Unexpected reboots, system freezes, application hang-ups, or even the dreaded blue screen – these could be indicative of RAM issues. Before considering a memory replacement for your computer, utilize Windows 10 Memory Diagnostic to investigate whether the problem genuinely resides there or not.
How the Diagnostic Process Works
Many Windows 10 troubleshooting tools continue to operate while you use your computer. However, this particular tool requires you to restart and then run during the boot process. By default, it runs in Standard Mode and conducts 2 test cycles. Afterward, your computer restarts once more and provides the test results.
Configuring Memory Diagnostic Tool
You need to schedule Windows 10 Memory Diagnostic to run in the next restart. Enter Memory in the Start search bar and run this application with administrator privileges (Run as administrator).

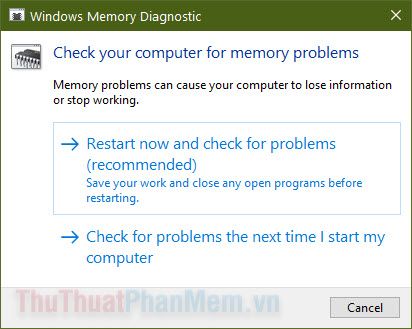
Next, you will be prompted:
- Restart now and check for problems: Restart and immediately check for errors.
- Check for problems the next time I start my computer: Run the error check after your computer restarts. If you have any unsaved work, choose this option and return to save your progress.
Run Memory Test
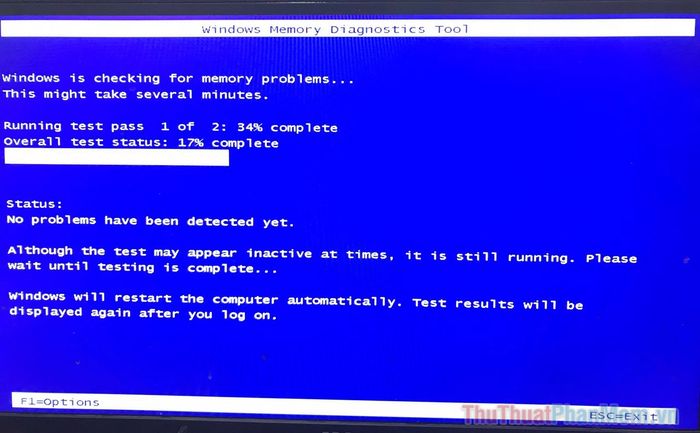
If you restart, Memory Diagnostic will initiate. Do not shut down your computer during this process. The computer will restart normally after the testing process is complete.
By default, this tool runs in Standard Mode, suitable for detecting most issues. The test takes about ten minutes.
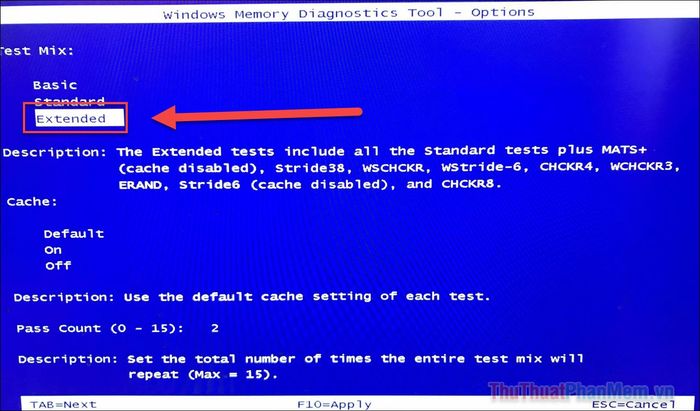
If you still encounter issues, run the tool again but press F1 on your keyboard as soon as the computer starts. Navigate to Extended and press F10 to run the advanced error-checking mode.
For a more efficient and streamlined check, opt for the Basic option if you're short on time.
Review your results.
Memory Diagnostic provides you with results once the restart process concludes. You'll find the outcomes displayed on your screen. If nothing appears, check the results in the Event Viewer.
- Type Event Viewer in the Start search bar and open this application with administrator privileges.
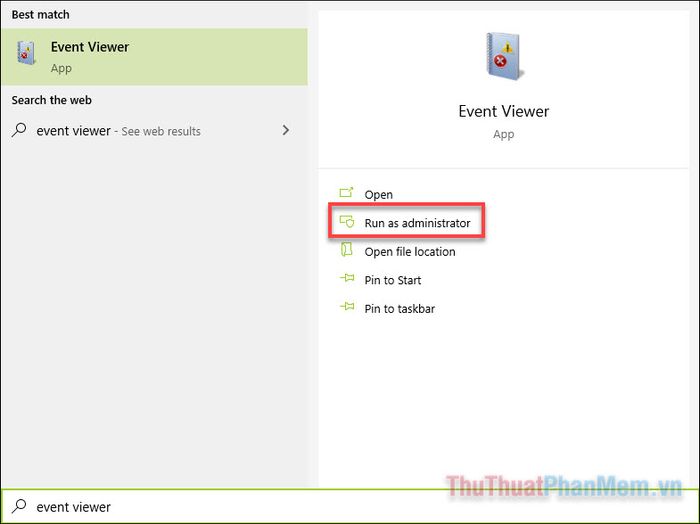
- Click on the arrow icon next to Windows Logs.
- Right-click on System and select Find...
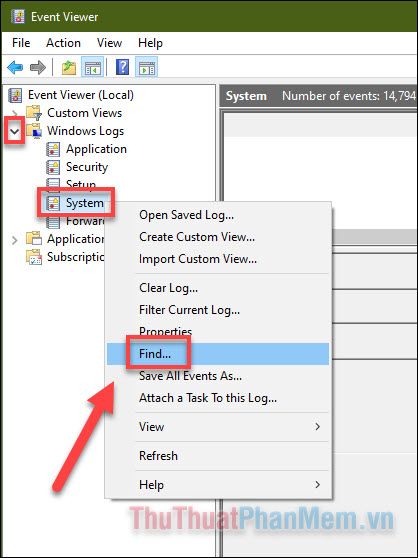
- Enter the following code in the search box: “MemoryDiagnostics-Results”, then press Find Next.
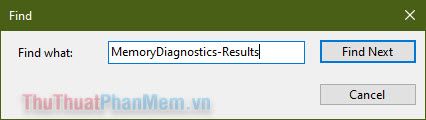
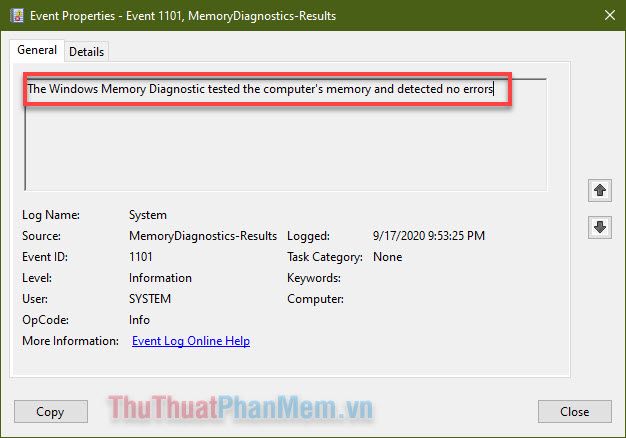
- The memory test results will appear with the Source as “Memor...”, click on this information to check for any errors.
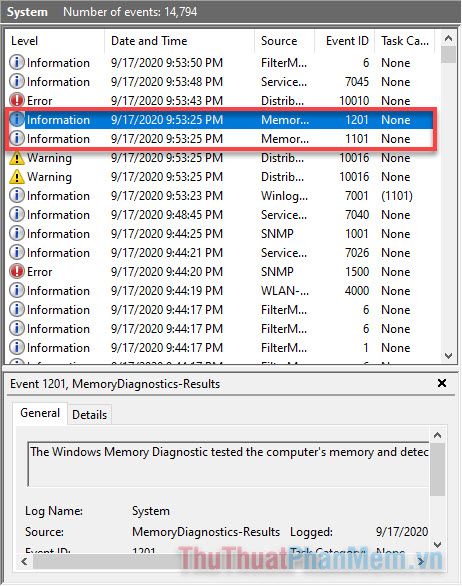
- Examine the result description; in my case, Windows did not detect any errors from the RAM.
Next Step
If your results show no errors, it may not be a memory issue. However, if errors are present, you can investigate the error description and details to determine if replacing the memory resolves the issue. Depending on your computer type, you can either replace the RAM yourself or take the computer for warranty service.
