The following article introduces you to the ERROR.TYPE function - one of the commonly used functions in the information group in Excel.

Description: The function returns a number corresponding to one of the error values in Microsoft Excel, or #N/A error if there is no error.
Syntax: ERROR.TYPE(error_val)
Here:
- error_val: The error value with the identifying number to be searched, is a mandatory parameter. The corresponding numeric values for errors in Excel:
+ error_val = #NULL -> the function returns value 1.
+ error_val = #DIV/0! -> the function returns value 2.
+ error_val = #VALUE! -> the function returns value 3.
+ error_val = #REF! -> the function returns value 4.
+ error_val = #NAME? -> the function returns value 5.
+ error_val = #NUM! -> the function returns value 6.
+ error_val = #N/A -> the function returns value 7.
+ error_val = #GETTING_DATA -> the function returns value 8.
+ error_val represents any error value other than those above -> the function returns value #N/A.
Example:
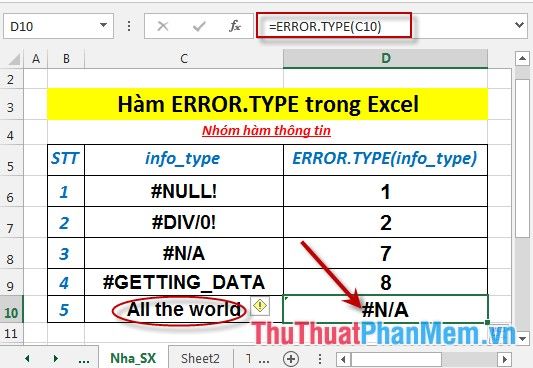
Identify the corresponding numbers for the errors described in the data table below:
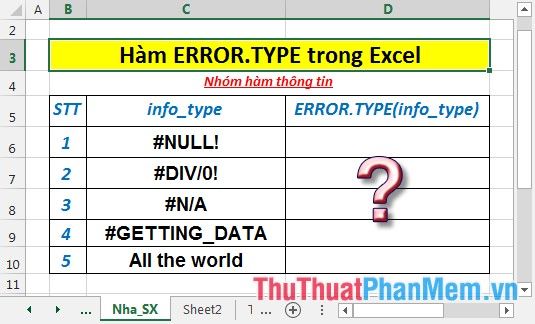
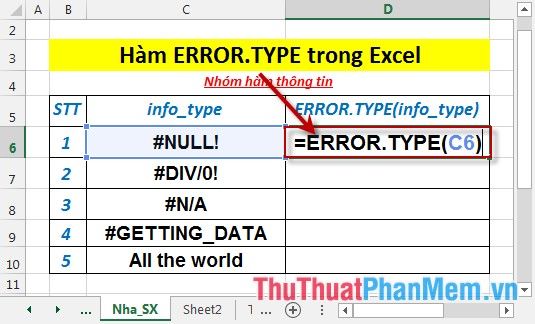
- In the cell where you want to calculate, enter the formula: =ERROR.TYPE(C6)
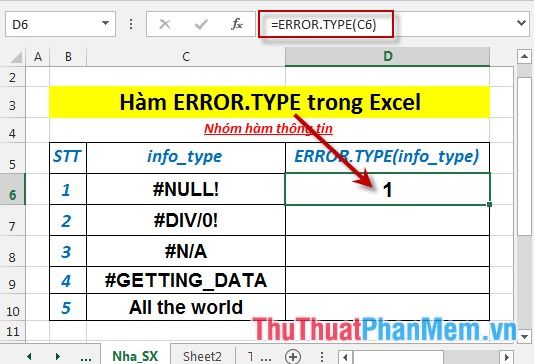
- Press Enter -> the returned value is:
- Similarly, copy the formula for the remaining values to get the result:
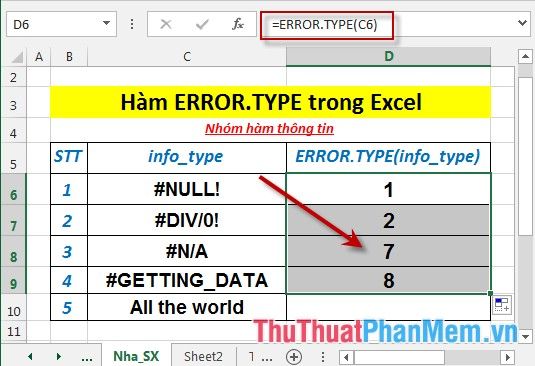
- If there are no errors outside the error values of the info_type -> the function returns value #N/A:
Above is the guide and some specific examples when using the ERROR.TYPE function in Excel.
Wishing you all success!
