
If you're wondering why using inverter air conditioners saves more electricity than other types, then don't skip this article to get the most detailed explanation.
1. Why are inverter air conditioners more energy-efficient than other types?
If you're wondering why using inverter air conditioners saves more electricity than other types, then don't skip this article to get the most detailed explanation.
Being a high-capacity cooling device, it's no surprise that air conditioners are among the most power-consuming appliances at home. That's why many people turn to Inverter technology air conditioners in hopes of reducing their monthly electricity bills. So why do inverter air conditioners save more electricity than conventional ones? Which is the best inverter air conditioner brand to choose? All will be explained right here in this article.

Why do inverter air conditioners save more electricity than other types?
1. What is an inverter air conditioner?
Before explaining why inverter air conditioners save more electricity than other types, you should understand the essence of what an inverter air conditioner is.

What is an inverter air conditioner?
In reality, similar to other conventional air conditioners, both single and double inverter air conditioners are products used for air conditioning, providing cool and relaxing space in the summer, and even warmth in winter for households. The biggest difference of the type of air conditioner applying inverter technology lies in the fact that after reaching the set temperature, the unit doesn't shut off but reduces its power and continues to maintain the cool temperature, avoiding energy loss from frequent restarts. This way, inverter air conditioners save more electricity compared to conventional ones, especially when used continuously for 6-8 hours.
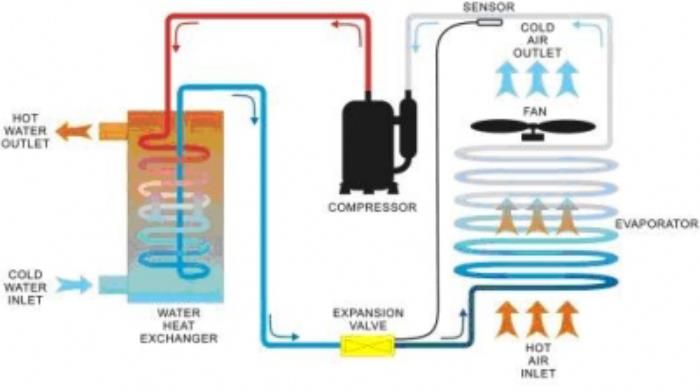
Basic structure of an air conditioner
In the outdoor unit of an air conditioner in general, and a single or double inverter air conditioner in particular, the compressor remains the most important and energy-consuming component. The main task of this compressor unit is to pump and compress the refrigerant gas from low pressure to high pressure and then deliver it to the indoor unit to cool down the indoor temperature. Afterwards, the compressed liquid gas will vaporize back into gas form and get sucked back by the compressor to pump for a new cycle. Hence, in simpler terms, the compressor is like the 'heart' of every air conditioner. Air conditioners with compressors operating at higher capacities consume more electricity.
Operation mechanism of an inverter air conditioner
Understanding the core issue, manufacturers have researched and found ways to reduce the electricity consumption of air conditioners by reducing the power of the compressor, optimizing energy savings while ensuring consistent work efficiency. And the introduction of inverter technology air conditioners, meaning air conditioners with variable frequencies, is a type of air conditioner with lower working power but unchanged energy usage efficiency. In fact, they perform even better than previous products.
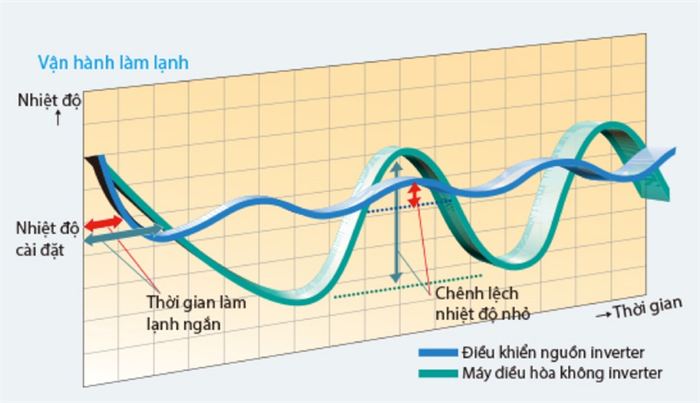
With conventional air conditioners, when users set a specific temperature level for adjustment, the air conditioner will run continuously at a constant power until it reaches the desired temperature and automatically switches off the relay to let the compressor rest. At this point, the indoor unit only operates the fan without any cooling effect. Due to the lack of continuous cooling, external heat affecting the room temperature gradually increases, until it reaches a difference of about 1-2 degrees Celsius from the set temperature, then the relay will automatically close, the compressor will restart, and continue running continuously until the room temperature reaches the required level again, and the cycle will repeat continuously like this.
Also, because conventional air conditioners operate on a continuous on-off mechanism like this, the compressor not only has to start multiple times but also has to run at maximum capacity when operating, consuming a lot of energy, leading to understandable electricity wastage.
On the contrary, inverter air conditioners have been developed and completely overcome these limitations and disadvantages, providing significantly superior electricity-saving efficiency.
Specifically, in single and double inverter air conditioners, when operating, the system will start and gradually increase the operating power, until the room temperature reaches the required level, the inverter will automatically reduce the frequency supplied to the compressor, adjusting the compressor speed reduction instead of stopping completely. Thanks to the continuous operation mechanism at low frequencies, inverter air conditioners effectively save energy while still maintaining stable room temperatures.

Inverter technology air conditioners excel in energy saving when used
In summary, inverter air conditioners save electricity because:
- The ability to maintain air conditioning operation at low power levels, not running at maximum levels like conventional air conditioners, therefore effectively limiting and reducing the amount of consumed energy.
- Eliminating significant electricity wastage due to frequent compressor startups in each on-off cycle of conventional air conditioners, whether it's single or double inverter air conditioners.
- Limiting heat loss and maintaining a stable room temperature, with fluctuations not exceeding 0.5 degrees Celsius, creating a comfortable environment for users.
Additionally, another reason inverter air conditioners save electricity is because nowadays, air conditioners applying inverter technology are all new-generation air conditioning products, using materials that contribute to energy saving while also being environmentally friendly, suitable for the modern green lifestyle of families.
The simplest evidence is that nowadays, most inverter air conditioners use R32 refrigerant gas - a type of gas that provides much higher cooling efficiency compared to previously used gases like R410A or R22, while still ensuring lower electricity consumption.
