1. COVID-19 Pandemic
Covid – 19 is short for Coronavirus disease 2019 – an infectious pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus – a novel strain of the coronavirus, causing acute respiratory tract infections in humans and capable of human-to-human transmission.
The first cases were recorded in Vietnam on January 23, 2020, with two confirmed cases in Ho Chi Minh City, both of whom had traveled from Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. As of March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic in Vietnam can be divided into two main infection phases, with 22 days nationwide without any new confirmed cases recorded between the two phases.
From March 6 onwards, Vietnam began recording a series of new cases continuously every day, the majority of which were people arriving from epidemic areas around the world. Community transmission is also occurring. As of April 4, Vietnam has recorded 240 cases of infection, of which 90 patients have been discharged from the hospital, and no deaths have been recorded.
Social and economic aspects have been affected by the pandemic. Control measures have been implemented, including restrictions on movement. In 2020, Vietnam managed the pandemic quite well with a total of 35 confirmed deaths throughout the year. However, by 2021, the situation had become more severe with a surge in COVID-19 cases and deaths. The COVID-19 pandemic has spread to all 63 provinces and cities in Vietnam. The most severely affected area is Ho Chi Minh City with a total of 480,104 cases and 18,375 deaths (as of December 7, 2021). The least affected area is Bac Kan with 29 cases of COVID-19 and no deaths.
COVID – 19 Symptoms:
- Most common symptoms: fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste or smell
- Less common symptoms: sore throat, headache, muscle pain, diarrhea, rash, or fingers or toes turning red or purple, red or itchy eyes.
COVID – 19 Prevention Measures:
- Limit close contact with individuals with acute respiratory infections
- Individuals with symptoms such as fever, cough, or difficulty breathing should not travel or go to crowded places
- Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water for at least 30 seconds
- Only consume foods that have been cooked thoroughly.
- Keep the body warm, enhance health through proper nutrition, rest, reasonable activities, and exercise.
- If there are signs of fever, cough, or difficulty breathing, wear a protective mask, immediately notify the nearest health facility for consultation, examination, and timely treatment.


2. Leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a long-standing infectious illness that damages the external appearance and peripheral nerves, gradually leading to physical debilitation. It spreads through close contact with respiratory droplets of infected individuals during sneezing or coughing.
In Vietnam, many have succumbed to this disease, facing stigma, ostracism, and mistreatment.
Treatment for leprosy:
- Medications like Dapsone, Rifampin, Clofazimine, Ethionamide, Aspirin, Thalidomide, and Prednisone are used to prevent and alleviate inflammation.
- Seek medical advice and visit specialized centers such as dermatological hospitals if you experience symptoms of leprosy, especially after suspected exposure to the leprosy-causing bacterium.
Preventive measures against leprosy:
- Avoid direct contact with nasal or oral discharges of leprosy patients.
- Thoroughly wash hands with soap after caring for or coming into contact with leprosy patients.
- Enhance understanding of the causes, symptoms, and progression of the disease.
3. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
SARS, also known as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, is a respiratory illness caused by a virus named the SARS virus. Between November 2002 and July 2003, the SARS outbreak occurred in Hong Kong, spreading globally and almost becoming a pandemic, with 8422 cases and 916 deaths worldwide (10.9% mortality rate) according to the World Health Organization.
In Vietnam, the SARS outbreak infected 44 nurses and doctors at the Vietnam-France Hospital, resulting in 6 deaths (both local and international). Additionally, 2 related individuals, patient Johnny Cheng and doctor Carlo Ubani, also died. The Vietnam-France Hospital had to undergo disinfection and closure for nearly half a year.
- Transmission Source: Infected individuals and those in direct contact with patients (healthcare workers, immediate family caregivers, etc.)
SARS is a virus capable of transmission through three routes:
- Contact with respiratory secretions containing the virus that are expelled and adhere to environmental surfaces
- Droplet transmission when infected individuals cough or sneeze, expelling respiratory secretions containing the virus within a distance of less than 1 meter
- Airborne transmission when these patients undergo respiratory procedures such as nebulization, suctioning of phlegm, mechanical ventilation, etc.
American researchers have successfully immunized monkeys against the SARS virus using a vaccine administered directly into the monkey's nose. With this method, they hope to produce a vaccine that can be easily used by healthcare workers during SARS outbreaks.
4. Swine Flu (H1N1)
The A H1N1 influenza, caused by the A H1N1 flu virus, was identified in 2009. Initially dubbed swine flu because scientists believed it originated from pigs (distinct from the previous A H1N1 strain), the outbreak of A H1N1 flu virus was vigorous in 2009, spreading rapidly.
In Vietnam, the first case was recorded on May 26, 2009, and the outbreak intensified in late 2009, with thousands infected and many fatalities.
Characteristics of the A H1N1 flu outbreak:
- The A H1N1 flu virus can easily spread from person to person, much like the transmission of common flu through airborne droplets containing small water particles when infected individuals cough, sneeze, laugh, or talk.
- Individuals can also contract the flu virus through contact by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus, touching tissues contaminated with the virus, and then touching their nose, mouth, or eyes.
- Sharing utensils, drinking cups, or toothbrushes with infected individuals can also transmit the A(H1N1) flu virus.
Preventing A H1N1 flu:
- Regularly wash hands with soap, minimize touching the face, and cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing; avoid spitting indiscriminately.
- Use nasal, throat, and eye disinfectants daily; avoid close contact with sick individuals or those suspected of having the flu.
- Eat a nutritious diet to prevent flu virus infection.
- Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces, daily contact items, and floors with soap or common detergents; keep living spaces, classrooms, and workspaces well-ventilated.
- In addition, individuals can receive vaccinations for flu prevention.

5. Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS)
HIV/AIDS, the disease of the century, remains one of the most challenging global health issues, directly threatening human health and lives. Despite numerous efforts, this disease has not been eradicated. Since its outbreak in the 1980s, the HIV/AIDS pandemic has claimed the lives of over 35 million people worldwide.
In the first 9 months of 2019, Vietnam detected nearly 7,800 new cases of HIV infection, with nearly 3,000 patients progressing to AIDS, and over 1,400 cases resulting in death. It is estimated that Vietnam currently has more than 211,000 people living with HIV.
- Routes of HIV/AIDS transmission: Bloodborne, sexual, mother-to-child transmission
With the aim of preventing and eliminating the HIV/AIDS epidemic, in recent years, Vietnam's healthcare sector has expanded and diversified HIV testing services, detecting nearly 10,000 new HIV cases through various testing methods such as testing at healthcare facilities, community-based testing, self-testing, and utilizing new specimens for early HIV detection. Antiretroviral therapy can also extend the lifespan of patients, estimated to be over 5 years on average.
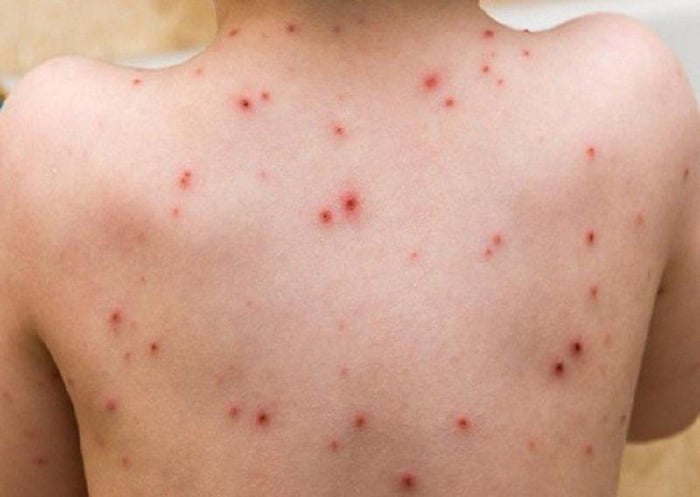
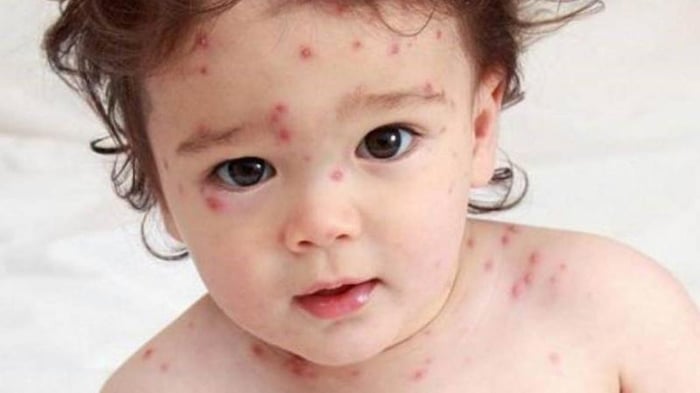
6. Smallpox
Smallpox is an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by two forms of the Variola virus: Variola major and Variola minor. The major type is more lethal, resulting in death in about 30-35% of cases, while the minor type causes a milder form of the disease, killing approximately 1% of patients. The aftermath of smallpox often includes scars on the skin, and in some cases, it can lead to blindness due to scarring of the cornea. Males can also suffer from infertility.
Vietnam's history records some individuals who died from smallpox. Among them was Prince Canh, the eldest son of King Nguyen The To (reign title Gia Long). Prince Canh died at the age of 22, leaving behind a wife and two children. King Tu Duc also contracted smallpox and became infertile, so he adopted a foster son to become king, reigning for only 3 days, known as King Duc Duc.
The Nguyen dynasty history also documents two major epidemic disasters before the French colonial period:
'In the year Canh Thin (1820) in November (lunar calendar), an epidemic spread from Ha Tien to Bac Thanh. Many people died. The state allocated a total of 73,000 coins to the people.'
'In the year Canh Ty (1840) in September (lunar calendar), in Son Tay, from spring to autumn, over 4,900 people died from the epidemic.'
7. Cholera
Cholera or Asiatic cholera is an intestinal infection caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, with the toxin produced by this bacterium causing severe diarrhea accompanied by heavy fluid loss that can lead to death. It is an extremely dangerous disease, with symptoms typically appearing 12 hours to 5 days after consuming contaminated food or water.
Cholera first appeared in Vietnam in 1850 with 2 million reported cases. From 1910 to 1938, the number of cholera cases ranged from 5,000 to 30,000 annually. El Tor cholera first appeared in the South in 1964 with 20,009 reported cases, including 821 deaths. Today, cholera occurs in Vietnam in the form of endemic outbreaks, with hundreds of patients diagnosed annually.
Common sources of infection include:
- Infected individuals during the period of illness;
- Healthy carriers of the cholera bacterium;
- Vegetables grown in water containing human waste;
- Raw or undercooked fish and seafood caught in polluted waters or wastewater.
Treatment measures for cholera:
- Implementing isolation methods for patients infected with cholera;
- Replacing lost fluids and electrolytes quickly and adequately through oral rehydration (using ORS) or intravenous infusion depending on the severity of the condition;
- Using antibiotics rationally based on antibiotic susceptibility test results;
- Early feeding, providing easily digestible liquid foods. For breastfeeding infants, breastfeeding should be increased.
Proactive cholera vaccination is an effective measure to prevent cholera.

8. Bubonic Plague
The bubonic plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. The disease progresses acutely with severe systemic infection symptoms. Humans become infected with the disease-causing bacterium from various rodent species such as rabbits, mice, etc., through an intermediate vector, the flea, which is infected with the bacterium. In Vietnam, the main disease vector is the rat flea Xenopsylla cheopis, primarily parasitic on rats.
In Vietnam, from 1960-1970, there were about 10,000 cases of the disease annually, ranking first in the world. The number of cases decreased sharply to only about 140 cases per year in the following years. Until now, almost no cases of the bubonic plague have been recorded in healthcare facilities. The disease spreads from rodent species (mainly rats) to humans, mainly through rat fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis). This is the primary vector transmitting the bubonic plague.
Factors increasing the risk of contracting the bubonic plague include:
- Polluted living environment, lack of sanitation
- Living in areas where the bubonic plague is prevalent
- Frequent contact with various rodent species
- Weakened body immunity