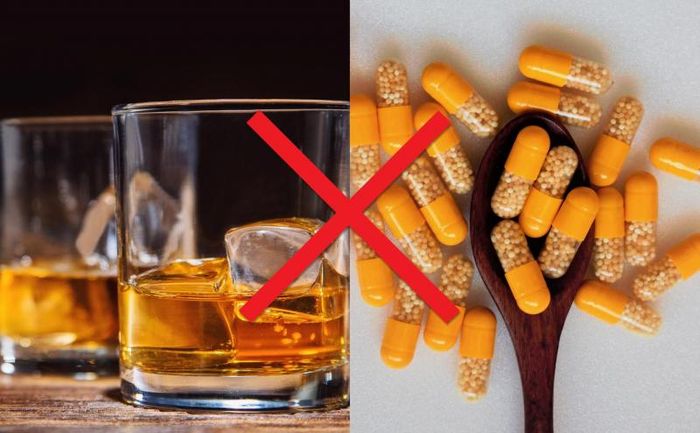
1. Alcohol
If taken together, alcohol and medication can significantly increase the harmful effects of alcohol or cause unfavorable reactions to the medication. During social gatherings, people often consume beer. Beer, or alcoholic beverages in general, contain absolute alcohol with a content usually ranging from 2 - 4%. The dangers of alcohol lie in its effects when consumed excessively. The inhibitory effects on the nervous system, liver damage, and gastric harm caused by alcohol lead to many medications not being recommended to be taken with it. If taken together, alcohol can amplify its harmful effects, or interfere with the medication, resulting in adverse consequences. Unfortunately, many people consider drinking alcohol while taking medication to be normal.
Statistics from 2008 show that about 64% of adults in the United States consume alcohol, accompanied by 3.8 billion prescribed medications. However, very few doctors emphasize the potential dangers of the interaction between alcohol and the prescribed medications. This lack of awareness contributes to a significant increase in hospitalizations due to alcohol-related issues. Did you know that ethanol, a substance found in alcohol, can interact with antibiotics, diabetes medications, and blood pressure medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness and causing adverse reactions that can impact life? Therefore, alcohol, especially beer, should be limited when taking medication. Men, in particular, should take note and strictly avoid drinking beer along with medication.


2. Milk
Milk is a common and nutritious beverage suitable for all ages. While it helps restore health and enhance physical fitness, the relatively high calcium content in milk, when combined with certain medications, can cause precipitation and neutralize the efficacy of the drugs. Many parents give their children medicine with milk, which can reduce drug absorption. Therefore, doctors recommend taking milk at least 2 hours away from medication to avoid compromising the drug's effectiveness. Some antibiotics, including ciprofloxacin, may form clumps with calcium, iron, and other minerals. Milk is a food rich in these minerals. This clumping reduces the body's drug absorption ability and decreases the drug's effectiveness.
As you may know, besides water and organic compounds, milk contains numerous trace minerals. With a high lipid content and alkalinity, milk slows the absorption of certain drugs, such as the antibiotic cefuroxime. Especially, the abundant calcium in milk can interact unfavorably with drugs (calcium can react with drugs, forming poorly soluble complexes that are not absorbable). Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin) may lose their effectiveness when taken with milk. Tetracyclines also interact with calcium when taken together. The effects of penicillamine and trientine may diminish if taken with milk. To help children overcome the fear of medicine, numb their tongue with an ice cube before taking the medicine, and after taking the medicine, give them a sweet candy to avoid the medicine's aftertaste. For younger children, dissolve pills or powder in a small amount of boiling water to cool, add a little sugar for easier consumption. For children whose main source of nutrition is milk, reduce this interaction by taking medicine at least two hours before or after consuming milk.

3. Coffee
Many scientific studies have shown that moderate consumption of coffee can bring health benefits. However, for those using pharmaceuticals, coffee can alter the effects of medications. Especially medications treating thyroid, musculoskeletal, antidepressants, estrogen hormones, and more. A study conducted in 2008 revealed that people who drank coffee shortly before or after taking levothyroxine (used to treat hypothyroidism) experienced a 55% reduction in drug absorption, and with alendronate, a drug for bone thinning, absorption was reduced by 60%...
Coffee contains high levels of caffeine. The darker the coffee, the higher the caffeine content, leading to potential adverse reactions when taken with medication. Some side effects of the interaction between Western medicine and coffee include flushing, irregular heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and more. Therefore, you should absolutely avoid drinking coffee with medication to prevent undesired consequences that may harm your health and well-being. If you are a coffee addict and cannot skip your morning routine, ensure a time gap of 2-3 hours between taking medication and drinking coffee.


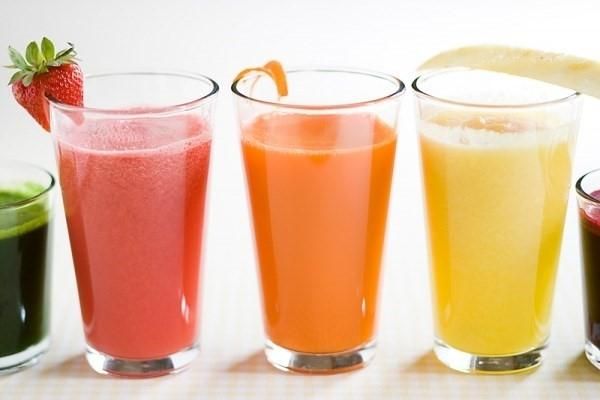
4. Fruit Juice
Fruit juice is rich in nutrients and beneficial for health. However, when taking medication, it's advisable to avoid certain types of fruit juice to prevent adverse effects. Health experts recommend not combining medication with fruit juice. Fruit juice contains many vitamins, enzymes, and when combined with certain medications such as heart, stomach, diabetes medications, it can reduce the efficacy of the drugs and even cause adverse reactions, posing a life-threatening risk. Therefore, remember to drink fruit juice at least 2 hours away from the time you take medication!
Grapefruit juice reacts with more than 40 different types of drugs, making you susceptible to dangerous side effects after taking medication. Avoid drinking grapefruit juice in the morning or when taking medication for high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or irregular heartbeat. Consuming grape juice with medication can reduce the drug's effectiveness and increase its side effects. The reason is that grape juice can inhibit enzymes during the drug absorption process. Additionally, orange and lemon juice are contraindicated when taken with certain antibiotics like ampicillin, erythromycin, lincomycin, as these antibiotics degrade in acidic environments. Meanwhile, combining drinks with citrus fruits with dextromethorphan for cough relief may increase the risk of adverse reactions.

5. Soft Drinks
The type and amount of water used to take medicine can affect its effectiveness by altering the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of the drug. In many cases, it can even lead to poisoning for the user. The amount of water needed to take medicine depends on the dosage form and the nature of the drug substance. Starting from the mouth, the drug is taken down the esophagus through the pharyngeal bifurcation, down to the stomach, small intestine, etc. In the small intestine, the drug is absorbed into the blood. The heart will distribute the drug through the blood to most organs in the body, including the target site of action. Next, the drug is metabolized in the liver into a less toxic or less toxic form, more soluble in water, and easily excreted by the kidneys through urine.
Many people mistakenly believe that drinking sweetened beverages will aid digestion, and drugs will be absorbed better. You should know that, sweetened beverages, especially carbonated drinks, are on the list of beverages not recommended to be taken with medication. Sweetened beverages contain preservatives, colorings, and gas, so when interacting with drugs, they can reduce the absorption into the body and may cause adverse effects. The water used to take medicine is not just a means to deliver the drug from the mouth to the digestive tract for absorption, but also acts as a solvent to dissolve the drug, helping it spread evenly over the surface of the digestive tract for better absorption. At the same time, drinking plenty of water will help the drug excrete faster through the kidneys, reducing the toxicity of many drugs.


6. Tea
Tea also contains caffeine, and when taken with medication, it can cause side effects such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure... Tannins in tea can cause precipitation, rendering some iron or alkaloid-containing drugs ineffective. Moreover, combining tea and medication can lead to insomnia, anxiety, and other issues. Tea is known as a benign herbal remedy, effective for human health and beauty: anti-aging, cancer prevention, and cardiovascular disease support… But when combined with medication, green tea is considered a “bane.” Tannic acid in tea can combine with certain drug components, creating precipitates and affecting absorption and efficacy of the medication.
Some studies suggest that using tea to take medication for tranquilizing effects will diminish the effects of tranquilizers, even rendering them ineffective. Besides avoiding tea for taking medication, some cases also restrict or absolutely prohibit tea consumption. Tea contains a high level of polyphenols and caffeine, which are unfavorable factors for the development of the fetus in the mother's womb. Therefore, pregnant women should refrain from or absolutely avoid consuming tea. The tannins in concentrated hot tea can combine with iron to form insoluble compounds, leading to inadequate iron absorption by the body.


7. Lemon Water
Lemon water is a beverage rich in vitamins, but not everyone drinking it is beneficial for the body. Many consider lemon water a 'miracle' for weight loss without realizing they may be harming their health. Consuming excessive lemon water can increase the acid levels in the stomach, leading to gastric ulcers. Citric acid and ascorbic acid in lemon water can erode your tooth enamel. Losing the protective layer, your teeth will turn yellow and have a rough surface. Lemon water is also restricted when used with medication.
Lemons contain a high amount of the amino acid tyramine. Drinking too much lemon water can cause an excess of this amino acid in the body. Tyramine amino acid can cause blood to suddenly rush to the brain, resulting in headaches. Additionally, lemon water, with its high vitamin C content and concentration of citric acid, can easily interact with medications. Lemon water may exacerbate gastric ulcer conditions and reduce the efficacy of medications for gastric and intestinal diseases. Therefore, remember not to use lemon water for medication!


8. Sports Drinks
Sports drinks are among the beverages that should not be taken with medication. Due to their complex mineral content, uncontrolled concentrations may precipitate with ions in the medication, rendering it ineffective. Additionally, sports drinks contain preservatives, colorings, or gases that can cause adverse reactions such as discomfort, flushing, palpitations when taken with medication.
For many people, taking medication with any water may seem unimportant, with some even choosing a water with a suitable flavor to eliminate the uncomfortable feeling of taking medicine. For example, some people take medicine with tea or fruit-flavored water (orange juice, lemon water...) or for women, even with alcoholic beverages, be it readily available or just for the pleasant sensation! This practice can seriously affect the effectiveness of medication, as using an unsuitable type of water can impact the absorption of the drug in the digestive system, leading to reduced or no therapeutic effects.


9. Ginseng Water
According to traditional medicine, ginseng is considered the leader among the four precious medicines in Eastern medicine: ginseng, velvet antler, cinnamon, and frankincense. It functions to tonify qi, nourish blood, generate body fluids, stabilize the mind, and benefit intelligence. It is used to treat symptoms of deficient vital energy, such as frequent fatigue, shortness of breath, weak limbs, cold extremities, weak pulse, thin and weak individuals, recent illness recovery, poor appetite, reduced memory, nervous tension, internal heat, thirst, frequent urination, irregular heartbeat, sexual dysfunction, and slow growth in children.
Everyone knows that ginseng water is a nutritious beverage that enhances health and boosts immunity. However, we should avoid overusing this type of water, especially when taken with medication. Many cases of using ginseng water with medication not only have no effect but also worsen the condition. Therefore, it is advisable to seek advice from a traditional medicine practitioner to use ginseng water properly.

10. Coconut Water
In reality, the type and quantity of water used to take medicine are crucial factors in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and resolution of medication for the body. Water used to take medicine not only acts as a conduit to deliver the medicine from the mouth to the digestive tract but also serves as a solvent to dissolve the medicine, helping it disperse evenly across the surface of the digestive tract for better absorption. Additionally, choosing the right type of water can facilitate the rapid excretion of medication through the kidneys, reducing unnecessary toxicity.
Coconut water is a type of water with many benefits for the body, helping cool down and providing essential nutrients as it contains numerous vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. However, many people excessively use coconut water, even using it to drink with medication without realizing the potential consequences. Some studies indicate that using coconut water to take medicine can be harmful, increasing the toxicity of the medication, as it inhibits the metabolism of drugs in the liver, elevating drug concentrations in the blood. Therefore, patients should absolutely avoid using coconut water as a solvent to deliver medication into the body.