Excel supports simple and user-friendly trigonometric calculations. Especially helpful in challenging problems, this tool provides great assistance. The following article introduces the trigonometric functions supported by Excel.
1. The Sin Function
- Syntax: Sin(number).
In this context: number represents the angle measure for which Sin needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Sin value of an angle, the value lies within the range from -1 to +1.
- Example:
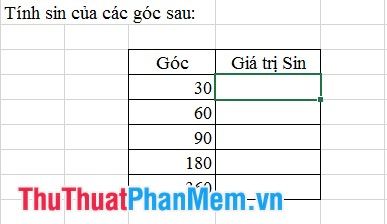
Be mindful when working with trigonometric functions in Excel, the unit of angle measurement is radians.
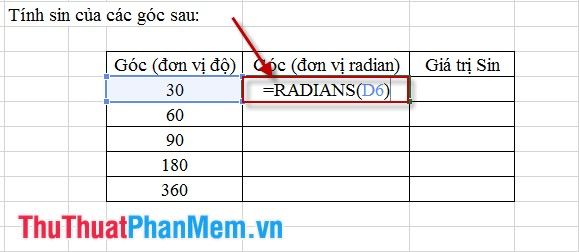
Step 1: Convert the angle measurement to radians. Insert an additional column and input the command as shown in the figure:
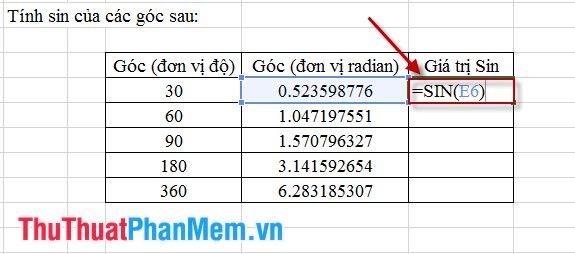
Step 2: Apply formatting to the remaining cells. Enter the formula to calculate the Sin value as depicted below:
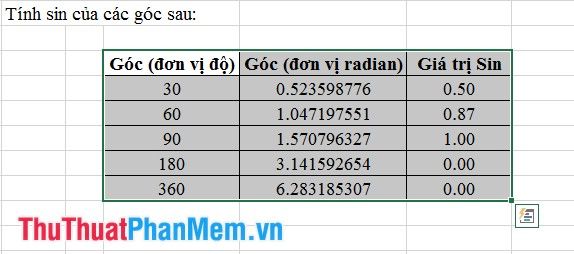
Finally, drag the formatting for the remaining cells to achieve results as shown in the figure below:
2. Cos Function
- Syntax: Cos (number).
Where: number represents the angle measure for which Cos needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Cos value of an angle, the value lies within the range from -1 to +1.
- Example:
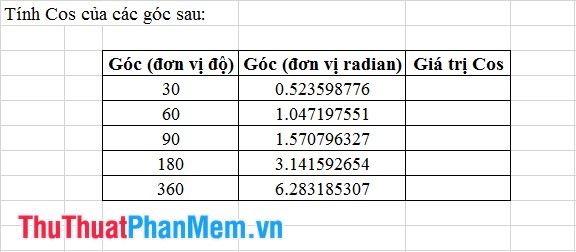
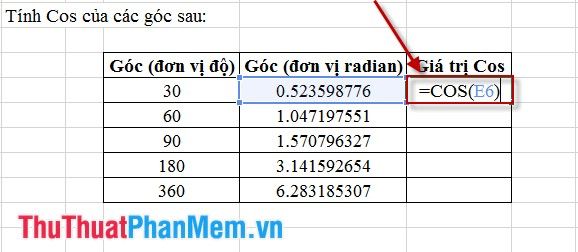
Step 1: Input the formula as shown in the figure.
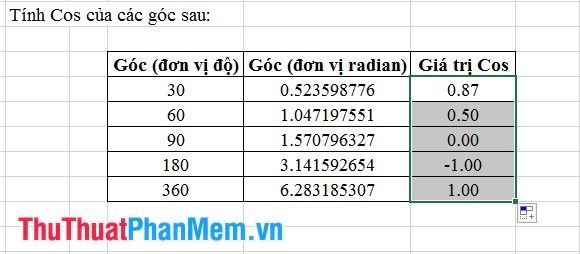
Step 2: Drag the formatting for the remaining cells to achieve results as depicted below.
3. Tangent Function
- Syntax: Tan (number).
In this context: number represents the angle measure for which Tan needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Tan value of an angle, the value lies within the range from -1 to +1.
- Example:
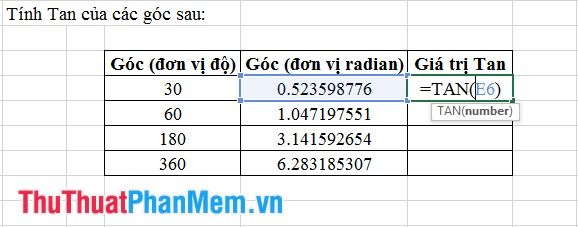
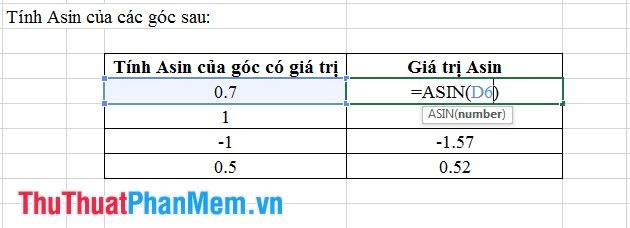
4. Asin Function
- Syntax: Asin (number).
Where: number represents the angle measure for which Asin needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Asin value of an angle, the value lies within the range from -1 to +1.
- Example:
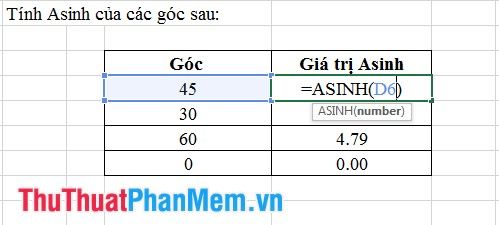
5. Asinh Function
- Syntax: Asinh (number).
Where: number represents the angle measure for which Asinh needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Asinh value of an angle, but this value is in radians.
- Example:
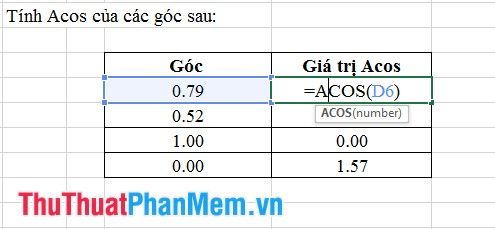
6. Acos Function
- Syntax: Acos (number).
Where: number represents the angle measure for which Acos needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Acos value of an angle, the value lies within the range from -1 to +1.
- Example:
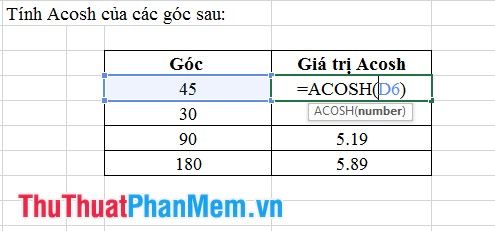
7. Acosh Function
- Syntax: Asinh (number).
In this context: number represents the value of the angle for which Acosh needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Acosh value of an angle, but this value is in radians.
- Example:
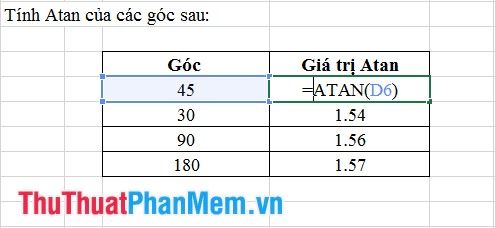
8. Atan Function
- Syntax: Atan (number).
Where: number is the value for which Atan needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the Atan value of an angle.
- Example:
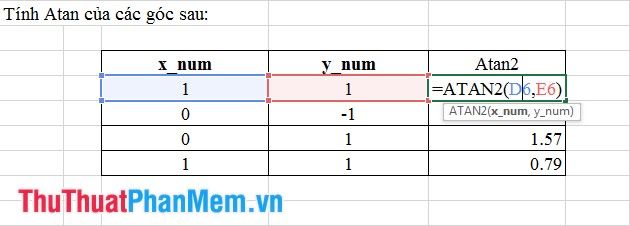
9. Atan2 Function
- Syntax: Atan2 (x_num, y_num).
Where: x_num, y_num are the values of the horizontal and vertical coordinates.
- Meaning: Returns the Radian value within the range from - Pi-> +Pi.
- Example:
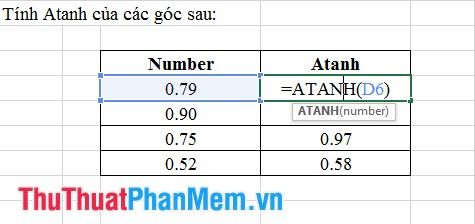
10. Atanh Function
- Syntax: Atanh (number).
Where: number is the value for which Atanh needs to be calculated.
- Meaning: Returns the value in Radians.
- Example:
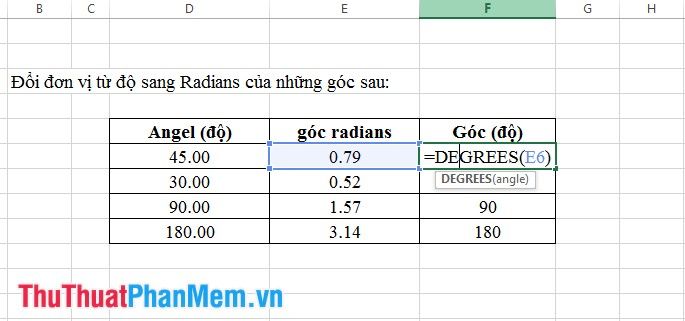
11. Degrees Function
- Syntax: Degrees (angle).
Where: angle is the degree value of an angle to be converted.
- Meaning: Converts the measurement of an angle from radians to degrees.
- Example:
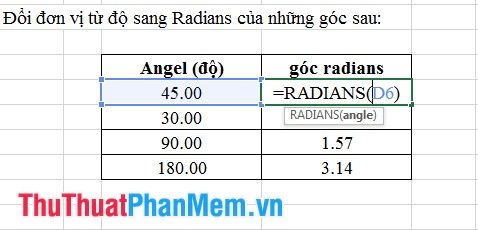
12. Radians Function
- Syntax: Radians (angle).
Where: angle is the degree value of an angle to be converted.
- Meaning: Converts the measurement of an angle from degrees to radians.
- Example:
Wishing you all the best of success!
