
What is the OR function?
As introduced, the OR function is a common type of logical function in Excel. Its purpose is to check certain conditions and return either 'TRUE' (correct) or 'FALSE' (incorrect).
- The result will return 'TRUE' if at least one of the input conditions is correct.
- Conversely, the result will return 'FALSE' if all input conditions are incorrect.
Formula for the OR function in Excel
Syntax: =OR(logical1, [logical2],...)
Meaning of each component in the formula:
- Logical1: the first condition to be checked (mandatory).
- Logical2, Logical3, …: the subsequent conditions to be checked (optional).
- Additionally, each condition must be a logical operator (comparison operation). Specifically, it can be the 'equals' (=) operation, 'less than' (<), 'less than or equal to' (<=), 'greater than' (>), 'greater than or equal to' (>=), or 'not equal to' (<>).
- Each condition can be a number, text string, reference value, formula, or Boolean data type (true or false).
- The OR function can also be combined with various other functions depending on the user's purpose. For example, OR can be combined with AND, IF, VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, etc.

Using the OR function in Excel to check two conditions containing numerical values
To better understand how to use the OR function in Excel, refer to the simple example below.
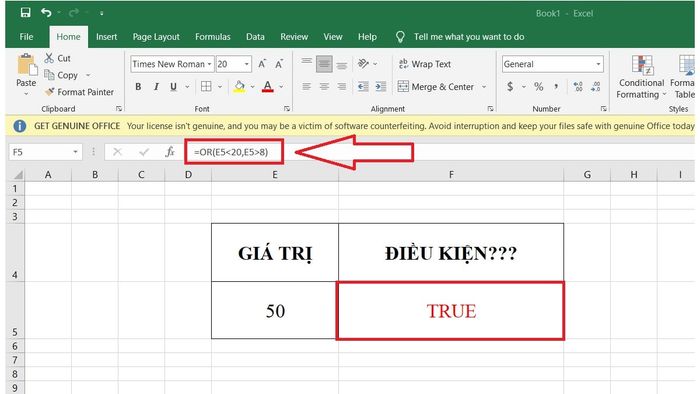
Example: Check the numerical value below with the condition that it must be less than 20 and greater than 8. Verify true or false?
- In cell F5, enter the function as follows: =OR(E5<20, E5>8)
- The result of the function returns 'TRUE' in cell F5 because there is one true condition in the function (condition: E5>8).
Using the OR function to check conditions with numerical and text values
In cases where the conditions of the OR function involve numerical and text values, you can refer to the following example:
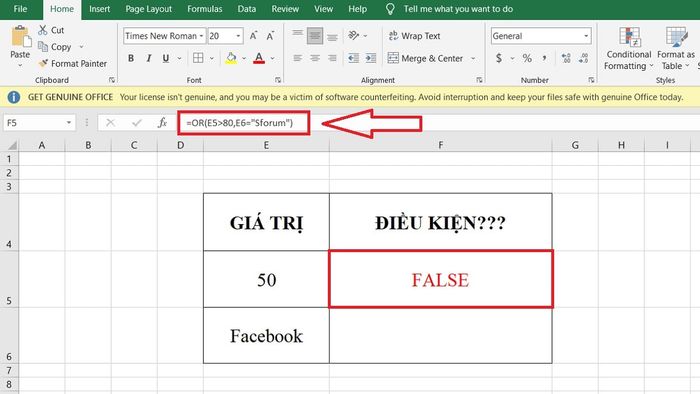
Example: Check two conditions (one numerical, one text) below. With the given values, check if the numeric condition is greater than 80 and the text is 'Mytour':
- In cell F5, enter the function as follows: =OR(E5>80, E6='Mytour')
- The result of the function returns 'FALSE' in cell F5 because no condition in the function is true.
Combining IF and OR functions in Excel
The OR function becomes more valuable when combined with other functions, notably the IF function.
The syntax of the IF function in Excel is: =IF(Logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
Note:
- The IF function checks the 'Logical_test' condition and returns the 'value_if_true' if the condition is true.
- Conversely, the function returns 'value_if_false' if the condition is false.
So how do you combine them correctly? Let's go through an example to understand how to combine these two functions effectively.
Scenario: Evaluating employees (Achieved or Not Achieved) in a data table (table 1) based on the sales performance of products A and B.
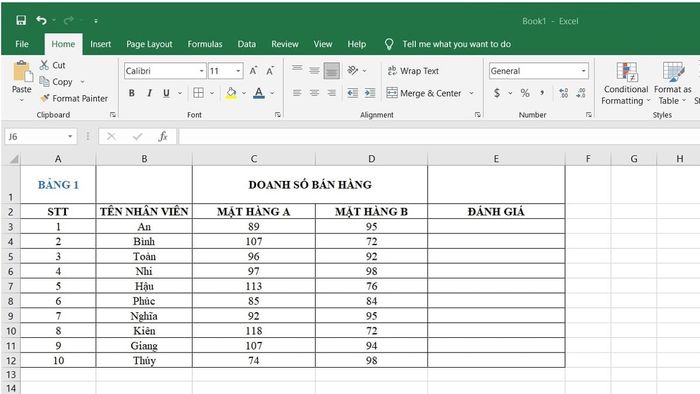 Table 1: Sales data table for employee sales of products A, B
Table 1: Sales data table for employee sales of products A, BIn cell E3, enter the function as follows: =IF(OR(C3>=100,D3>=90),'Achieved','Not Achieved')
And here is the evaluation result for all employees in the data table after combining the IF and OR functions.
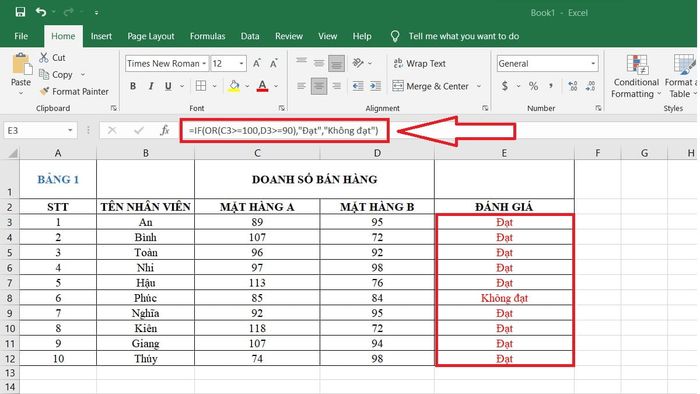 Evaluation results of 'Achieved' or 'Not Achieved' after using the formula
Evaluation results of 'Achieved' or 'Not Achieved' after using the formulaIn summary, this article helps you understand how to use the OR function in Excel through illustrative examples. This is a fundamental function in Excel, and there are many other Excel functions that can be combined with multiple conditions. Follow Mytour for updates on the latest functions. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below!
