
Understanding the workings of a refrigerator is relatively simple, but its components are prone to malfunctions. What should you do when you notice your refrigerator not reaching the correct temperature?
1. Troubleshooting Refrigerator Issues and Solutions
The mechanism of a refrigerator is relatively simple, but its components are prone to malfunctions. What should you do when you notice your refrigerator not reaching the correct temperature?
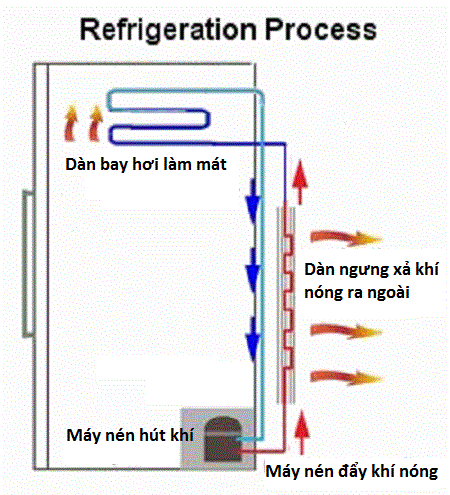
Understanding the workings of a refrigerator is relatively simple, but its components are prone to malfunctions. What should you do when you notice your refrigerator not reaching the correct temperature? In most cases, the cold air flow of a non-frost refrigerator is located in the freezer compartment – only a small part of the cold air circulates down to the other compartments to maintain the cold temperature. In fact, hot air will be brought into the refrigerator through the freezer compartment, then heat removed to generate cold air. In general, if the airflow in the refrigerator is obstructed in any way, the cooling process for the refrigerator will also be hindered.
The second thing you need to know is that the compressor (the black metal block behind the refrigerator) is the component responsible for cooling the entire refrigerator. Only when the compressor of the refrigerator works properly can your refrigerator operate as intended.
If your compressor is still running, you'll need to check all the items listed below. But if the compressor isn't running or keeps trying to start but fails (making noise and shutting off), you'll need to pay attention to this part first. As mentioned earlier, a faulty compressor may be the only reason why the refrigerator cannot cool down.

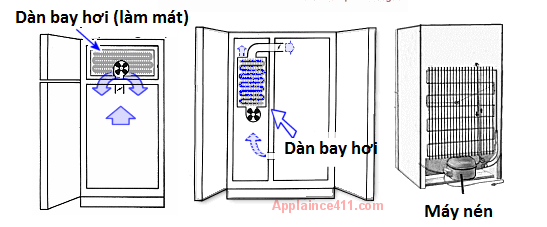
Compressor Running But Not Cooling
There are many reasons why a refrigerator may not cool. One of the most common reasons is the evaporator coil freezing up. In this case, one or more other components may keep the refrigerator running normally, but the temperature will often rise sharply in a short period of time.
You can tell if the compressor is still operating by the fans (evaporator fan and condenser fan) still running. When the refrigerator is still operating properly, all of these fans will run normally.
Distinguishing Between 'Frost' and 'Ice'
When inspecting the refrigerator, it's important to clearly distinguish between 'frost' (white, fluffy, snow-like) and 'ice' (clear, solid). Being able to clearly differentiate between frost and ice will help the troubleshooter pinpoint the exact cause more accurately.
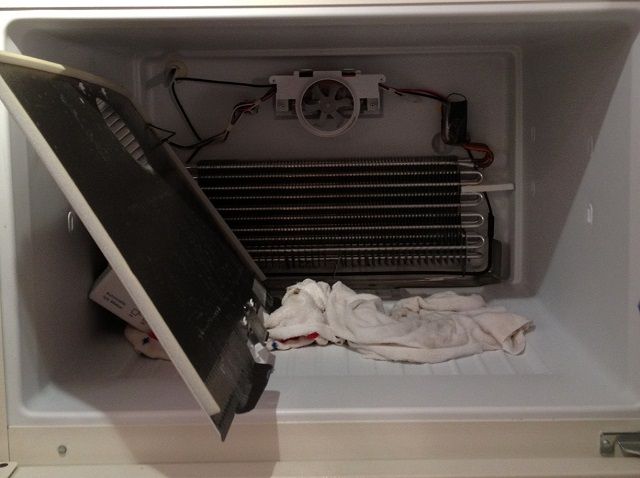
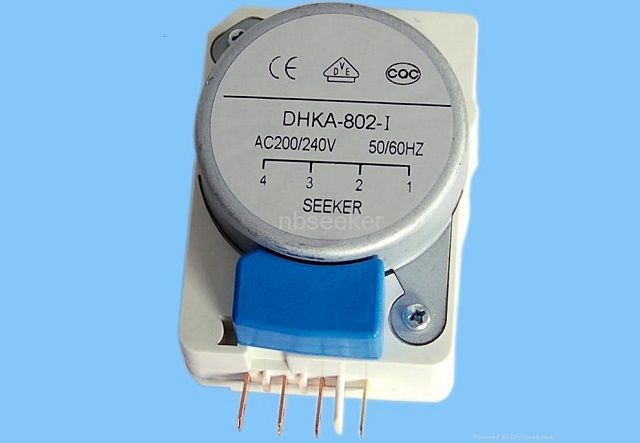



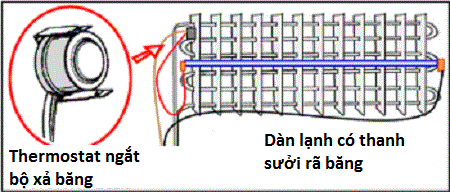
The contact area between the clock and the ice defrosting system, or even the defrosting system itself, may ignite, causing the defrosting electrical circuit to be exposed. In such cases, when the clock switches to defrost mode, the defrost heating system will also fail to operate. Upon returning to cooling mode, ice will accumulate more, and the evaporator coils will gradually be completely blocked.
The thermostat, responsible for halting defrosting, will activate the defrosting circuit when the temperature inside the refrigerator reaches a predetermined level, set in advance. At this point, the temperature inside the appliance is high enough to completely melt the frost on the evaporator coils. If the thermostat malfunctions and keeps the circuit continuously open, the defrosting system will never be activated.
Sometimes, the defrosting timer of the refrigerator may malfunction, causing both the evaporator coils and the defrosting system to activate. This will prevent the refrigerator and freezer compartments from cooling properly, especially noticeable in the lower compartments. The temperature of the freezer compartment may still remain at normal levels in this scenario. It is important to note that while this possibility exists, it is very low.
Evaporator Coils
The condenser of the refrigerator is referred to as the evaporator coils. This component releases hot air from the refrigerator into the room air. Most modern refrigerator models feature a fan near the compressor to blow air over the evaporator coils. This design is not intended to cool the compressor but rather to efficiently circulate air over the evaporator coils.
