This article provides a detailed guide on how to use the CHOOSE function combined with SUM to perform conditional summing in Excel.
1. Choose Function
Description: The CHOOSE function is a simple and frequently used lookup function in Excel.
Syntax: CHOOSE(index_num, value1, [value2]...).
Where:
- index_num: The position of the returned data, for example, if index_num = 1 => the returned value is value 1, index_num = 2 => the returned value is value2. The index_num must be an integer or the result of a formula but must be an integer value. The index_num is limited to a range from 1 to 29.
- value1: The first value to return.
- value2: The second value to return.
Values range from 1 to 29.
Note: If the index_num value is not an integer, the function returns a #Value! error value.
2. Sum Function
Description: The Sum function is used to calculate totals in Excel.
Syntax: SUM (number1, number2, …).
Where: number1, number2, … are the values to sum.
3. Example of using the Choose function combined with the Sum function
Consider the following data table for example, calculate the total sales amount and the total number of items sold using the Choose function combined with Sum.
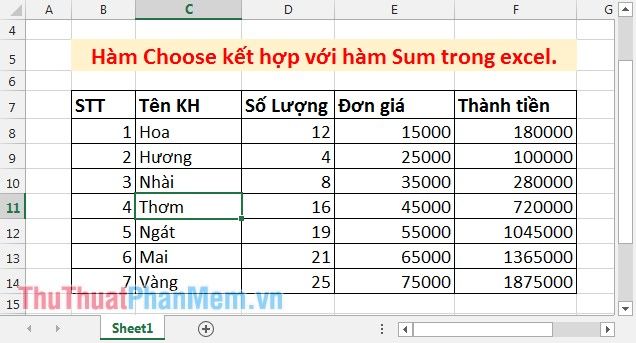
- Calculate the total sales amount
In the cell where you want to calculate, enter the formula: =SUM(CHOOSE(2,D8:D14,F8:F14)).
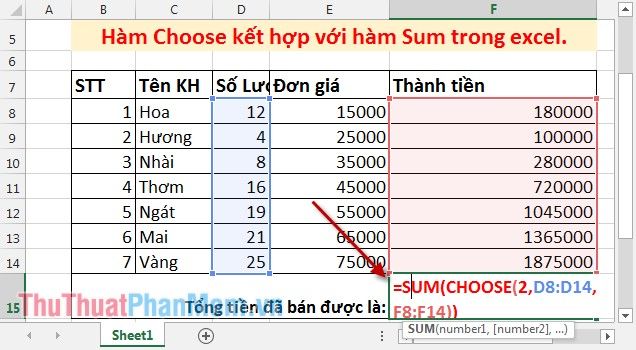
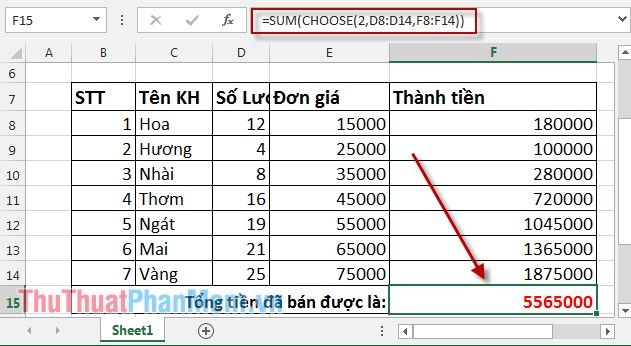
Press Enter -> the total sales amount is:
Calculate the quantity of items sold.
Paste the formula to sum the total value of index_num in the Choose function as 1: =SUM(CHOOSE(1,D8:D14,F8:F14)). Since the quantity column value is positioned at the 1st place among the values of the Choose function, Index_num =1.
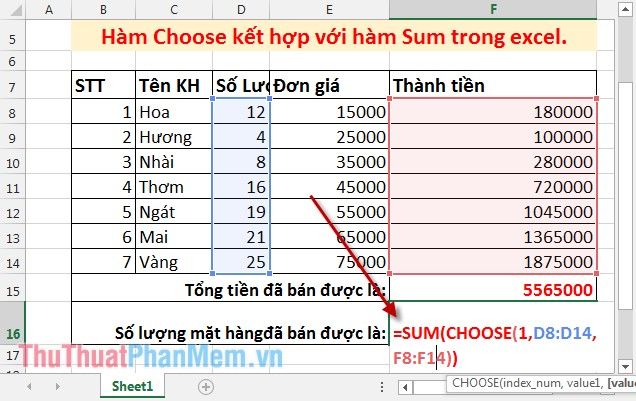
Press Enter to get the result:
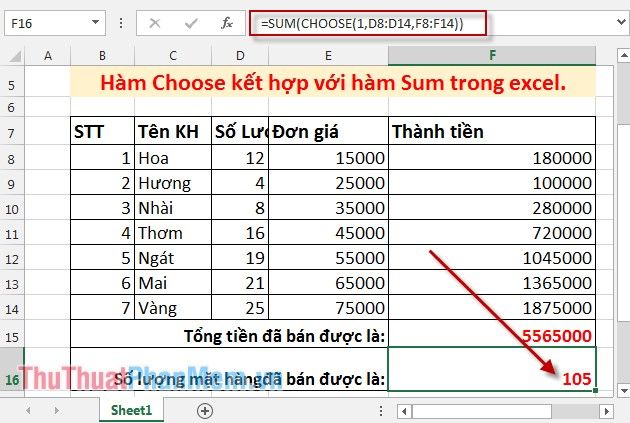
Therefore, utilizing the Choose function facilitates the fastest way to calculate conditional sums.
Wishing you all success!
