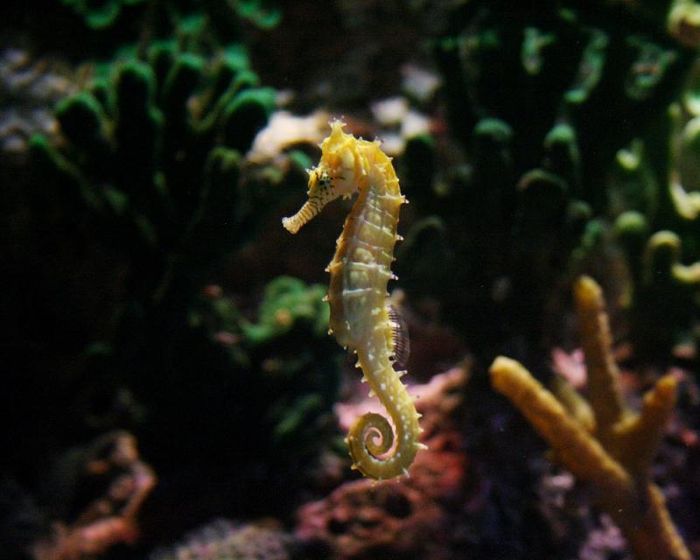
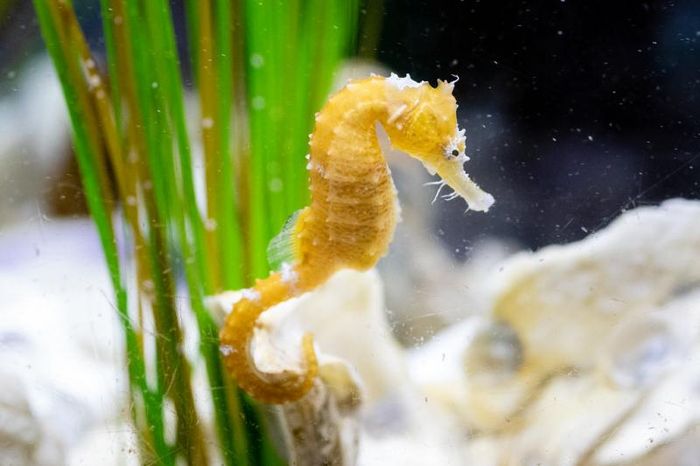
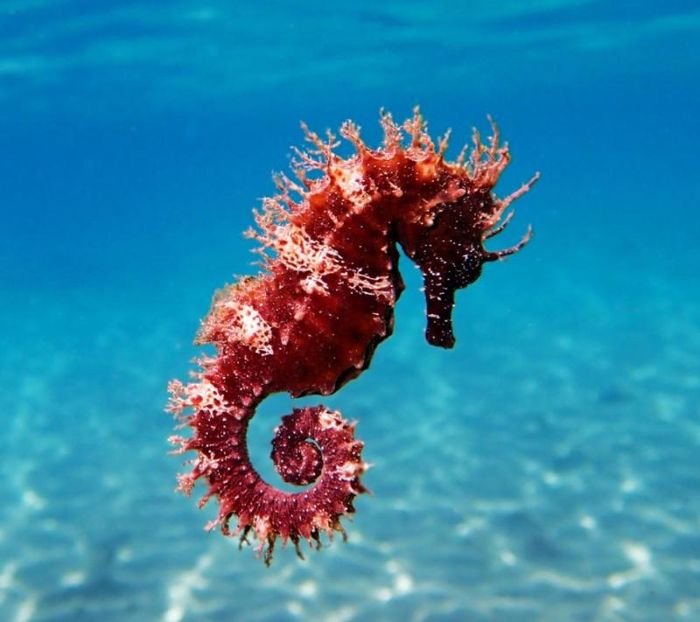

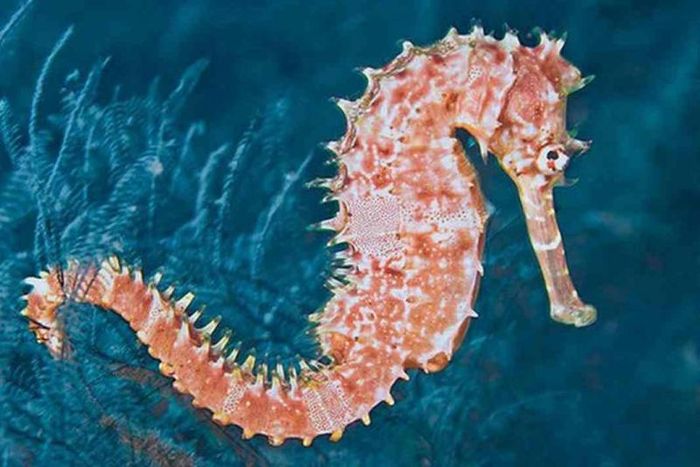
Identifying Characteristics of Seahorses
The head of a seahorse closely resembles that of a horse, with prominent spikes protruding from the top. This species typically ranges from 15-20cm in length, with a slightly flattened and bulging belly. The head features numerous bony protrusions and sharp spikes, with a series of bony rings running from the body to the tail. Their small, tube-like mouths lack teeth, and their deeply set eyes can move independently. Male seahorses have a pouch on the tail for carrying eggs, formed by two folds of skin.
Seahorses have been listed as near-threatened species in the IUCN Red List due to their increasing rarity and high demand.
- Scientific Name: Hippocampus
- Other Names: Seahorse, sea horse, sea dragon
- Family: Syngnathidae
Seahorses typically exhibit shades of brown, black, or light yellow, with a slightly musky scent. Their size, color, and morphology vary depending on the natural habitat conditions.
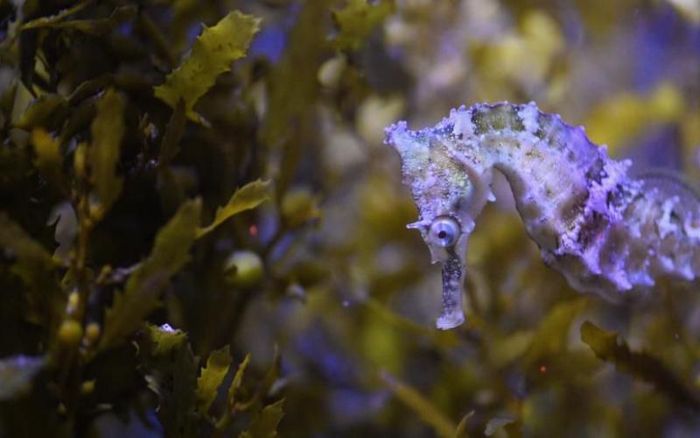

The Beneficial Uses of Seahorses
Seahorses offer numerous health benefits thanks to their chemical components. According to traditional medicine, seahorses have warming properties, are non-toxic, and have a sweet-salty taste. They can directly affect the liver and kidneys. Dried seahorses have the effect of nourishing the kidneys, regulating qi, activating blood circulation, and enhancing libido. Modern research also indicates that enzymes play a crucial role in synthesizing prostaglandins.
This substance helps stimulate the secretion of oxytocin hormone, prolonging sexual intercourse for men. Therefore, dried seahorses are often used for male infertility, erectile dysfunction, etc. Seahorses are typically processed by soaking in alcohol to maximize their efficacy.
Seahorses are also used to treat symptoms of bronchitis and wheezing in young children. Medications derived from seahorses are an effective, safe, and side-effect-free therapy. Moreover, they can be combined with Western or traditional Chinese medicine with appropriate dosages.
Additionally, seahorses help treat other conditions such as:
- Inflammatory swelling of lymph nodes
- Abdominal tumors
- Chronic kidney inflammation
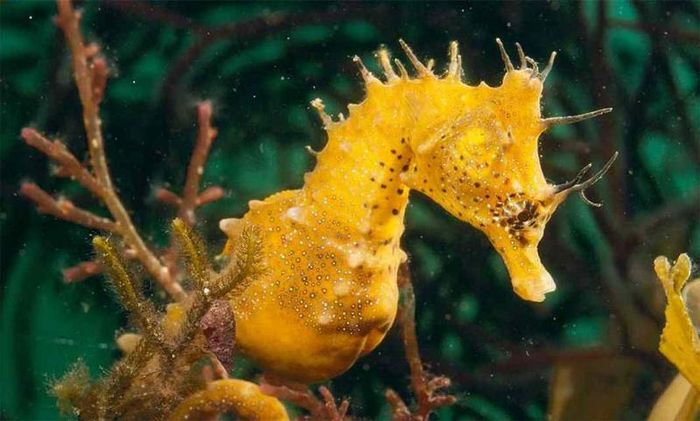

Chemical Components in Seahorses
The truth about the chemical components in seahorses. According to scientific research, seahorses contain numerous essential chemical components beneficial to human health, including:
- High levels of protein, supporting antioxidant properties and prolonging youthfulness.
- Enzymes that synthesize prostaglandins, aiding in immune system improvement and regulating nervous system activity.
- Stimulating the production of oxytocin hormone, influencing male sexual behavior.
- Peptides that combat bacteria and protect the body from external factors.
- Genes that help prevent the formation and growth of tumors.
Seahorses are typically harvested in the summer and fall. The entire seahorse body can be used after gutting.
Processing method: Clean the fish, remove the gut and outer membrane. Finally, sun-dry or air-dry the fish. Seahorses are often consumed in dried form, tied into pairs, consisting of one male and one female.
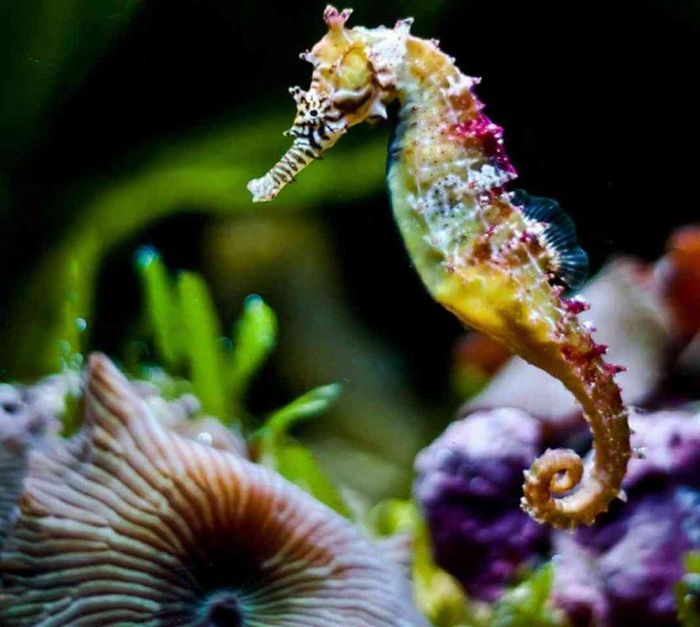

Seahorses as Pets
Many people keep seahorses as pets. Seahorses only eat fresh food such as shrimp, and they often lie upside down in the tank, which can weaken their immune system, making them susceptible to diseases.
Recently, more seahorses are being bred in captivity. In captivity, they live better and are less prone to diseases. These seahorses are fed shrimp pellets and are less likely to experience shock or stress when suddenly caught from the sea and released into the tank. Although captive-bred seahorses may be more expensive, they adapt and survive better than wild seahorses.
Seahorses should be kept in suitable tanks. They eat slowly, but when kept in tanks, they become aggressive, competing for food. Therefore, owners need to ensure an adequate amount of food for each seahorse.
Seahorses can coexist with certain types of shrimp or bottom-dwelling creatures, sometimes with gobies. However, some species pose a danger to seahorses, such as eels, octopuses, or tube worms.
Some freshwater seahorse species sold may resemble sticklebacks in rivers. These freshwater seahorses cannot be considered true seahorses. Recently discovered seahorse species live in brackish water.
Unusual Reproductive Behavior of Seahorses
Seahorses exhibit peculiar reproductive habits, with males carrying the embryos. Recent studies reveal that male seahorses release sperm into the surrounding water rather than directly into the brood pouch. The gestation period lasts 2-3 weeks.
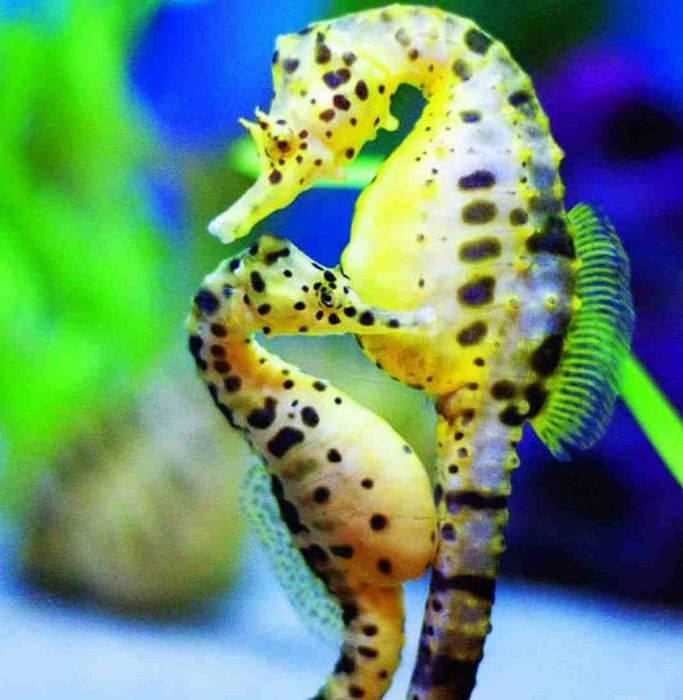

The Astonishing Ability of Seahorse Hearts to Self-Regenerate
Exploring the Phenomenon of Seahorse Cardiac Regeneration

Male seahorses defy traditional gender roles by taking on the role of pregnancy.
The unique reproductive process of seahorses involves the male carrying the developing embryos in a pouch until birth.

Researchers have found that seahorses may hold the key to unlocking the mysteries of leukemia in humans.
The genetic similarity between seahorses and humans, combined with their rapid reproductive abilities, makes them ideal subjects for studying leukemia and potential treatments.
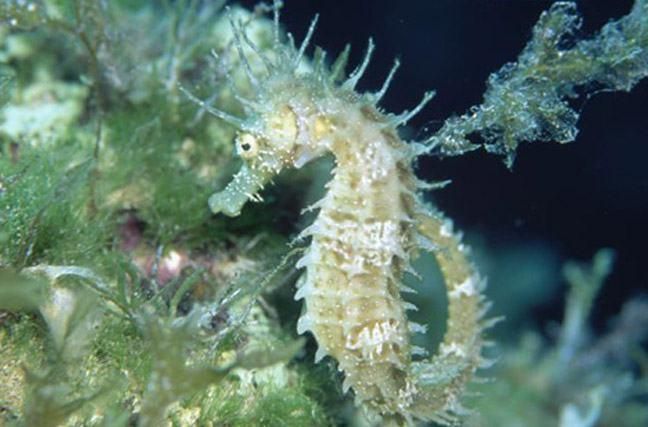

Seahorses are masters of prey capture, striking with incredible speed.
Despite their small size and slow movement, dwarf seahorses possess a unique hunting ability, striking their prey in just 1/1000th of a second.

The Chameleon Horsefish: A master of disguise in the pursuit of love. Researchers have uncovered the remarkable ability of the horsefish to change color in order to attract mates. While these fish typically show no visible differences in color between males and females to the human eye, a study from the University of Veterinary Medicine in Vienna, Austria, reveals subtle gender-specific changes during mating season.
A recent study has revealed that male and female horsefish undergo subtle color changes, particularly in their stripes, during mating season, making gender distinctions more discernible. Furthermore, male horsefish boast more vibrant and eye-catching colors, seemingly to woo potential mates, while their less attractive counterparts appear less flamboyant. This sheds light on the significant role of body coloration in the mating behavior of these ornamental fish.
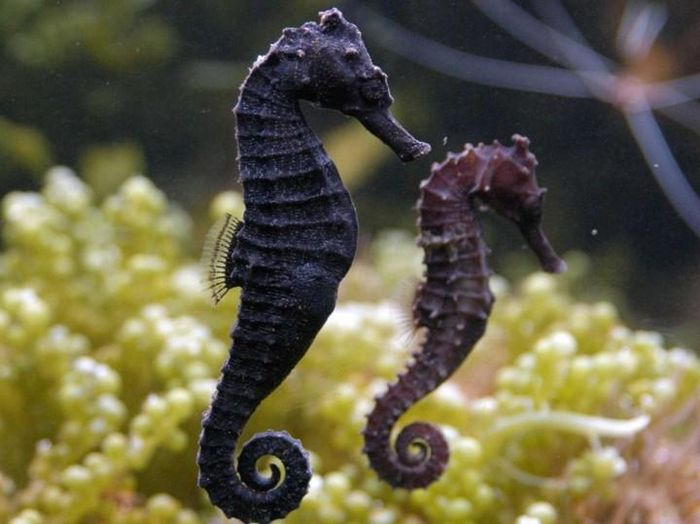

Male seahorses take on the responsibility of nurturing their offspring.
Recent research reveals the surprising role of male seahorses in nurturing their developing embryos.
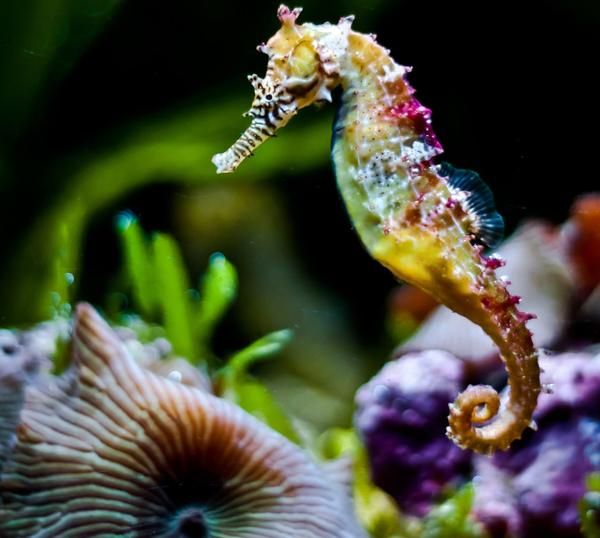

Habitat Characteristics
Seahorses inhabit various marine environments, predominantly tropical and warm temperate seas. They thrive in areas with high coverage, such as coral reefs or mangrove forests.

