1. Virtual Super Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is a simulated experience that can be similar to or completely different from the real world. Applications of virtual reality can include entertainment purposes (such as gaming) and educational purposes. Different styles of virtual reality technology include augmented reality and mixed reality. Current standard virtual reality systems use virtual reality headsets or multi-projected environments to generate realistic images, sounds, and other sensations that simulate the user's physical presence in a virtual environment.
In the 22nd century, Virtual Reality (VR) devices like Oculus Rift will become relics as the technology to regenerate images directly in the human brain becomes more advanced. These VR experiences will be transmitted to users through all 6 senses, making them indistinguishable from reality. By using nanobots - super small robots with the ability to infiltrate and control molecular-level components, scientists will manipulate the brain, which is the central control of environmental perception. surroundings, from colors, flavors to shapes.


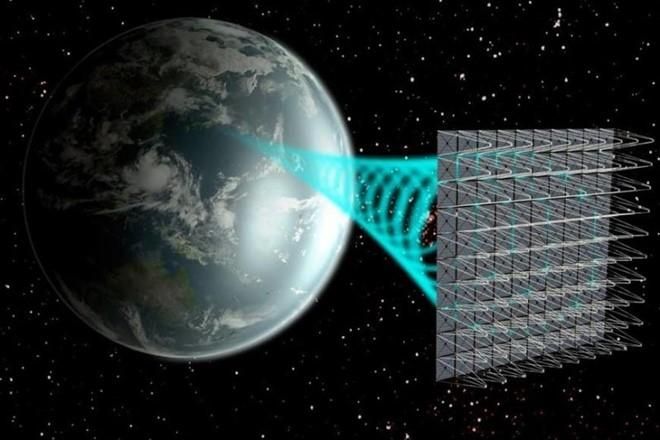
2. Outer Space Solar Power Station
As humanity grapples with the severe consequences of climate change, the utilization of clean and sustainable energy sources becomes crucial for nations worldwide. Since the 1960s, the concept of satellites capable of beaming solar energy to Earth from space has emerged. Pioneering this endeavor, the SSPS system consists of Japanese satellites orbiting 36,000 km above the equator, generating 1 gigawatt, enough to power half a million households.
The space-based solar energy system involves an enormous solar power satellite equipped with solar panels. These panels generate electricity, which is then transmitted wirelessly to Earth via high-frequency microwave beams. With global energy demand predicted to increase nearly 50% by 2050, space-based solar power may be one of the most efficient ways to meet the growing needs of the world's energy industry and address the challenges of rising global temperatures.

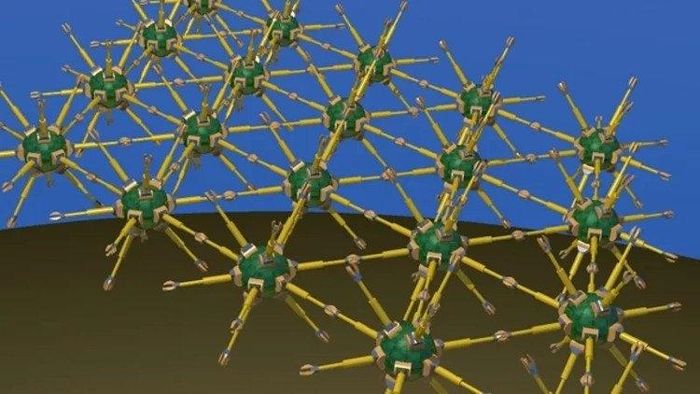
3. Utility Fog
Utility Fog is a term proposed by Dr. John Storrs Hall to describe a hypothetical collection of small robots working together to perform a specific function. A network of nano-scale technological devices linked together forms a complex grid in the air, capable of acting collectively in any direction or transmitting information among themselves. This would allow users to control almost entirely their environment.
With nanobots linked in the air, 'Utility Fog' takes the form of thin clouds capable of changing shape to envelop, even move tangible objects. J. Storrs Hall - the originator of the idea, hopes that his technology will soon be applied in reality. Nano-technology is based on the concept of tiny self-replicating robots. Utility Fog is a straightforward extension of the idea: imagine, instead of building the object you want atom by atom, tiny robots have linked their arms together to form a solid block shaped like the object you desire.

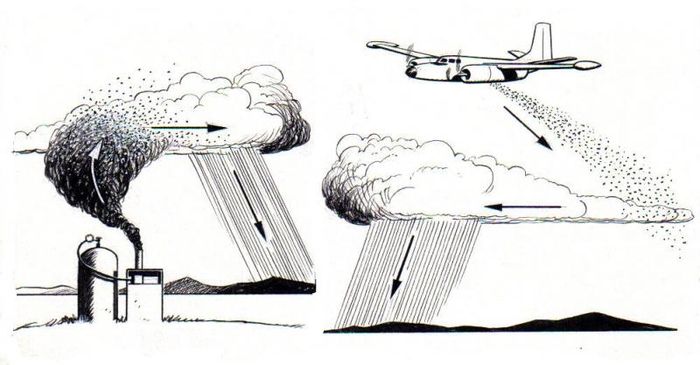
4. Weather Control
While not entirely under control, humans are gradually altering Mother Nature with attempts at weather control. To maintain the success of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, the Chinese government launched 1,100 rockets to induce heavy rain before a potential storm could arrive. Some scientists even shoot laser beams into clouds in hopes of triggering controlled rain.
In the future, weather engineers may construct large walls or windmill farms to prevent the formation of tornadoes and minimize damage. Further ahead, humans will manufacture weather machines capable of producing pre-programmed air with calculated sunlight, precipitation, and wind direction.

5. Digitizing Existence
In its simplest terms, “digitization” means converting analog information into digital form. The history of digitization can be traced back to the dawn of the computer age. As computational capabilities increased, the speed and efficiency of digitization also rose. This process was significantly propelled with the advent of the Internet era. Digitization is employed in every aspect of human endeavor. The technological advancements are happening at an exponential rate, with microprocessors becoming increasingly smaller and communication networks breaking new barriers in speed and bandwidth. The brain, in one way or another, can be encoded at the molecular level, either in part or entirely. Everything about a person, from memories, information, and even personality, can be stored on a computer. Scientists assert that this digital technology can feasibly be realized in the not-too-distant future. However, concerns persist about the ethical implications as well as the potential emergence of “virtual zombies” on the network.

6. Mind-to-Mind Communication
Throughout almost the entire history of humankind, only five natural senses were known as pathways to the brain, and language and gestures were the outward channels. Now, researchers are breaking those boundaries of the mind, moving information in and out, traversing space and time, manipulating it, and potentially enhancing it. The challenge lies in the power of computation and programming, and particularly in the connection between the brain and computers, especially the bidirectional connection from computers to the brain that helps transmit signals to the right group of nerve cells.
Continuous advancements in communication technology and neuroscience will help humanity develop the ability of telepathic communication. People will connect more easily through conscious communication. The individual ego of each person will gradually disappear and be replaced by collectivism. In 2014, a group of researchers successfully conducted an experiment in mind-to-mind communication between two people thousands of kilometers apart. It is highly likely that this technology will be applied in the near future.


7. Molecular Assembly
Molecular assembly involves creating nanostructures and desired material properties by organizing designed molecular building blocks that exhibit interactions within and between suitable molecules, along with controlling parallel assembly paths of solutions, to achieve the desired structural outcome. Because it enables the easy production of materials with appropriate properties and performance, the field of molecular self-assembly is a booming area of interest from various molecular perspectives.
3D printing will be nothing compared to molecular assembly technology. Molecular expert K. Eric Drexler, in the book Engines of Creation, shares: “The world will enter the ‘post-scarcity’ era if this technology is successfully developed.” New and existing materials will be formed in unimaginable ways. For example, to produce a piece of beef, instead of traditional farming, basic substances such as carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen would be used, then sorted into amino acids and proteins to create the final product.

8. Artificial Living Entities
Unrestricted by genetic technology, future scientists will craft and bring forth entirely new species from scratch. Researchers from Synthetic Genomics and the J. Craig Venter Institute have succeeded in creating 473 genes of artificial bacteria, albeit much smaller than natural bacteria. This breakthrough enables biologists to explore ancient capabilities, including bacteria that can consume plastic, detoxify hazardous waste, and microorganisms that can act as internal medicines.
Furthermore, a collaborative group of scientists and robots has unveiled their formula to create a novel form of life called xenobots from stem cells. The term “xeno” originates from cells of the frog (Xenopus laevis) used in their creation. One researcher described this innovation as 'not a traditional robot or a known animal,' but rather a 'new kind of artifact: a living, programmable organism.'

9. Energy Fusion
Energy production, primarily from burning fossil fuels, accounts for about 3/4 of global greenhouse gas emissions. Not only is energy production the largest contributor to climate change, but burning fossil and biomass fuels also exacts a heavy toll on human health: at least five million deaths due to air pollution annually. Therefore, the world needs to transition from fossil fuels to a dominant energy mix led by low-carbon energy sources—renewable technology and nuclear energy.
Earlier this year, physicists in Germany used a 2-megawatt microwave collision to heat low-density hydrogen to 80 million degrees Celsius. While it lasted only a fraction of a second, the experiment promised the initiation of a new energy production technology called nuclear fusion. This is a reaction that produces a single, heavier nucleus from two lighter nuclei than other types. Scientists believe that from here, it could harness clean energy as a replacement for fossil fuels and conventional nuclear reactors.


