Electrical appliances, such as microwave ovens, can face issues if users operate them incorrectly. Below are the causes and solutions for the situation where the microwave oven fuse breaks, which many may have encountered due to careless usage. Let's explore!
Microwave oven fuse breakage
1. Causes and solutions for microwave oven fuse breakage
1.1. Voltage Discrepancy at the Input
Microwave ovens come in various types, each with different power and voltage levels. If users connect the oven to electricity, but the power supply voltage is excessively high, it can lead to fuse breakage. Additionally, sudden voltage spikes while using the microwave can cause circuit overload, resulting in fuse blowing.
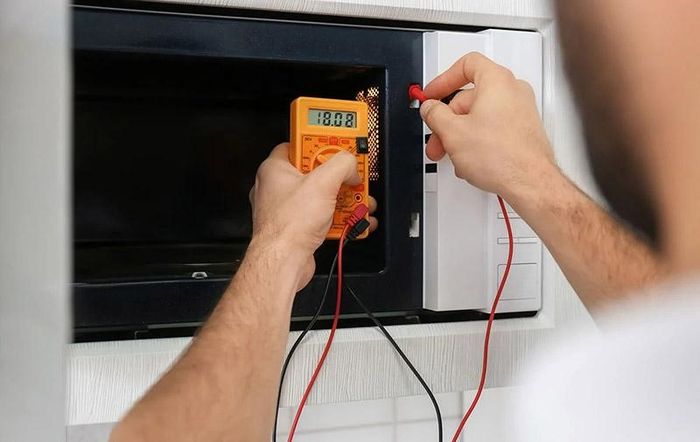

Checking the resistance of the microwave oven
If you reside in areas with unstable power sources, consider installing a voltage stabilizer to regulate the electric flow. This will enhance the microwave's performance and prevent sudden increases or decreases in voltage.
1.2. Microwave Operating Beyond Capacity
Using a high-power microwave continuously can lead to the microwave operating beyond its capacity. In such instances, the fuse is prone to breaking or there is a high risk of explosion.

Microwave overheating
To address the issue of microwave fuse breakage, pay attention to the microwave usage. When reheating or defrosting food, set the temperature at a moderate level to ensure safe operation and efficient cooking.
1.3. Malfunctioning Cooling Fan
During the microwave cooking process, the motor and cavity of the oven generate significant heat and require cooling. Hence, manufacturers have integrated a cooling fan in microwaves to cool down the thermal components. If the fan gets stuck due to motor issues or any malfunction causing it to stop spinning, the heat will increase, leading to fuse breakage.
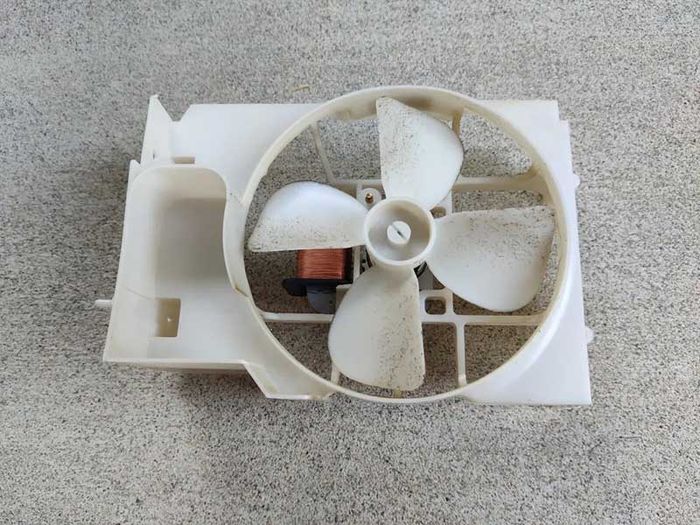
Excessive grease on the microwave's cooling fan
While using the microwave, remember to check its cooling fan. If you notice an accumulation of grease, clean it immediately. Additionally, if the fan seems stuck, notify the warranty service center for inspection and repair.
1.4. Malfunctioning Emission Source
The Magnetron emission source is a component inside the microwave. This part is responsible for generating microwave radiation to cook food. In cases where the current through the Magnetron surges, it can lead to fuse breakage, causing a complete power outage in the microwave.
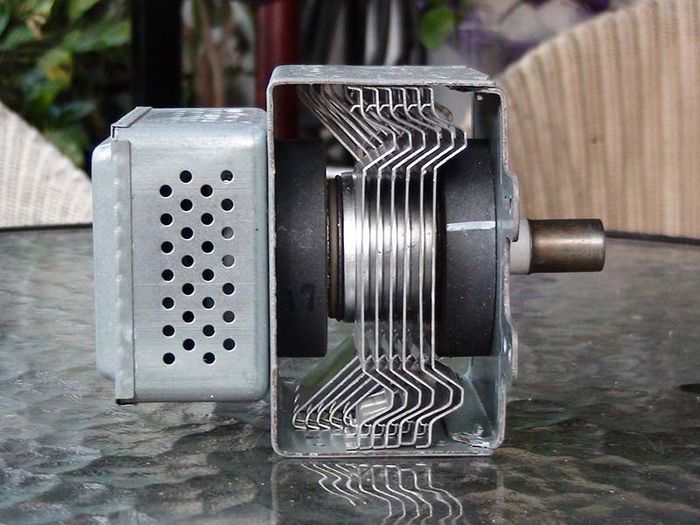

Magnetron emitting vibrational waves
Because the microwave emission source is crucial, in case of any malfunction, disconnect the power and contact the warranty service center. If you lack electrical expertise, avoid attempting to disassemble the device for inspection.
1.5. Faulty Microwave Conduction Components
The conduction components for microwaves, generating electrical waves, include: High-voltage capacitor, high-voltage transformer, and Diode. If any of these three elements malfunctions, it can lead to short circuits and fuse burning.
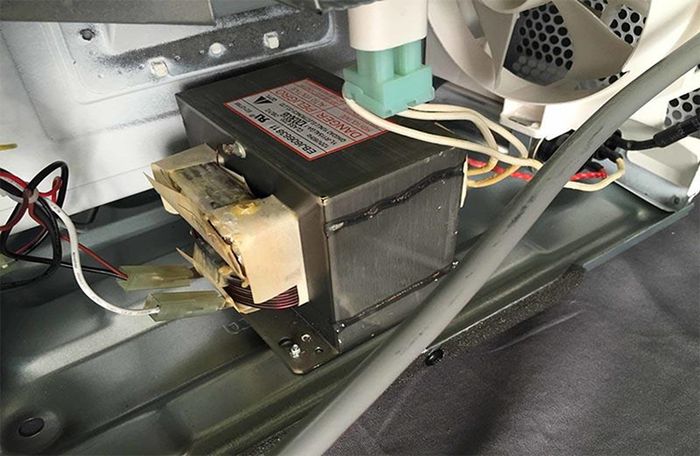

Microwave's conduction components
In cases where the internal conduction circuits of the microwave are damaged, it's crucial to contact the warranty service center immediately. Avoid attempting self-repair or replacement, as it may lead to improper microwave functioning.
1.6. Faulty Door Switch
The microwave door switch (Interlock) is designed to prevent microwave radiation leakage. If the switch, whether open or closed, malfunctions, it can lead to fuse explosion. Therefore, when using the microwave, pay attention to the door mechanism, check it before plugging in. The automatic door lock has many intricate details, requiring a skilled technician. If you detect any issues with the lock, contact the warranty center or a professional repair technician for assistance in resolving this problem.
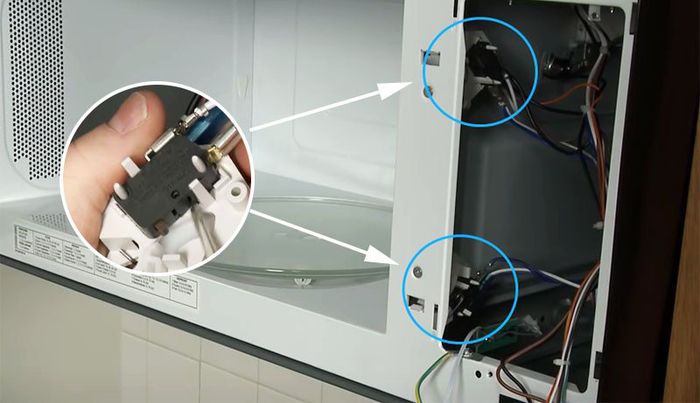

Faulty microwave door switch
1.7. Aging Microwave
Besides the factors related to the components of the microwave, another crucial element is its lifespan. If the microwave is used for an extended period, the internal parts may experience reduced lifespan, loosened screws, or damaged fuses. Therefore, don't be complacent; use the microwave without checking its operational status.
2. Safe and Efficient Microwave Usage
A microwave is an electrical appliance, so when using it for food preparation, users should carefully read the instructions and warnings in the user manual. Here are essential tips to help users use the microwave safely and efficiently.
- Close the microwave door properly to avoid misalignment or jamming, as it can lead to dangerous radiation leakage.
- Use a dedicated power outlet for this appliance.
- Set the cooking temperature at a moderate level for even food preparation; avoid setting it at excessively high power.
- Always clean the microwave cavity, especially the heat-emitting parts, after processing ingredients rich in fats. Accumulated grease, when overheated, can emit smoke or catch fire, posing extreme danger.
- Absolutely refrain from self-repair or modification of microwave parts, especially during the warranty period.
Above are the causes and solutions for the phenomenon of microwave fuse breakage. We hope this information is helpful to users, guiding you on how to use the microwave safely and with caution.
