While CPU is a crucial part of a computer, not everyone truly understands what CPU is, its significance, and the components that make up a CPU. Follow this article to discover interesting information about CPUs!
1. What is CPU?
CPU, an acronym for Central Processing Unit, is the central electronic circuitry in a computer. It executes program instructions by performing arithmetic, logic, comparison operations, and basic input/output operations specified by the instruction code.
What is CPU?
2. Architecture of CPU
- Control Unit (CU)
As a crucial CPU component, the Control Unit interprets program instructions and regulates processing operations. Precisely controlled by the system clock pulse, this core part is constructed from logic circuits, comparing with semiconductor components like transistors.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Its function involves performing arithmetic and logic operations, then returning results to registers or memory.
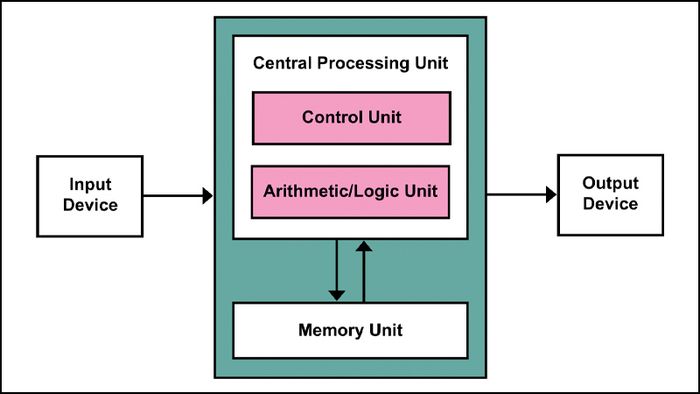
Architecture of CPU
- Registers
These are nimble memory units with petite capacities but boast lightning-fast access speeds. Nestled right within the CPU, they serve to transiently store operands, computation results, memory cell addresses, or control information. Each register has a specific function, with the pivotal one being the Program Counter (PC), pointing to the next instruction to be executed.
- Operation Code
This memory section holds the CPU's machine code (not obligatory) to enable the execution of instructions in the executable file.
- Control Unit
Handles the control of blocks and pulse frequency. The system clock circuit is used to synchronize processing operations within and outside the CPU at fixed intervals. The waiting time between two pulses is known as the clock cycle. The rate at which the system clock generates standard time pulses is called the clock speed, measured in megahertz (MHz).
CPU Structure
3. What makes CPU processing speed fast?
With a high CPU speed, users can smoothly play games or perform complex tasks on the iPhone 14 series. So, why hesitate? Grab the genuine iPhone Pro Max 128GB now available at Mytour with ATTRACTIVE PRICES and EXCITING PROMOTIONS.
CPU speed, also known as CPU clock speed, is measured in Gigahertz or GHz, representing the number of processing cycles per second that the CPU can perform.
A higher clock speed implies a faster CPU. However, numerous other factors come into play.
What makes CPU processing speed fast?
CPU speed is influenced by various factors such as:
- Number of processing cores (2, 4, 10, 22 cores, etc.), more cores mean more power.
- Manufacturing technology (32nm, 22nm, 14nm, etc.), smaller sizes save power and offer higher efficiency.
- Technologies enhancing CPU processing speed (pipeline, turbo boost, hyper-threading, etc.).
CPU speed is also dependent on other factors.
- Cache memory is utilized to store frequently used instructions/data or those likely to be used in the near future, reducing CPU wait times.
- Integrated Graphics
- TDP (Thermal Design Power), the amount of heat the processor chip emits that the cooling system must dissipate. TDP typically indicates the chip's power consumption; the lower, the better.
You might be interested in: How to check and measure the temperature of your computer's CPU, simple and accurate methods.
4. Current Types of CPUs in Use
Presently, the two largest global CPU manufacturers are AMD and Intel. The development of these two major brands has provided users with more choices and comparisons to select the best product.
- Intel CPU
Intel CPUs: Intel Core i3, i5, i7, i9, and Intel Xeon.
Examples of popular CPU types include: Intel Core i9 9900k, Intel Core i7 8700k, and Intel Core i5 9400F.

Intel CPU
- AMD CPU
AMD CPUs: AMD Ryzen 5, AMD Ryzen 7, and AMD Ryzen Threadripper.
Examples of popular CPUs include: AMD Ryzen 7 2700X, AMD Ryzen 7 2700, and AMD Ryzen 7 3700X.

AMD CPU
For Mytour/ĐMX products excluding Non-electrical Household, Non-electrical Accessories & Used items, you can choose one of the following methods:
- 12-month committed warranty.
- Immediate exchange for any defects.
- Refund: Applicable for both faulty and non-faulty products.
Refer to the detailed warranty and return policy: HERE.
Note: The warranty policy was updated on 11/02/2021. The policy may change in the future, and your understanding is appreciated.
This article provides valuable information about CPUs. Thank you for following along.
