monaco
Monaco is an incredibly tiny country with an area of 1.96 km2 and a population of only about 35,675 people. Positioned between France and Italy, Monaco has been known as a principality since the 15th century. From the early 16th century to the mid-17th century, Monaco was invaded by the Spanish, and by the late 18th century and the early 19th century, it fell under the protection of France.
In 1861, Monaco officially separated from French territory and became an independent country. The reigning monarch leads Monaco and holds legislative power along with a National Council. Monaco's economy relies mainly on industry and taxes collected from the casinos in Monte Carlo. Despite being a small principality along the Mediterranean, Monaco is one of the wealthiest and most extravagant countries in the world, surpassing Dubai in tradition and sophistication in spending money.


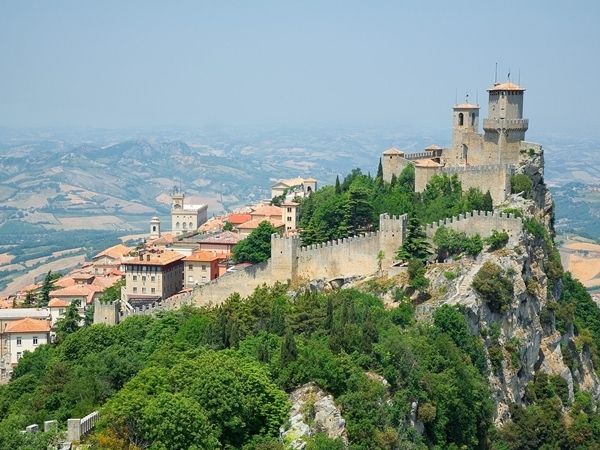
4. Republic of San Marino
Republic of San Marino is the name of a country located in northeast Italy. With an area of only 61 km2 and a population of about 28,117 people, San Marino was established in 301 BC by a Christian named Marino. The country is known for having one of the highest life expectancies in the world.
The economy of San Marino relies mainly on agriculture and tourism. Every year, the country welcomes around 3 million tourists from all over the world. Therefore, the income of the people in San Marino is considered high worldwide. San Marino has 220 km of roads within the country, and the main road is the San Marino Highway. There is no public airport, but there is a small private airstrip in Torraccia and an international heliport in Borgo Maggiore. Most tourists arrive by air at the Federico Fellini International Airport near the city of Rimini, then travel by bus. There is no major water transportation, and there is no port in this tiny country.


5. Tuvalu
Tuvalu is an island nation in the South Pacific, consisting of 9 coral atolls with a surface area just above sea level. Tuvalu's land area is only about 26 km2, and it has a population of 10,441 people. Tuvalu is a country within the British Commonwealth, with the head being Queen Elizabeth II. During World War II, thousands of Americans flocked to Tuvalu, and the archipelago became an Allied base. Many airports were built here, but they were abandoned after the war.
Due to the low sea level, Tuvalu's land is infertile, lacking mineral resources for exploitation. The country's economy relies heavily on fishing, seafood, and subsistence agriculture. The government's primary revenue comes from selling stamps and old coins, as well as foreign exchange from overseas migrant workers. Additionally, Tuvalu receives annual aid from the UK, Australia, and New Zealand, totaling around $100 million per year since 1987, and other countries such as the US, Japan, South Korea, and the European Union through bilateral economic agreements.


6. Marshall Islands
With a population of just under 60,000 people, the entire surface area of the Marshall Islands is approximately 181.4 km2. In 1986, the US and the Marshall Islands signed the Compact of Free Association, establishing self-government with economic and military assistance from the US, around $65 million annually. The Marshall Islands joined the United Nations in 1991. The economy relies mainly on deep-sea fishing, tourism, and US aid. Agriculture only meets domestic consumption needs.
In the Marshall Islands, compulsory and free basic education is provided for children aged 6 to 14. Afterward, students must pass a national exam to enter high school. English and Marshallese are used in primary school, and only English is used in higher grades. The Marshall Islands has a community college in the capital, Dalap-Uliga-Darrit. Most young adults go to the US or other countries for higher education if they wish to continue their academic journey.


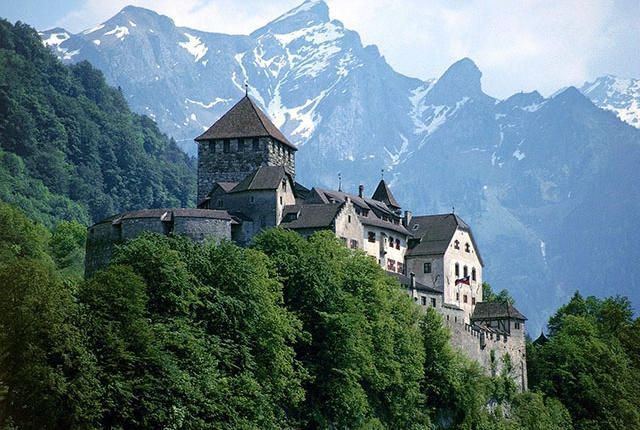
7. Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein is a small landlocked country in Western Europe, surrounded by landlocked countries. It boasts one of the world's highest average Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. With a population of around 33,300 people and a modest area of 160 km2, Liechtenstein's ruling prince is one of the six wealthiest monarchs, with an estimated net worth of about 5 billion USD. The standard of living for its residents is also among the highest globally.
The economy of Liechtenstein is primarily industrial, focusing on processing imported raw materials. It manufactures components, electronics, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, printing machines, office supplies, and dentures. The country hosts 35 mostly Swiss-owned industrial firms employing approximately 4,000 people. Agriculture is self-sufficient, contributing 14% and mainly involves livestock farming, viticulture, and wheat cultivation. The nation's income comes from exporting industrial products, taxes, producing stamps for tourism purposes.


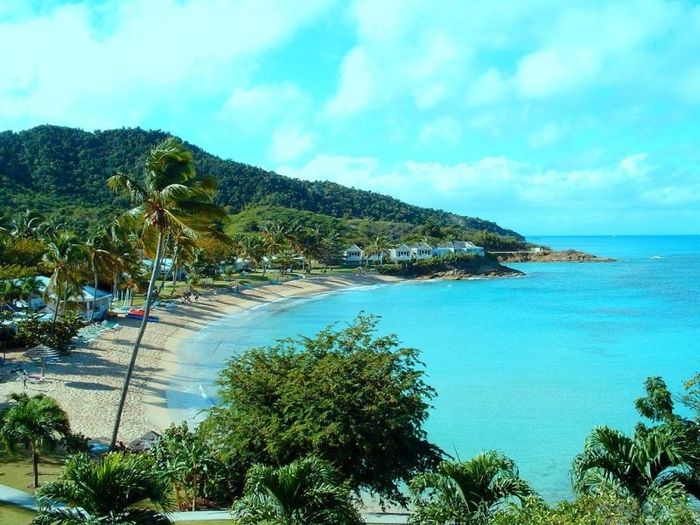
8. Antigua & Barbuda
With a population of approximately 70,000 people, Antigua & Barbuda is a relatively small country with an area of about 442 km2. The nation is located in the southern part of the Windward Islands in the Lesser Antilles. In 1632, Antigua was occupied by the British. By 1667, it became a British colony. In February 1967, the country achieved internal self-government and became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations.
Barbuda is a coral island known for its abundant wildlife, including wild pigs, jungle fowl, deer, and more, making it a paradise for hunting enthusiasts. Due to their proximity, about 40 km apart, the two islands are often referred to as 'sister islands' in the Caribbean region. Before the 1960s, the country's economy relied heavily on sugar cane cultivation, but high production costs and soil erosion made this industry unsustainable. Today, tourism plays a significant role in the economy, contributing to over half of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), with renowned luxurious resorts making it a top destination worldwide.


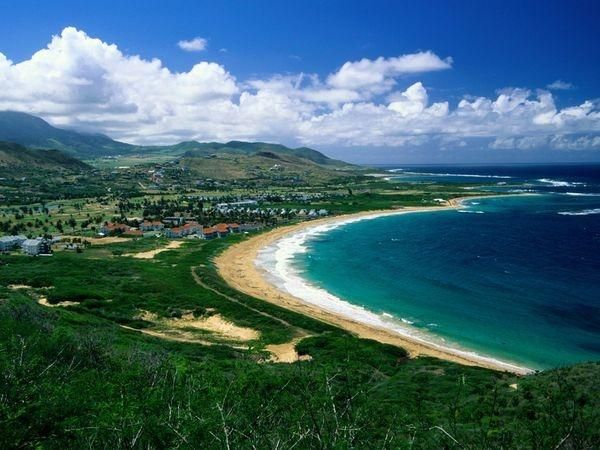
9. Federation of Saint Kitts & Nevis
The Federation of Saint Kitts & Nevis is an island nation in the Leeward Islands, West Indies. With a population of approximately 42,000 people, it covers a total area of 261 km2. Saint Kitts and Nevis is bordered by Saint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, and Saint Martin to the North-Northeast; it shares an eastern border with Antigua and Barbuda. To the Southeast, it is adjacent to the uninhabited island Redonda and the island of Montserrat, an area prone to frequent volcanic activity.
The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1983. Saint Kitts & Nevis, an island federation, has a developed economy with a focus on tourism. Agriculture and other manufacturing industries are also relatively advanced. The island's tourism sector has seen significant development and expansion since 1978. In 2009, approximately 587,479 visitors came to the islands, a substantial increase from the 379,473 visitors in 2007.


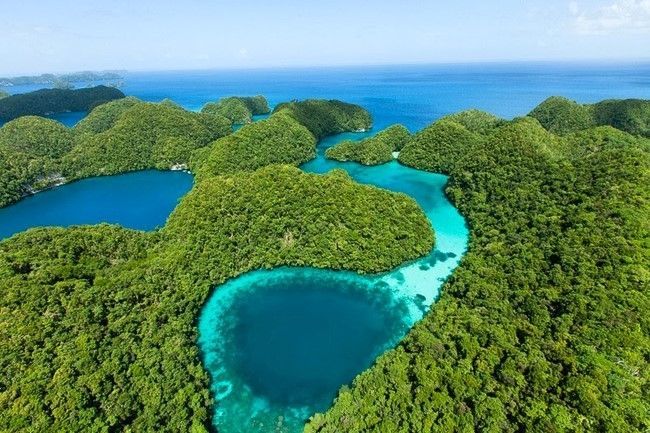
10. Republic of Palau
With a population of approximately 20,000 people and a total area of 459 km2, Palau is situated on a small island in the eastern Philippines, seemingly isolated in the central Pacific. Palau currently operates under a Constitutional government as outlined in the Compact of Free Association with the United States, effective since 1994.
The economy of Palau relies heavily on tourism, subsistence agriculture, and fishing, with a significant portion of the Gross National Product (GNP) coming from foreign aid. The official currency is the U.S. Dollar. The island's culture is a blend of Micronesian, Melanesian, Asian, and European influences. The majority of Palauans are the result of the mixing of three ethnic groups: Micronesia, Melanesia, and Austronesia. The remaining minority includes descendants of Japanese and Filipino settlers. The official languages are Palauan and English, with Japanese, Sonsorolese, and Tobian recognized as local languages.