USB, a seemingly familiar device in our computer usage, yet not everyone truly grasps what USB is. In this article, Mytour Blog introduces common USB types in the market, along with the structure and operation of USB. Read on to select the USB type that suits your electronic devices!
Devices with USB Ports
USB (Universal Serial Bus), also known as USB drive or flash drive, is a compact and convenient data storage device. USB allows devices with USB ports to connect and transfer digital data. Additionally, USB can be used to provide power to other devices that require electricity. Currently, there are two types of USB connections: wired and wireless. However, the wired USB connection remains more popular. Here are some common devices with USB ports:
Devices Connectable via USB Port
Beyond tablets and smartphones, the majority of electronic devices nowadays can connect through a USB port. Below is a list of some common devices:
 USB Ports on Electronic Devices (Source: Internet)
USB Ports on Electronic Devices (Source: Internet)Structure of USB
Understanding the structure of a USB drive provides insights into what USB is. A typical USB drive consists of the following components:
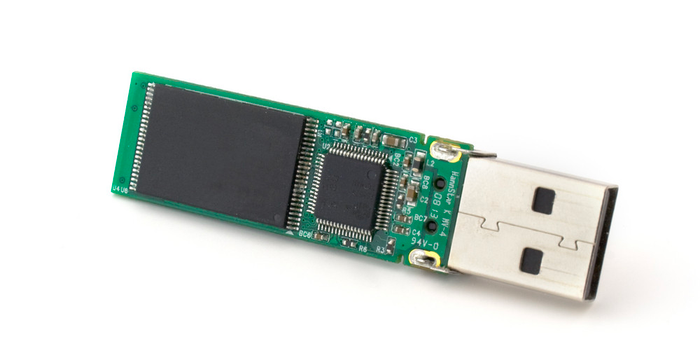 Structure of a USB Drive (Source: Internet)
Structure of a USB Drive (Source: Internet)- Compact Circuit Board: Housing electronic components along with one (or multiple) directly soldered flash chips.
- Plug Connecting to USB Port: Typically using standard Type A plugs, enabling direct connection to USB ports.
- External Protective Casing: Enveloping the entire circuit board and flash chip, with only the USB connecting end exposed. The protective casing serves as both a safeguard and a decorative layer, often designed in various colors to appeal to buyers. Some USB casings also offer water or shock resistance.
- Activity Indicator Light: Most USB types in the market feature a small indicator light to display the working status. The light patterns vary among manufacturers; for example, some USBs illuminate when reading or writing data, while others blink continuously throughout the process.
Explore more: Versatile and Authentic Mini Cameras
Common USB Classifications
USB comes in numerous types, and here are two criteria for classifying USB: based on connection standards and based on speed
Based on Connection Standards
USB Type-A
USB Type-A connection standard is the most common USB standard in today's market. The majority of desktop computers and laptops use Type-A connection ports.
 Standard design of a USB Type-A (Source: Internet)
Standard design of a USB Type-A (Source: Internet)The connector of USB Type-A is a rectangular plastic piece with metal contacts on top for data transmission. Its outer part is encased in a flat metal layer, making it easy to disconnect the USB. Additionally, USB Type-A ports are commonly found on keyboards and computer mice.
USB Type-B
Unlike the Type-A standard, USB Type-B is commonly used in cameras, printers, and gaming consoles. USB Type-B has a square shape with beveled edges at both connecting ends.
 Close-up of the USB Type-B Connector (Source: Internet)
Close-up of the USB Type-B Connector (Source: Internet)Mini USB Type-B
Due to the large size of USB Type-B, it is not suitable for many devices such as tablets or mobile phones. Therefore, manufacturers introduced a smaller version called Mini USB Type-B. However, the Mini USB Type-B connection standard is no longer widespread at present.
 Mini USB Type-B features a compact design (Source: Internet)
Mini USB Type-B features a compact design (Source: Internet)Micro USB Type-A
The Micro USB Type-A connection standard is commonly found on mobile devices such as phones, cameras, or mp3 players. Additionally, Micro USB Type-A features On-The-Go functionality, allowing phones or tablets to become hosts for connecting peripheral devices. The connector of Micro USB Type-A is designed with a compact size and houses 5 internal pins, all surrounded by a sturdy flat metal layer.
Micro USB Type-B
Unlike Micro USB Type-A, the connector of Type-B has beveled edges at the top. However, inside the connector, it still accommodates 5 compact connecting pins and a metal prong section to ensure secure USB connection on the opposite side. Both connection standards have similar transmission speeds (480 Mbps) and support OTG (On-The-Go) functionality.
 Comparison image of USB types based on connection standards (Source: Internet)
Comparison image of USB types based on connection standards (Source: Internet)USB Type-C
USB Type-C is one of the most widely used USB connection standards today. It boasts a sleek design with high aesthetic appeal. Notably, with identical reversible plugs on both ends, users no longer need to distinguish the correct orientation. Additionally, to fit the increasingly slim profiles of mobile devices, many manufacturers have opted for USB Type-C as the connection port for phones and laptops.
 USB Type-C is widely adopted due to its compact design (Source: Internet)
USB Type-C is widely adopted due to its compact design (Source: Internet)Based on Speed Standards
USB 1.x
USB 1.x is a USB port with a data transfer speed of 12 Mbps and the capability to support up to 127 peripheral devices. However, this USB type is no longer commonly used.
 Close-up image of USB 1.0 (Source: Internet)
Close-up image of USB 1.0 (Source: Internet)USB 2.0
Introduced to the market in 2001, USB 2.0 was developed by major computer companies worldwide such as Hewlett Packard, Intel, Lucent, Microsoft, NEC, and Phillips. USB 2.0 boasts a data transfer speed of up to 480 megabits per second (Mbps) or 60 megabytes per second (MBps), 50 times faster than USB 1.x. Moreover, USB 2.0 is cost-effective and supports multiple connection formats, making it widely prevalent in electronic devices.
 The advent of USB 2.0 is considered a revolution in data transfer speed (Source: Internet)
The advent of USB 2.0 is considered a revolution in data transfer speed (Source: Internet)USB 3.0
USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, officially hit the market in 2010. After nearly a decade, USB 3.0 has seen significant improvements over USB 2.0 in terms of transfer speed, operational efficiency, power management, and bandwidth. Typically, SuperSpeed USB ports are colored blue or marked with the abbreviation SS for easy identification. However, after the introduction of USB 3.1, USB 3.0 was officially renamed USB 3.1 Gen1.
USB 3.1
A more advanced version of USB 3.0 is USB 3.1, also known as SuperSpeed+. Introduced in the mid-2013, this USB port boasts a transfer speed of up to 10 Gbps, aligning with the first generation of Apple's Thunderbolt port.
 Many contemporary devices leverage the USB 3.1 port to optimize performance
Many contemporary devices leverage the USB 3.1 port to optimize performanceUses of USB
As highlighted in the article, the primary function of USB is data storage and transfer between various tech devices. Nevertheless, USB serves many other useful purposes, such as:
Computer Repair Support
USB goes beyond being a simple data storage and transfer device; it can act as a 'rescuer' for your computer. After a period of using the Windows operating system, many users encounter issues like slow performance or lag. In such cases, a USB Boot device can help resolve the problem. A USB Boot can store information containing the ISO image (a copy of the content of the Windows installation CD or DVD) saved on the operating system. Thanks to this, users can boot the computer from USB and recover, repair, or install the operating system.
System Administration Assistance
Many network administrators use USB to assist in managing systems. By saving a setup from the first computer to the USB, administrators can then plug the USB into other computers to apply the copied setup to new machines without manual reconfiguration. This ensures that all computers in the system can have identical setups without consuming much time.
Electronic Key
USB can also play the role of an electronic key to initiate highly secure computer systems. Some software companies use USB as an activation key whenever the software needs to be used to prevent unauthorized copying or usage.
Data Security Support within USB
With modern technology, many types of USB devices may require users to enter a password before usage. Furthermore, advanced USBs may incorporate biometric confirmation (fingerprint recognition), ensuring that only individuals with registered fingerprints can access and modify the data within that USB.
 Premium USB types might demand fingerprint confirmation for data access
Premium USB types might demand fingerprint confirmation for data accessCommon Questions When Using USBs
- How many USB standards are there today?
There are three common USB standards: USB 2.0, USB 3.1, and USB 3.0. Among them, the 3.1 standard is the latest. Additionally, there are other standards like USB 1.x, but these are not as widely used anymore.
- What is the purpose of higher-generation USBs?
Higher-generation USBs offer faster data transfer speeds.
- Is USB an external or internal storage device?
USB is an external storage device. USBs are typically compact, easy to store, and can be conveniently detached and folded.
We hope that Mytour's compiled information in this article has helped you answer the question What is USB. With the incredibly convenient features of USBs, don't forget to visit Mytour to find the product that suits your needs!
