Key Information to Keep in Mind
Actionable Steps
Understanding Brownouts

A brownout involves a partial reduction in power to an electrical grid. While they can occur accidentally, utility providers often plan brownouts ahead of time to prevent grid overload caused by sudden spikes in demand. For instance, during a heatwave, millions of people may simultaneously switch on their air conditioners. To prevent dangerous power surges, utility providers may temporarily reduce voltage across the grid.
- During a brownout, lights in your house may dim slightly.
- Electronic devices may turn off or operate improperly.
- After a brief period, power levels typically return to normal.
- Brownouts can affect part or all of an electrical grid.
Understanding Blackouts
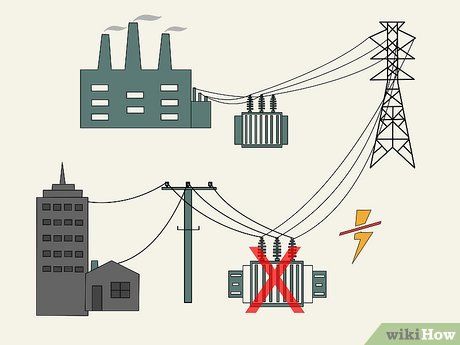
A blackout refers to an unplanned, complete loss of power to an electrical grid. They often occur due to equipment failures, such as substation malfunctions caused by power surges. Local blackouts, like those affecting neighborhoods, can also result from downed power lines or transformers due to falling trees, heavy snow, strong winds, or bird collisions.
- Blackouts can affect part or all of an electrical grid.
- During a blackout, all electricity-dependent devices in your home will shut off.
- Smartphones and other battery-powered devices may still function if charged.
- The duration of a blackout can vary from minutes to days, depending on its cause and extent.
- Power restoration depends on the utility company resolving the issue, which may involve anything from repairing a single power line to restarting entire power plants.
Preparing for Brownouts and Blackouts


