Acquiring the skill to interpret email headers is essential for unveiling the route an electronic message traverses from sender to recipient. This proficiency finds application in diverse scenarios, from safeguarding individuals, especially children, against malicious emails to assisting email providers in identifying spam and aiding in detecting email-borne scams or viruses. The ensuing information delineates the significance of each typical tag in an email header and how it can benefit both senders and recipients.
Essential Knowledge
- Examine the 'Received from' tags in reverse chronological order to ascertain the sender of an email.
- Utilize the 'Deliver to' tag to identify the intended recipient.
- Investigate any server delays by scrutinizing the information provided by the 'Received' tag.
Procedures
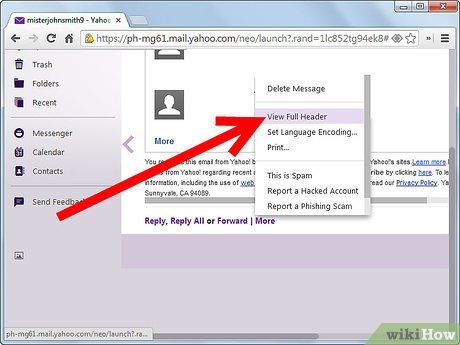
Unveil and explore the email headers. This data isn't usually disclosed automatically due to its potential space consumption. Many email platforms or websites (like Gmail, Hotmail, and Yahoo! Mail) offer the option to scrutinize email headers by clicking on a designated box or link adjacent to the sender's address in the email viewing interface.
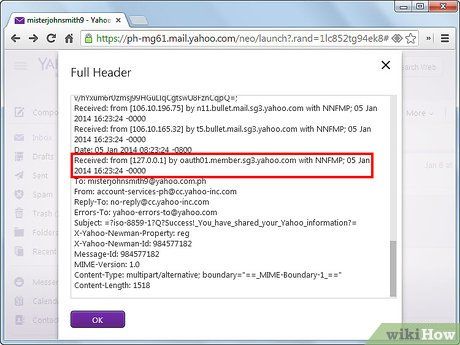
Identify the sender of the email by analyzing the 'Received from' tags, starting from the bottom. Since email headers are presented in reverse chronological order, the bottommost header furnishes details about the original sender. You can ascertain the sender's email address, the date and time of transmission, along with server and domain particulars, including the Internet Service Provider (ISP) address.
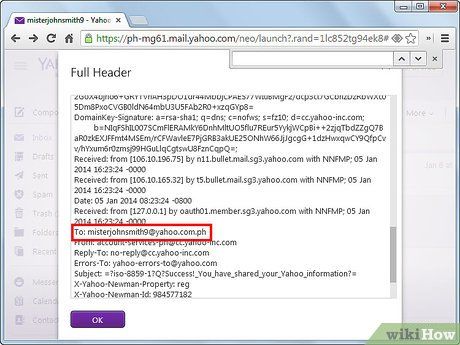
Verify that you are indeed the intended recipient. This can be valuable if you suspect receiving an email erroneously. By inspecting the 'Deliver to' tag, you can validate that your email address matches the intended recipient.
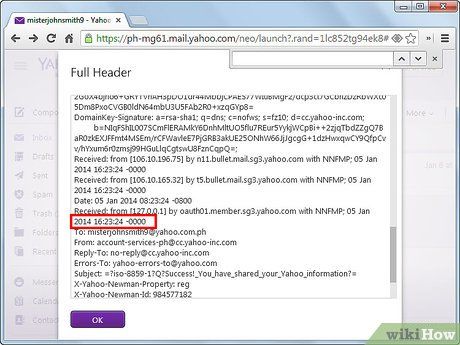
Determine if there was a delay in server processing. The 'Received' tag reveals the time your email server received the message. If this predates the message's appearance in your inbox significantly, there might be server-related issues. Reach out to your Internet Service Provider or network administrator if such occurrences are frequent.
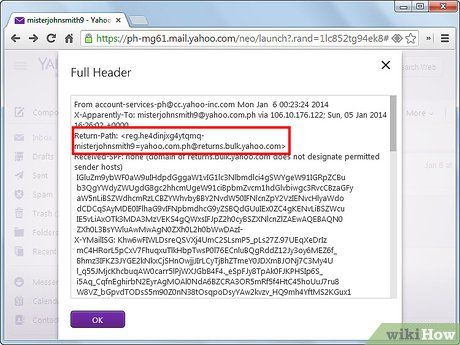
Locate the email address from which the message originated. The 'Return-Path' tag contains this information.
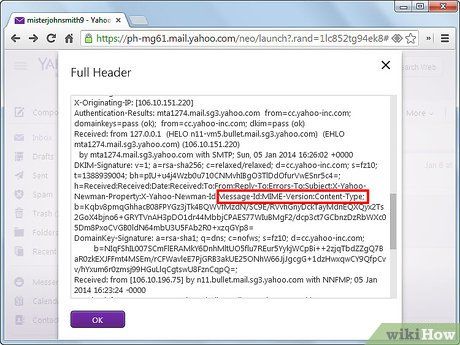
Discover details about the sender's email provider. The 'Received-from' and 'Message ID' tags provide information about the sender's email provider, including server details, date, time, and transmission method.
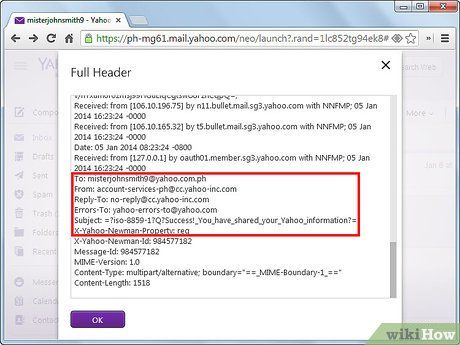
Review user-provided information. Details inputted by the sender can be found at the bottom of the email headers. These details encompass tags such as 'Subject,' 'From,' and 'To.' The system also logs the date and time, indicating when the message was submitted by the sender to the provider.
Tips
- If given the choice to unsubscribe, opt for that instead of marking a message as SPAM. SPAM filters can be trained and might incorrectly classify newsletters you want to read as SPAM if you don't do this.
- Always read email headers before labeling a message as SPAM. This helps prevent unnecessary blacklisting.
