A comprehensive guide to understanding US title regulations and combatting fraudulent practices
Essential Insights
- Discover the illegal methods used to convert rebuilt or salvage titles into clean titles within the US. Learn how scammers resort to forging clean titles or transporting vehicles across state borders.
- Ensure the authenticity of a vehicle's title status by conducting a VIN check or obtaining a comprehensive vehicle history report online.
- Prior to investing in a rebuilt vehicle, enlist the expertise of a qualified mechanic for a thorough inspection. Additionally, obtain insurance quotations from multiple providers to secure cost-effective coverage.
Procedures
Is it permissible to convert a salvaged title to a clean one?

Converting a salvaged or rebuilt title into a clean one is deemed a federal offense. Once a vehicle has endured significant damage and its title has been designated as salvaged or rebuilt, it is legally impossible to restore it to a clean status. Engaging in illegal alterations or fabrication of titles constitutes a crime known as title washing, encompassing various fraudulent activities such as:
- Producing or procuring an illicit title to conceal a vehicle's history
- Physically modifying or falsifying a title to portray it as clean
- Obtaining counterfeit documents to present a salvaged or rebuilt vehicle as clean
- Omitting signatures of previous owners on the title
- Manipulating odometer readings

Scammers produce counterfeit clean titles to inflate prices of rebuilt vehicles. In cases of forgery, fraudsters fabricate documents resembling clean titles, indicating that the vehicle has never undergone significant damage and/or that no other entity holds ownership rights to it. The objective is to deceive potential buyers into believing that the vehicle is clean and free of major accidents, enabling dishonest sellers to demand higher prices.
- Additionally, scammers may transfer vehicles between states with varying or lenient title regulations. Due to the absence of a federal standard for branding used car titles, a vehicle considered salvaged in one state might be deemed “clean” in another.
- Penalties for title washing vary across states and depend on the gravity of the fraud. In severe instances, convicted individuals can face sentences of up to 116 months in prison and fines exceeding $600,000.
Varieties of Titles

Clean title Clean titles indicate that a vehicle has never sustained extensive damage resulting in its classification as totaled by an insurance provider. The definition of “totaled” varies among insurers, typically indicating that repair costs amount to 70-90% of the vehicle’s value, rendering repairs uneconomical.
- A clean title does not guarantee the absence of minor damage or mechanical issues in the vehicle. It simply denotes that it has not been totaled.

Salvage title Salvage titles are assigned to vehicles that have undergone significant damage, rendering them totaled by insurers. These titles typically feature the term “salvage” prominently, distinguishing them from clean titles, although this can vary by state. Vehicles with salvage titles are deemed hazardous and unfit for operation on public roads.
- Various methods exist to dispose of a totaled vehicle, commonly involving the insurer assuming ownership and compensating the owner with the vehicle’s cash value (minus the deductible).
- Insurers often sell salvage vehicles to third parties interested in either restoring and reselling them (with a rebuilt title) or dismantling them for parts (with a junk title).
- Salvage vehicles cannot be legally operated, sold, or registered until they have undergone repairs and inspection.

Reconstructed title Reconstructed titles (also known as rebuilt titles) are issued to salvage vehicles that have been sufficiently repaired to meet safety and legal standards for operation on US roads. These titles inform potential buyers of the vehicle’s history and indicate that it has passed safety inspections (in some states). However, certain states have minimal or no requirements regarding disclosure of the vehicle’s past.
- There remains a possibility of overlooked issues during the vehicle’s reconstruction. Reconstructed titles serve as a warning to buyers regarding the potential for undiscovered problems in the future.
Nonrepairable or scrap title A scrap title signifies that a vehicle is suitable only for salvage or scrap metal purposes. Such vehicles are typically damaged to an extent where utilizing the frame or chassis for constructing a new vehicle is impractical, or the vehicle cannot be safely operated. Scrap vehicles are ineligible for operation, re-titling, or registration, although specific regulations may vary across states.

Unencumbered title An unencumbered title confirms full ownership of the vehicle by its possessor. When a vehicle is financed (subject to a lien), the lender holds the vehicle’s title and retains legal ownership until the buyer repays the loan in full. Upon complete repayment, the buyer assumes legal ownership and obtains an unencumbered title.
Verifying a Vehicle’s Title History
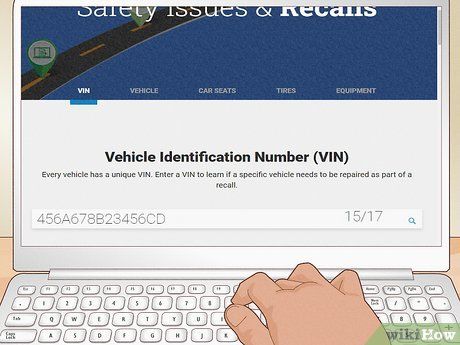
Perform a complimentary VIN check on the vehicle. Conducting a VIN (vehicle identification number) check provides comprehensive insights into a car’s fundamental history, encompassing details regarding accidents, repairs, insurance claims, and manufacturing particulars. Access a complimentary basic VIN check by inputting your vehicle’s 17-digit VIN into a VIN report platform such as the National Insurance Crime Bureau or VehicleHistory.com.
- While a VIN check may not furnish title specifics, it does furnish prior accident or damage records. This proves invaluable if the deal you’re contemplating appears too good to be true.
- VINs are typically situated on the dashboard or the driver’s side door jamb. Federal legislation mandates their legibility and conspicuousness—any absence or illegibility of a vehicle’s VIN warrants caution and discontinuation of the deal.
Invest in a comprehensive vehicle history report. State DMVs maintain archives of every registered vehicle’s accident history and title status. Refer to your state’s DMV website for instructions on procuring a complete history report. Typically, a nominal search fee is remitted online or via mail (usually around $10), alongside the provision of the vehicle’s license plate number. Subsequently, the DMV conducts a search of their records and dispatches the report upon payment of an ordering fee (typically around $15).
- History reports offer greater depth than VIN checks and invariably encompass accident and title particulars. They may additionally incorporate details regarding odometer tampering.
- You have the option to initiate a complimentary basic vehicle history report on platforms like CarFax or AutoCheck, though the findings might not encompass all desired information.
Guidelines for Acquiring Reconstructed Vehicles
Engage a certified mechanic for an inspection of a rebuilt vehicle prior to purchase. Despite a vehicle’s apparent excellence during a test drive, it’s prudent to have it assessed by a mechanic as a precautionary measure. While private sellers typically consent, certain auto dealers might resist, citing prior inspections—nonetheless, proceed with the inspection. A mechanic’s evaluation typically incurs a fee ranging from $100 to $300, potentially saving considerable sums by identifying undisclosed damages by the seller.

Evaluate your insurance provider’s stance on insuring a rebuilt vehicle. Obtain and compare quotes from multiple insurers before finalizing the purchase of a rebuilt vehicle to ascertain coverage affordability. Rebuilt vehicles may harbor residual issues, prompting certain insurers to decline coverage altogether or impose significantly higher premiums. In some instances, insurers may offer liability coverage exclusively, omitting comprehensive or collision coverage.
- Insurers extending coverage to rebuilt vehicles encompass American Family, Farmers, Infinity, Kemper, Nationwide, Root, State Farm, and USAA (available to active military personnel, veterans, and their families).

Alert law enforcement if you suspect you've purchased a vehicle with a laundered title. Regrettably, some buyers inadvertently drive off the dealership premises with a vehicle bearing a laundered title. Should a mechanic uncover concealed damages or if post-purchase VIN checks or vehicle history reports reveal accident records, promptly notify local law enforcement authorities and furnish all pertinent documentation pertaining to the vehicle purchase (such as the title, registration, or bill of sale).
- In the event of legal proceedings regarding title laundering and the seller is convicted, they may face substantial legal penalties, potential incarceration, and restitution payments to the affected buyer.
