Ketosis strips, also known as urine strips, are paper strips used to measure ketone levels in urine. These strips utilize a color code to indicate ketone concentration. Elevated ketone levels indicate high fat levels in urine, demonstrating the effectiveness of the keto diet. However, in diabetic individuals, high ketone levels may signify dangerously high blood sugar levels.
Procedures
Using Ketone Strips

Obtain ketone strips from a nearby pharmacy. Ketone strips are commonly used by individuals following a ketogenic (keto) diet or by those managing diabetes. They are readily available at pharmacies and larger drugstores. Look for them in the dietary supplies section or the diabetic equipment aisle. Ketone strips typically come in plastic containers or cardboard boxes labeled with “Ketone.”
- You can also find ketone strips in the pharmacy section of most major supermarkets, as well as through prominent online retailers.

Submerge the ketone strip in a urine sample. Collect urine in a disposable plastic cup. Then, immerse approximately 1⁄4 inch (0.64 cm) of the ketone strip into the urine. Ensure the end containing ketone-sensing chemicals is dipped. This end will be slightly thicker than the other.
- Disposable plastic cups can be found at any grocery store, typically in the dental or plastic ware section.
Directly urinate on the ketone strip if you prefer not to gather a sample. For convenience, many individuals opt to urinate directly onto the strip. Do this over a toilet. After urinating, hold the ketone strip over the toilet bowl to prevent dripping on the floor.
- If urinating while seated, take care not to dip the ketone strip into the toilet water, as it will dilute the urine and compromise the sample.
Evaluating Your Ketone Level
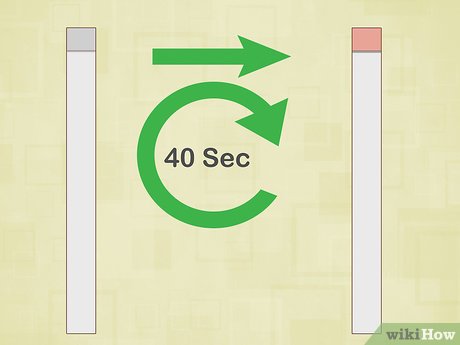
Allow the ketone strip to change color. Upon interaction with urine, the strip will change to yellow, maroon, or purple. Refer to the instructions on the packaging, which dictate the appropriate waiting time. Most ketone strips recommend a 40-second wait for optimal results.
- Failure to wait adequately or waiting too long can yield inaccurate readings.

Compare the ketone strip to the color indicators on the packaging. The ketone-strip container typically features colored squares. Hold your ketone strip against the container and locate the color square that closely matches your strip.
- If your strip's color falls between two squares on the packaging, consider the higher reading as more accurate.
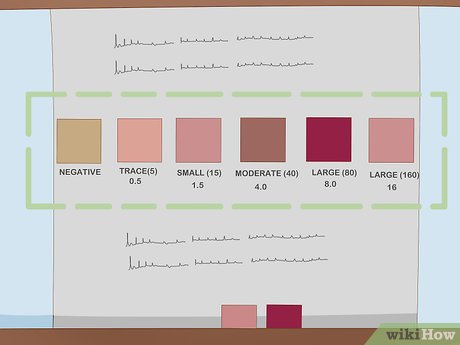
Review the numerical value corresponding to the matched color square. Once you've aligned the color of your urine strip with a square on the chart, carefully observe the associated number and description. Typical ketone-level descriptors include: “Trace,” “Small,” “Moderate,” and “Large.”
- The colors also correspond to numerical values such as 0.5, 1.5, 4.0, etc., indicating ketone concentration in milligrams per deciliter or millimoles per liter.
- In individuals not following a keto diet, ketone levels in urine are typically very low.
Understanding Ketone Strip Results
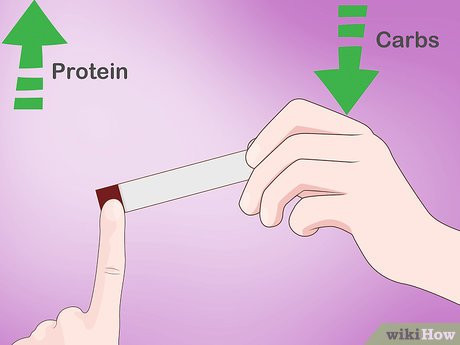
Adjust your protein and carbohydrate intake if your result is low. Initially on a keto diet, the body expels significant ketones through urine, resulting in a deep maroon-colored strip indicating a “Large” ketone presence. If your urine strip shows “Trace” or “Small” ketones while on a keto diet, consider modifying your dietary approach.
- This may involve reducing carb intake or increasing protein consumption.

Anticipate a lighter ketone-strip color as your keto diet progresses. At the start of a keto diet, urine strips may display a dark maroon or purple color. After several months, however, strip results may lighten, possibly indicating only a “Moderate” ketone presence. This is a normal progression and does not indicate diet failure.
- Once the body adapts to burning stored fat for energy, ketone elimination through urine decreases.

Consult your doctor if you have high ketone levels with type-1 diabetes. Elevated ketones in type-1 diabetics may signal dangerously high blood sugar levels. Test for ketones if concerned about blood sugar levels. If urine testing reveals high ketone levels, seek immediate medical attention.
- Other symptoms of high blood sugar include weakness, nausea or vomiting, excessive thirst, and breathing difficulties.
Insights
-
Keep in mind that ketone strips may not provide 100% accuracy. Ketone levels in urine can vary depending on the time of day (e.g., morning vs. after meals).
-
Some prescription medications, such as those used for treating UTIs, might affect the reliability of ketone strip results. If you're worried about the accuracy of your ketone strip readings due to your regular medication, consult your doctor.
-
A ketogenic diet entails burning stored fat by consuming low carbs, low calories, and high protein.
Cautions
- For individuals with diabetes, presence of ketones in urine or blood can be concerning, indicating insufficient insulin and high blood acidity.
- Individuals with type-1 diabetes should monitor blood ketone levels for medical reasons. While urine strips are not recommended for this purpose, medical blood tests are more comprehensive and less likely to produce false results.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition that can develop in individuals with diabetes, characterized by high ketone levels in urine, increased thirst, frequent urination, high blood sugar, nausea, fruity breath, difficulty concentrating, and fatigue. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of DKA.
