What is AzaSite?
AzaSite is an ophthalmic product containing azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic that acts against bacteria. It is indicated for the treatment of certain bacterial eye infections caused by bacteria such as H.Influenzae, S.mitis, S.pneumoniae, Staphylococcus Aureus... Therefore, for some eye infections caused by other causes, the use of Azasite is ineffective or misuse of this antibiotic may cause unwanted effects.

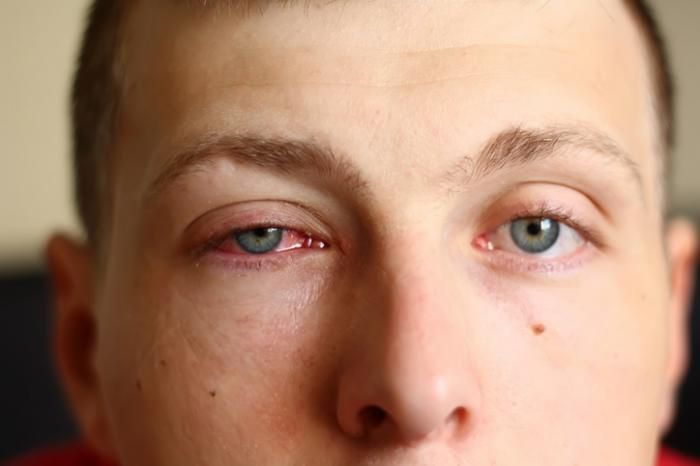
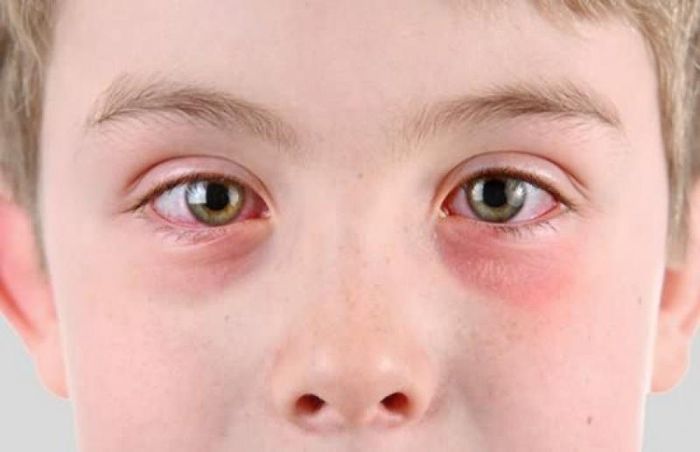
Side Effects of Azasite
Potential Side Effects of Azasite:
Dosage of Azasite
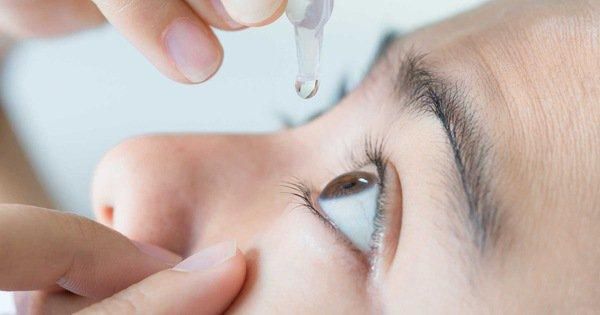
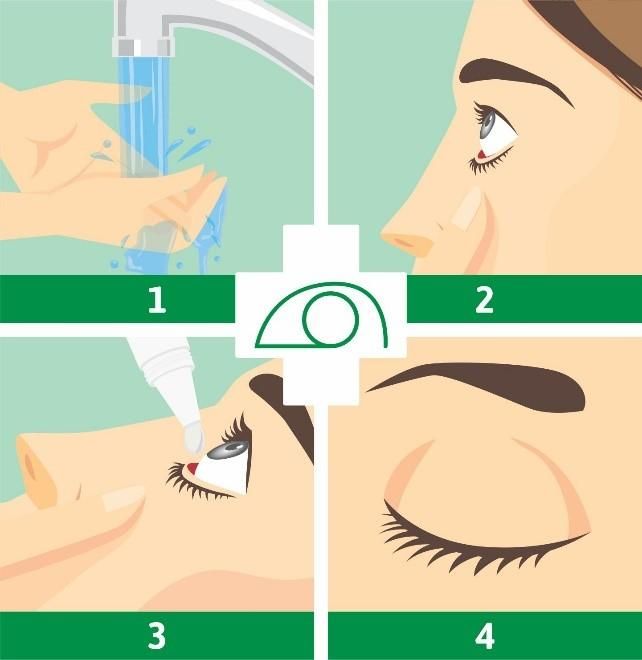
Dosage of Azasite for treating conjunctivitis in adults and children over 1 year old: Initial 2 days: Instill 1 drop per eye twice daily, 8 - 12 hours apart; Subsequent 5 days: Instill 1 drop per eye once daily as directed by the treating physician. Azasite belongs to the prescription drug group, so its use should be prescribed by the treating physician. Patients need to use the product at the correct dose and regimen to achieve high efficacy and minimize the risk of resistance. Some precautions when using Azasite are as follows: Patients need to wash their hands before use, gently shake the bottle before use; The position of using the product needs to be noted as follows: Tilt your head back, look straight up with both eyes, gently pull down the lower eyelid with your hand and instill AzaSite into the eye. After instilling, patients should gently close their eyes and maintain the position for 1 - 2 minutes and then look down.
Precautions for Using Azasite
Azasite is contraindicated in the following cases: Patients allergic to the antibiotic Azithromycin or any component of Azasite; Pregnant women, women planning to become pregnant; Children under 1 year old. Patients need to consider some issues before using Azasite as follows: History of allergies: Patients need to inform the treating physician of any allergic reactions to drugs, especially Azithromycin antibiotics or antibiotics in the Macrolide group, Ketolide group; History of underlying diseases, especially eye diseases. There is currently no study demonstrating the excretion of Azasite into breast milk, so Azasite should not be used in the treatment of nursing women.


