1. What Are the Contraindications for Fericap?
Conditions where Fericap should not be used:
- Avoid using Fericap for individuals with a history of allergic reactions to any of its ingredients.
- Do not use in individuals with iron overload conditions, such as hemolytic anemia, hemosiderosis, or iron-storage diseases.
Additionally, Fericap should be avoided in the following cases due to potential side effects from some of its components:
- High doses of Vitamin B12 may stimulate the growth of rapidly growing tissues, which can promote the development of tumors in patients with malignant cancers. Individuals with allergic conditions, such as asthma, should also avoid this ingredient.
- High doses of Vitamin C in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a history of kidney stones, or those with increased urinary oxalate or oxalate metabolism disorders may increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Thalassemia patients are at increased risk of excessive iron absorption.

2. Side Effects of Fericap
Before prescribing Fericap, doctors carefully evaluate the benefits and effectiveness of the product against the potential risks of side effects. However, some unwanted reactions may still occur when using Fericap. Along with its therapeutic effects, Fericap may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and heartburn. Less common side effects include itching, hives, and rashes.
This list does not cover all possible side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms that you suspect are related to the product, it is important to inform your doctor for advice and possible adjustments to the dosage.

3. Fericap Interactions
Before being prescribed Fericap, patients should inform their doctor about all other medications they are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, prescription medications, and herbal products. This helps minimize the risk of interactions between Fericap and other drug groups. Never start, stop, or adjust the dosage of any medication without consulting your doctor. Some drugs may interact with Fericap, including:
- Vitamin C combined with Aspirin increases the excretion of Vitamin C while decreasing the excretion of Aspirin in the urine. After taking Vitamin C, the acidification of urine may alter the excretion of other drugs.
- Oral contraceptives can reduce the metabolism of Folate, leading to reduced levels of Folate and Vitamin B12.
- Pyridoxine can reduce the effectiveness of Levodopa used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
- Taking Fericap with antacid products like Sodium carbonate, Calcium carbonate, or tea may decrease iron absorption. Iron can also reduce the absorption of Levodopa, Quinolin, Penicillamine, Methyldopa, thyroid hormones, and zinc salts.

4. Important Considerations When Using Fericap
Here are some key considerations for using Fericap that will help you maximize its benefits while minimizing the risk of side effects:
- Keep the product out of reach of children.
- Fericap will not be effective if it has expired. If the product is deformed, discolored, or has been exposed to air for too long, it should be discarded.
- Prolonged high doses of Vitamin C can lead to a rebound deficiency when the dose is reduced. Large doses of Vitamin C during pregnancy may cause scurvy in newborns.
- Patients with folate-dependent tumors should use Fericap with caution.
- Iron should not be used to treat hemolytic anemia unless iron deficiency is also present. Do not use iron supplements for more than 6 months without medical supervision. Iron injections should not be combined with oral iron to avoid iron overload. Patients who frequently receive blood transfusions should avoid Fericap.
- Fericap does not affect the ability to drive or operate machinery.
- Normal daily doses of Vitamin C pose no risk, but excessive amounts during pregnancy can increase Vitamin C requirements and potentially cause scurvy in the infant.
- Folic acid supplementation is recommended for pregnant women, especially those undergoing malaria treatment or managing epilepsy.
- Vitamin B6 is safe for the fetus if taken at normal daily doses, but high doses may cause dependency syndrome in newborns.
- Vitamin C is present in breast milk, and no issues have been reported in infants when Vitamin C is consumed at normal daily levels.
- Folic acid is safe for breastfeeding mothers.

5. What is Fericap?
Fericap is a supplement containing a variety of vitamins and minerals designed to provide essential nutrients to the body in cases of congenital deficiencies, insufficient intake, or common health and physiological conditions. By supplementing the body with vital nutrients, Fericap promotes overall health and normal development, which is why it is often referred to as a dietary supplement.
Currently, Fericap is available on the market in soft gelatin capsules, conveniently packaged in boxes containing 10 strips of 10 capsules each. The ingredients in Fericap include Ferric fumarate (60mg), folic acid (1.5mg), vitamin B12 (5.2mcg), Vitamin C (30mg), Vitamin B6 (3.8mg), CuSO4 (4mg), and other excipients to complete the formulation of one capsule. All components in Fericap are natural, safe, and ensure consumer health.


6. What Are the Effects and Benefits of the Main Ingredients in Fericap?
Fericap is a well-balanced combination of essential nutrients, with each component serving a specific function. As a result, consumers benefit from multiple advantages when using Fericap, including:
- Ferric Fumarate: This ingredient provides elemental iron, which is crucial for synthesizing hemoglobin and participating in various oxygen-dependent processes in living tissues. Iron helps replenish deficiencies and promotes red blood cell production.
- Folic Acid: A B-vitamin that is converted into tetrahydrofolate, a coenzyme involved in numerous metabolic processes, including purine and pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis. This directly impacts DNA synthesis. With Vitamin C, folic acid is converted into leucovorin, playing an essential role in the synthesis of both DNA and RNA. Overall, folic acid is indispensable for nucleotide production and normal red blood cell formation.
- Vitamin B12: Vital for cell replication, Vitamin B12 helps form active compounds like methylcobalamin (which aids in methionine production) and 5-deoxyadenosylcobalamin. It also affects the function of folic acid in cells and is crucial for tissues with rapid cell turnover, such as the uterus, bone marrow, and small intestine. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can damage nerve myelin.
- Vitamin C: An organic compound essential for collagen formation, tissue repair, and numerous redox reactions in the body. It participates in various enzymatic processes involving drug metabolism, iron absorption, and immune defense. Vitamin C is also crucial for maintaining vascular integrity and cellular respiration.
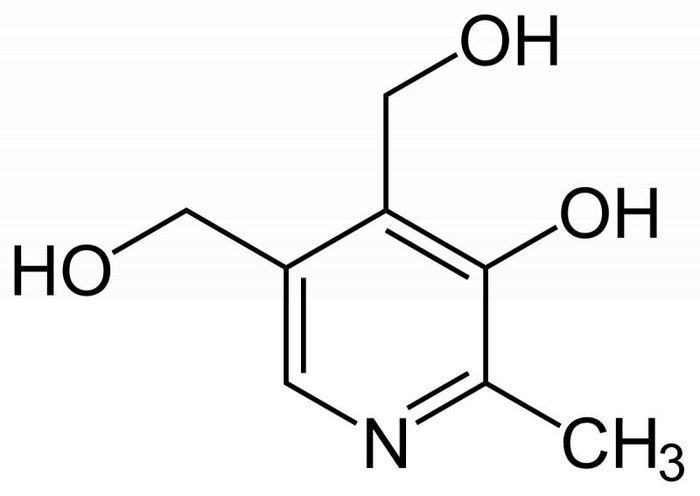
- Vitamin B6: Involved in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, Vitamin B6 transforms into active coenzymes such as pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxamine phosphate. It also contributes to neurotransmitter synthesis, including the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and plays a role in hemoglobin production.
- Copper Sulfate: Provides copper, which is essential for the synthesis and absorption of iron in the body.


7. Indications and Dosage of Fericap
Fericap is commonly prescribed for the following conditions:
- To supplement vitamins and minerals for pregnant and breastfeeding women, as this group has high nutritional needs, especially for folic acid.
- For individuals with iron deficiency anemia.
- For the prevention and treatment of folic acid and iron deficiency in women of childbearing age, post-surgical patients, malnourished individuals, and blood donors.
Fericap comes in tablet form and should be taken orally. It is recommended to be consumed with warm water or plain water, not with fruit juices or alcoholic beverages. The dosage varies depending on the individual. Below is the recommended dosage for different groups:
- For pregnant and breastfeeding women: Take 1 tablet once a day.
- For those with iron deficiency anemia: Take 1 to 2 tablets daily.
- For the treatment of folic acid and iron deficiency in malnourished individuals, women of childbearing age, blood donors, and post-surgical patients: Take 1 to 2 tablets per week.


