An echocardiogram offers a window into your heart's inner workings, utilizing ultrasound technology to capture real-time images. Harmless sound waves traverse your body, bouncing back to create a visual representation. This non-invasive procedure aids in diagnosing various cardiac conditions, guiding treatment plans, and assessing their efficacy. Understanding these images empowers patients in their journey to wellness.
Deciphering the Process
Decoding the Findings

Consult Your Physician Regarding Heart Size. Enlargement or thickening of the heart walls may signal underlying issues. Measurement of the left ventricle's wall thickness is crucial; a thickness exceeding 1.5 cm warrants attention. Such thickening could indicate conditions like:
- Elevated Blood Pressure
- Weakened Heart Valves
- Valve Damage
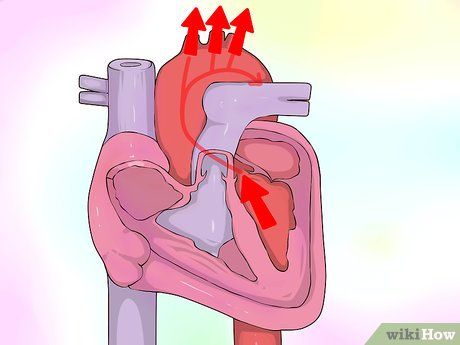
Evaluating Heart Pumping Strength. These metrics gauge the heart's ability to supply oxygenated blood to the body. Inadequacy may indicate heart failure. Two key measurements are discussed:
- Left ventricular ejection fraction: Percentage of blood expelled from the heart per heartbeat. Normal: 60%.
- Cardiac output: Volume of blood pumped per minute. Average at rest: 4.8 to 6.4 liters.

Assessing Heart Pumping Action. Weak contractions in certain areas may signal damage, possibly from prior cardiac events or coronary issues. Your doctor will observe for:
- Hyperkinesis: Excessive heart or wall contractions.
- Hypokinesis: Weak contractions.
- Akinesis: Lack of contraction.
- Dyskinesis: Abnormal bulging during contractions.
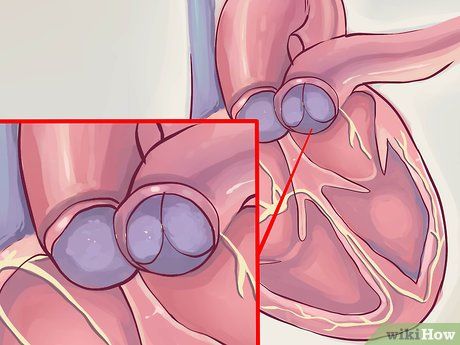
Inspecting Heart Valves. Valves, appearing as gray lines, regulate blood flow between chambers. Possible issues include:
- Leaky valves allowing reverse blood flow.
- Restricted flow due to partially open valves.

Detecting Heart Defects. Structural abnormalities such as:
- Abnormal chamber openings.
- Connections between heart and blood vessels.
- Developing fetal heart defects.
Deciphering Echocardiograms

Inquire About the Purpose of Your Echocardiogram. Echocardiograms aid in diagnosing various conditions. Your doctor may recommend one if they suspect:
- Heart murmurs
- Heart valve issues
- Atrial fibrillation
- Valve infections
- Pericardial effusion
- Blood clotting
- Cardiac hypertrophy
- Congenital heart anomalies
- Pulmonary hypertension
Clarify the Type of Echocardiogram. Various types are available, chosen based on required information:
- Transthoracic: Noninvasive, uses gel and a handheld transducer to produce images.
- Transesophageal: Involves a transducer-equipped tube inserted down the throat.
- Stress: Conducted during exercise or with medication to assess heart function under strain.
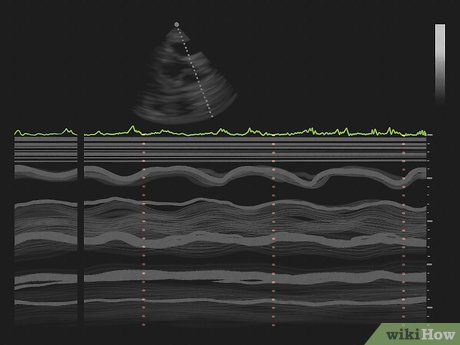
Observe the Doctor's Techniques on the Monitor. Different techniques enable varied measurements:
- M-Mode: Outlines heart size, chambers, and wall thickness.
- Doppler: Measures blood flow velocity and direction.
- Color Doppler: Highlights abnormal blood flow directions.
- 2D Echocardiography: Provides two-dimensional images of heart structures.
- 3D Echocardiography: Offers detailed three-dimensional images for treatment planning.
