1. What is Berberine?
In Vietnam, amidst the perilous time of the resistance war against the United States, when dysentery was rampant, pharmacist Phan Quoc Kinh took on the responsibility of researching and formulating a medication to combat dysentery. The effective medication that played a role in quelling the epidemic at that time was Berberine, and it continues to be produced until today.
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid, yellow in color, found in numerous medicinal plants such as Yellow vine (Coscinium fenestratum), Amur Cork Tree (Phellodendron amurense), Chinese Goldthread (Coptis chinensis or Coptis quinquesecta), some plants in the Berberidaceae family, and some in the Mahonia nepalensis family...
Product information:
- Active ingredient: Berberine
- Subgroup: Gastrointestinal pharmaceuticals
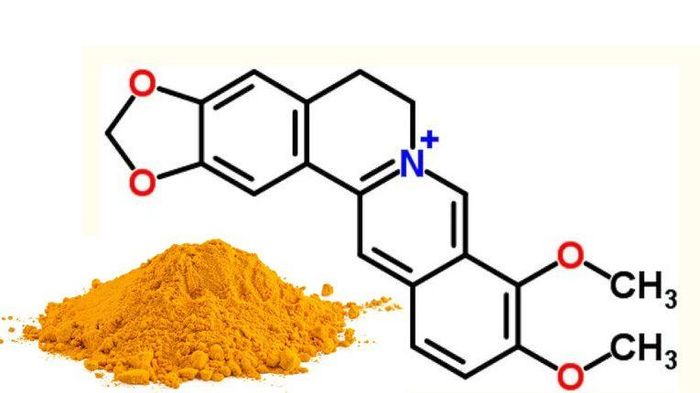
2. How to Use and Dose Berberine
The information provided is not a substitute for the advice of healthcare professionals. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist before deciding to use Berberine.
Common doses of Berberine include Berberine 10mg, Berberine 50mg, Berberine 100mg, and Berberine 500mg. Dosages (convertible to mg for other formulations, e.g., 10mg tablets):
- Adults and children over 15 years old: Take 12 - 15 tablets of 10mg each time x 2 times/day
- Children aged 2 - 4: Take 2 tablets of 10mg each time x 2 times/day
- Children aged 5 - 7: Take 5 tablets of 10mg each time x 2 times/day
- Children aged 8 - 15: Take 10 tablets of 10mg each time x 2 times/day
Usage: preferably taken in the morning and evening, 1 - 2 hours before meals.
3. What are the Effects of Berberine?
Berberine affects bacterial strains such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, avian trichomoniasis, fowl pox, dysentery, and tuberculosis.
Furthermore, other researched effects of this active ingredient include:
- For digestion: temporarily increases motility and intestinal contractions, improves symptoms of ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome.
- For respiratory: low doses stimulate respiration, while high doses impair respiration and may lead to suffocation due to respiratory center paralysis.
- For heart and circulation: reduces blood pressure, lowers cholesterol, and prevents arrhythmias.
- Treats liver and gallbladder disorders such as jaundice and indigestion.
- Has a positive impact on blood sugar, showing potential in preventing and treating diabetes.
- Anti-cancer properties.
Berberine is often prescribed to treat intestinal infections, diarrhea, and dysentery.


4. Precautions When Using Berberin
Do not use Berberine for patients allergic to any component of the product. Additionally, avoid usage for pregnant women. Patients with liver or kidney impairment should also exercise caution.
Berberine, originating from plants, rarely exhibits side effects. However, patients should be aware of the following issues:
- Exercise caution for individuals with weak digestion or poor gastrointestinal function.
- Avoid use in cases where patients show signs of sensitivity to any component of the product. Be cautious if there is a history of allergies.
- If any unusual health symptoms arise, inform your doctor. Berberine may lose effectiveness in individuals with low blood pressure or diabetes. Notify your doctor even during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Inform your doctor about any pharmaceuticals you are taking, including non-prescription drugs, herbal products, or dietary supplements.