Expert Advice for Managing and Preventing Pubic Pimples
Key Points to Remember
Useful Tips for Dealing with Pubic Pimples
Steps to Follow
Managing Pimples in the Male Pubic Area
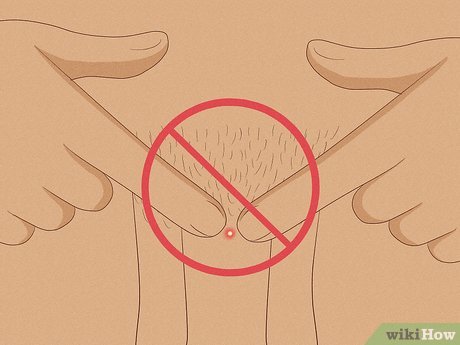
Allow the pimple to heal naturally without popping or touching it. Most pimples will resolve on their own without intervention. Maintain cleanliness and dryness in the area to aid healing. Avoid popping or scratching the pimple to prevent infection, scarring, or further outbreaks.
Shower daily, especially after physical activity. Regular showers help remove sweat and oil, reducing the likelihood of developing pimples. Use a loofah to gently exfoliate the pubic area during showers to unclog pores and prevent future breakouts.

Cleanse the area with mild antibacterial soap twice daily. Wash the pubic area and any emerging pimples with warm water and antibacterial soap twice daily. Ensure thorough rinsing to avoid irritation, and gently pat the area dry to maintain cleanliness.
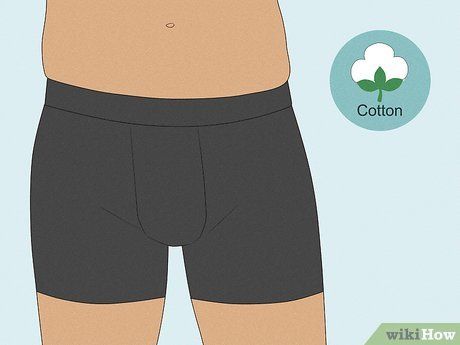
Opt for cotton underwear over synthetic fabrics. Cotton underwear promotes breathability, preventing moisture buildup and reducing the likelihood of pimples. Avoid synthetic materials like polyester, nylon, and spandex, which can trap moisture and exacerbate skin issues.

If approved by your doctor, consider oral acne medication. While many pimples respond well to topical treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, the delicate skin in the pubic region may react unfavorably. Consult your doctor about oral antibiotics to target the bacteria causing pimples. Alternatively, inquire about Isotretinoin, a prescription medication for severe acne.
Identifying Pubic Pimples
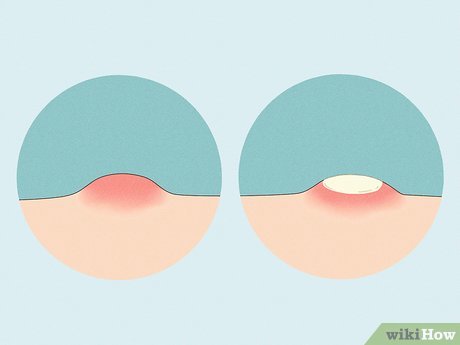
Pubic pimples typically appear as raised red spots, often with a white head. When touched, they may feel firm and tender. Some pimples develop blackheads or whiteheads due to clogged pores. Others may contain pus, which can be drained if necessary. Consult a doctor if concerned.
Causes of Pimples in the Male Pubic Area
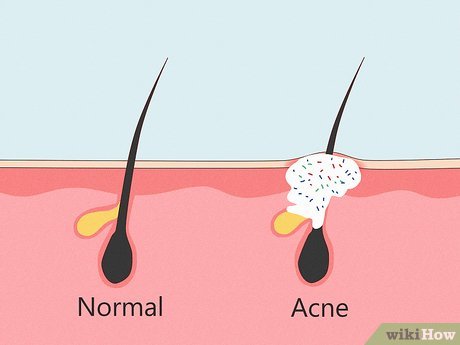
All pimples result from clogged pores. Pores, responsible for regulating skin surface gases and liquids, can become blocked by oil, dirt, or dead skin cells. Factors like infrequent showers, humid environments, oily skin, pubic hair shaving, or tight underwear may increase pimple risk. However, not all bumps are pimples; consider other causes if unsure.
Other Causes of Bumps Similar to Pimples in Your Pubic Area
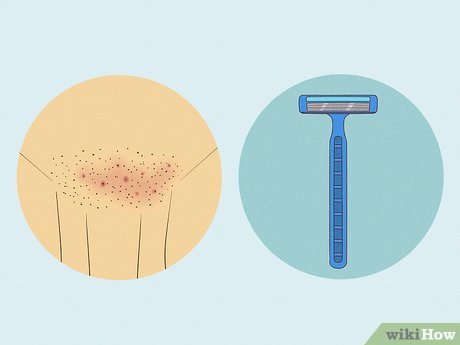
Razor Irritation Shaving with a razor can irritate sensitive skin, leading to razor burn. This condition causes redness, irritation, and sometimes bumps due to ingrown hairs. Razor burn typically resolves on its own, but using an oatmeal-based lotion can soothe the skin and using a fresh razor helps prevent razor bumps.
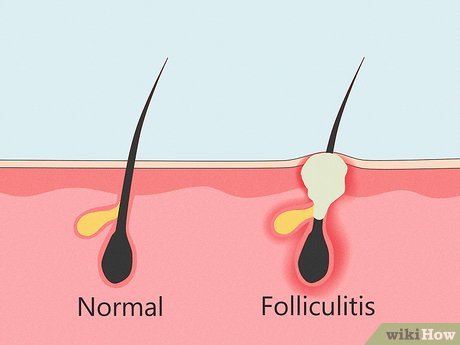
Folliculitis Inflammation of hair follicles, known as folliculitis, results in red, pimple-like bumps. Mild cases often resolve without treatment, but persistent folliculitis may require medical intervention. Treatment typically involves topical antimicrobial products to clear existing bumps and prevent future inflammation.

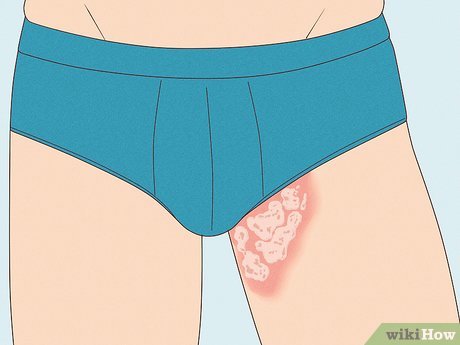
Jock Itch Jock itch is a common fungal infection characterized by itchy red patches, typically around the groin. Athletes, overweight individuals, and those with diabetes are at higher risk. Treatment involves topical antifungal creams and wearing loose, breathable clothing.
Eczema Eczema, an inflammatory skin condition, can affect the pubic area, causing dryness, itching, and rashes. Treatment usually involves moisturizers or topical steroids to relieve symptoms.
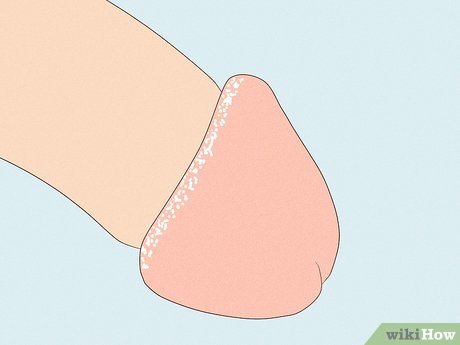
Fordyce Spots Fordyce spots, also known as Tyson glands, are visible sebaceous glands that appear as small white or yellow spots. They are harmless and often found around the frenulum beneath the penis. While typically benign, clusters of Fordyce spots can be removed with dermatological procedures like laser therapy.

Allergic Contact Dermatitis This condition occurs when your skin reacts to a chemical in clothing or skincare products, resulting in a rash or red, pimple-like bumps. Identifying and avoiding the allergen usually improves symptoms, but doctors may prescribe antihistamines or steroids for severe cases.
Psoriasis Psoriasis, a chronic condition, manifests as thickened, scaly, red patches on the skin. It can affect the pubic area and other parts of the body. While there is no cure, treatments like hydrocortisone cream or salicylic acid products can alleviate symptoms.
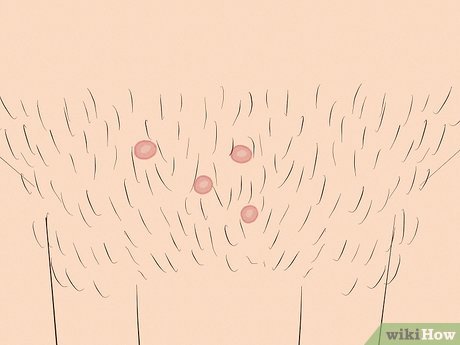
Molluscum Contagiosum This viral skin condition appears as small, dome-shaped bumps that are usually painless and resolve on their own. It can be contracted through sexual intercourse or sharing personal items. Severe cases may require prescription cream with imiquimod or tretinoin.
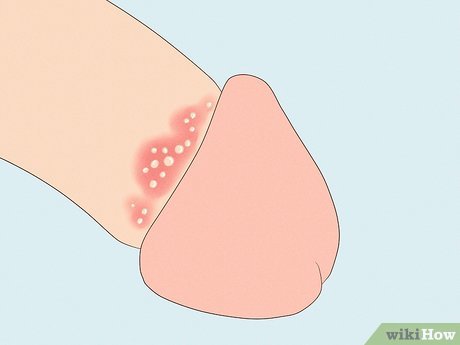
STIs Some pimple-like bumps in the pubic area may indicate sexually transmitted infections such as genital herpes, genital warts, or syphilis. These conditions require medical evaluation and treatment. Symptoms may include pain, discharge, or fever. Avoid sexual contact until properly evaluated and treated by a doctor.
When You Should Consult a Physician
If you notice additional symptoms accompanying the presence of pimples, it’s advisable to seek medical advice. Although pimples themselves pose no significant threat, prolonged persistence of a pimple beyond a week warrants a consultation with your doctor. If uncertainty arises regarding the nature of the skin condition, or the possibility of it being a different dermatological issue or STI, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended. Moreover, contact your doctor if you experience any supplementary symptoms such as:
- Skin irritations
- Muscle soreness
- Development of sores in other bodily regions
- Localized swelling
- General fatigue
- Recurring headaches
- Presence of fever
