Morse Code is often transmitted in a form perceptible through human senses such as touch, movement, sound waves, light, or oral pronunciation. It serves as a unique message, and only those who decipher it can truly understand the conveyed information.
History and Origin of Morse Code
On 06/01/1838, American artist Samuel Morse publicly introduced Morse Code as a means to transmit encoded communication through telegraph wires. Subsequently, this code continued to undergo further development in the 1840s.
Around 1844, the Morse system for electric telegraphy was first employed. In the initial Morse telegraph machines, the response mechanism emitted noise every time it moved in and out of the marked position. Thus, telegraph operators translated this noise into dots (.) and dashes (-), recording them on paper.
To mirror the sound of the Morse receiver, dots and dashes were vocalized as 'dit' and 'dah.' From then until now, the Morse Code system has been widely used on an international scale.
 Morse Code was initially invented by an American artist in 1838
Morse Code was initially invented by an American artist in 1838In the 1890s, Morse Code found predominant use in wireless communication. By the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Morse Code was the primary mode of international communication, utilized over telegraph wires, wireless circuits, and undersea cables.
In the aviation sector, Morse Code became a regular feature from the 1920s onward. Notably, it became a widely adopted signal code, especially during World War II, facilitating message transmission between naval ships and bases.
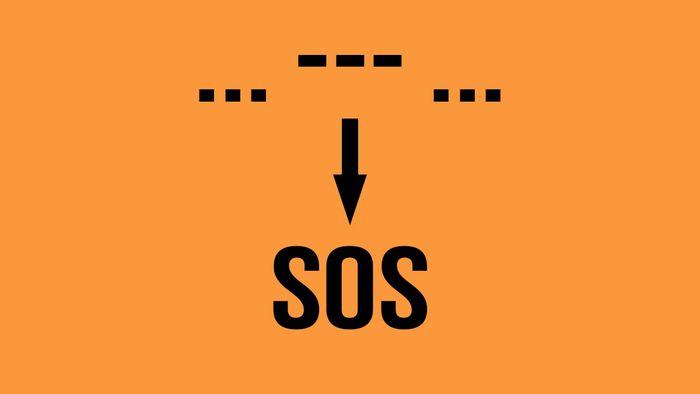
Today, Morse Code characters serve valuable roles in emergency situations. If you want to signal 'SOS,' you can use Morse Code: ...---...
Morse Code continues to find applications in various fields in different forms.
 Many fields have embraced and continue to use Morse Code
Many fields have embraced and continue to use Morse CodeAn Easy and Quick Way to Remember Morse Code
Understanding the Morse Code concept can be challenging, making the learning process even more difficult. However, there are several helpful methods to aid in remembering, studying, and practicing Morse Code. For example, you can follow the basic steps outlined below:
Step 1: Grasp the meanings of basic symbols in the Morse Code system.
As introduced, Morse Code consists of two primary signaling units: the dot (.) and the dash (-).
- The dot (.) is pronounced as 'dit,' with a short 'i' and a silent 't.'
- The dash (-) is pronounced as 'dah,' with a short 'a.'
 Morse Codes will include these two signaling units, (.) and (-)
Morse Codes will include these two signaling units, (.) and (-)Step 2: Learn the Morse Code chart in English, Vietnamese, and use it to reference various characters.
Here is the Morse Code chart for English characters and Arabic numerals:
 The Morse Code chart encodes English characters and numerals
The Morse Code chart encodes English characters and numeralsFor Vietnamese, letters and accents are encoded according to the following rules:
 The Morse Code chart encodes Vietnamese characters and accents
The Morse Code chart encodes Vietnamese characters and accentsThe best way to learn Morse Code is through visual learning and repeated note-taking. For instance, use a pencil to copy the code chart, then trace it with a pen. Additionally, group similar encoded characters, use images to visualize them, and place those images in easily visible locations.
Learning Morse Code is similar to learning a new language. The most effective way to master a language is to immerse yourself in an environment where that language is spoken.
Step 3: Combine characters to form simple, easily memorable words.
After learning the Morse Code chart, you can independently combine some encoded characters. For example, CAT consists of the characters C, A, and T, so the Morse Code for CAT is:
C -.-.
A .-
T -
CAT -.-..--
 Example of how characters are combined to form words using Morse Code principles
Example of how characters are combined to form words using Morse Code principlesStep 4: Practice translating Morse Code and hone your listening skills through recorded audio.
After learning Morse Code for a while, you should translate Morse Code on your own to refine your reflexes.
For instance, you can translate Morse Code from children's books, convert short sentences from Vietnamese to Morse Code and vice versa. Additionally, practicing listening is crucial because Morse Code is often signaled in audio form. When listening to audio recordings, make note of the decoded characters on paper.
 Practice listening and translating Morse Code regularly
Practice listening and translating Morse Code regularlyBasic Rules in Morse Code
Each Morse Code symbol (or each character) is formed by a sequence of dots (.) and dashes (-). Where:
- Dot (.): is the basic time unit in the Morse Code system, with 1 dot representing 1 time unit.
- Dash (-): has a duration three times that of a dot, equivalent to 3 time units.
- The space between parts of the same letter is 1 time unit.
- The space between letters in the same word is 3 time units.
- The space between complete words is 7 time units.
 Rules regarding the duration of characters in the Morse Code system
Rules regarding the duration of characters in the Morse Code systemGuide on Simple Morse Code Translation for Beginners
If you are a beginner learning Morse Code, it's advisable to have a Morse Code chart with you. Using the chart to translate Morse Code involves the following steps:
Step 1: Record the words you need to decipher in Morse on paper or memorize them, for example: SOS.
Step 2: Open the Morse Code chart, look up each character in Morse, and link those characters.
For example:
 Link characters to form meaningful words based on the Morse Code chart
Link characters to form meaningful words based on the Morse Code chartStep 3: Read aloud the Morse translation or transmit the message using paper to the recipient. You can also use sound sources such as horns, turning on/off lights, etc., to signal Morse Code.
Popular Morse Code Encoding Software Today
Currently, there are many software, websites, and applications that help you translate Morse Code quickly. You can refer to some free Morse Code translation sources below:
- Morse Code Translator (https://morsecode.world/international/translator.html)
- Morse Code App (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=me.lam.morsecode)
- Morse Chat (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=digital.dong.morsechat)
- Learn Morse Code - Translate (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=holecek.pavel.MorseCode)
- most - Morse Code Translator (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.venchild.morse)
 Utilize free Morse Code translation software and apps
Utilize free Morse Code translation software and appsExpect the provided information helps you grasp what Morse Code is and learn Morse Code quickly. If you wish to translate Morse Code swiftly and accurately, use available software and apps on your mobile phone.
