This is an ancient ape species weighing nearly 50 kg, once thriving in Africa, particularly South Africa and Ethiopia.
In the scientific community, there's much debate about the human evolutionary link with apes and monkeys. While humans share some traits with these primates, there's no evidence suggesting humans are direct descendants.
Additionally, we know that present-day ape species differ from those living thousands of years ago. Enter Dinopithecus.

Dinopithecus, also known as the 'menacing ape,' was a large genus that went extinct during the Pliocene to Pleistocene Epochs. These apes were distributed in Africa, particularly in South Africa and Ethiopia.
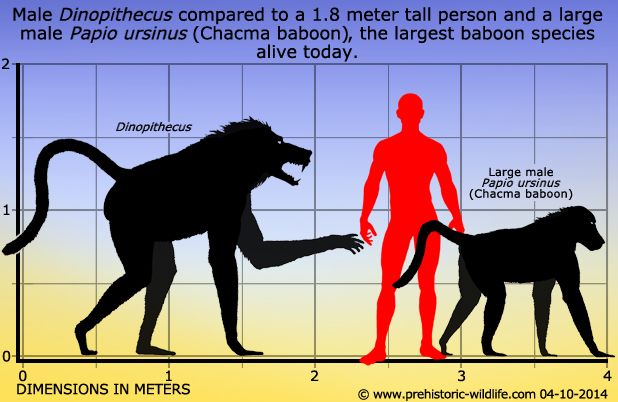
The 'menacing ape' is also among the largest recorded ape species globally. Dinopithecus stood approximately 1.5 to 1.6 meters tall at the shoulders and weighed around 50 kg. In some instances, adult males are estimated to have reached a weight of 77 kg.
Despite incomplete fossils, experts can confirm that this ape species was remarkably large, surpassing many present-day apes.
Their astonishing size is the main reason they are called terror apes. Due to the inability to assemble complete fossils, their external appearance is speculative and considered approximate.
While working to unveil all details about the appearance and behavior of Dinopithecus, paleontologists have compared them to modern ape species.
Similar to many modern apes, Dinopithecus is believed to have lived in various-sized groups, likely migrating to different areas in search of food.
It is also believed that these apes spent a significant amount of time in caves, at least when not on the move. There is a possibility that these apes also spent some time in trees, but regardless of their decision, they always had to be close to a water source.
Due to the many unknowns about this ape species, there is no conclusive information about their diet. Nevertheless, it is believed that these apes had a more diverse diet compared to modern apes.
Additionally, studies on the dental structure of this ancient ape reveal that their teeth were adapted for chewing coarse food. It's highly likely these apes were omnivores, consuming insects and other small animals.
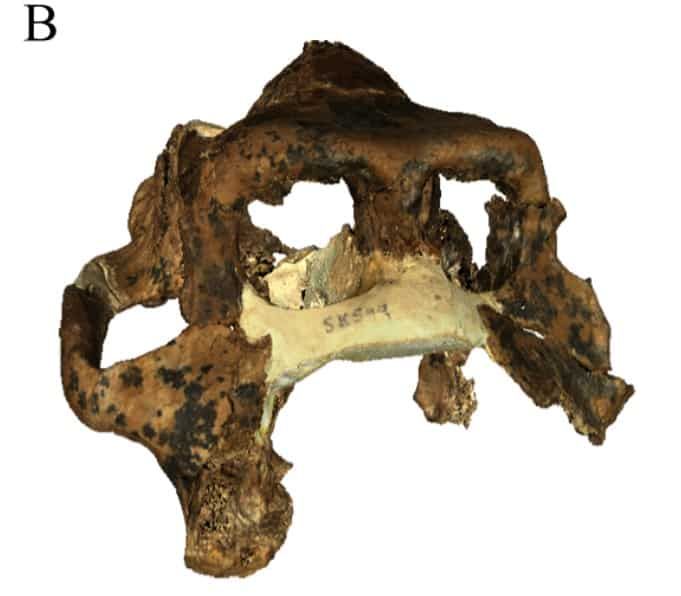
Further research into their teeth indicates that these apes had a diverse diet, although their digestive system could process both plants and small animals. However, it seems these apes preferred fruits over leaves.
Due to their genetic makeup, Dinopithecus exhibits more distinctive features compared to modern apes. The first evident difference between the two lies in their size.
Most of the time, apes are herbivores, occasionally incorporating small animals or insects to complement their diet. For example, apes consume various fruits but also eat leaves, flowers, and insects. However, Dinopithecus is believed to have consumed significantly more small animals than modern apes.
Nevertheless, a common trait among all ape species is their preference for living in small family units ranging from two to six individuals. Gibbons, being the most socially inclined ape species, form communities of 15 to 120 individuals, whereas chimpanzees live in family groups with up to 30 members.
It is believed that Dinopithecus went extinct between 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, during the Pleistocene Epoch. While experts haven't pinpointed the primary cause of their extinction, climate change is considered one of the significant contributing factors.
Source: Animalia; Incredible; ZME
