Urea is a sustainable organic fertilizer that enhances soil quality, provides nitrogen to plants, and boosts crop yields. It typically comes in the form of dry granules. While it offers several advantages, urea also has some downsides. By applying it correctly and understanding how it interacts with other fertilizers, you can avoid negative effects and maximize its benefits.
Steps
Applying Urea Fertilizer Individually

Minimize ammonia loss by applying urea on cool days. The best time to apply urea is on cool days when temperatures are between 0°-15.6°C and the wind is calm. When temperatures drop below this range, the soil may freeze, making it difficult for the fertilizer to dissolve. When the temperature rises and wind conditions are present, the breakdown of urea will occur faster than the rate at which it is absorbed into the soil.
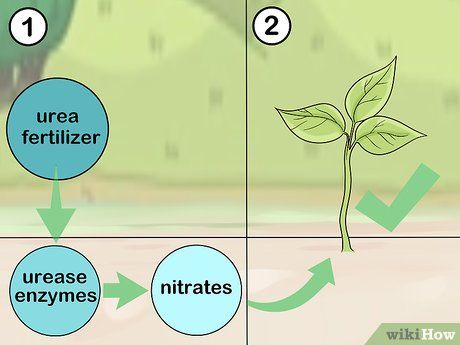
Use urea fertilizer with a urease inhibitor before planting crops. Urease is an enzyme that triggers the chemical reaction converting urea into nitrates, which are essential for plant growth. Applying urea before planting leads to significant loss of urea before it can benefit the plants. By using urea combined with a urease inhibitor, the chemical reaction can be slowed down, allowing more urea to remain in the soil for plant use.
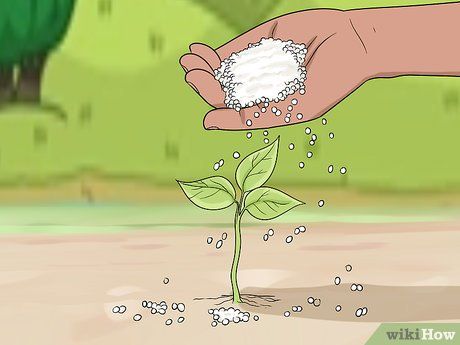
Spread urea fertilizer evenly across the soil surface. Urea fertilizer is sold in pellet or granular form. It can be applied with a fertilizer spreader or by hand to ensure even distribution across the soil. For most crops, it is recommended to apply urea close to the roots or in areas prepared for seed planting.
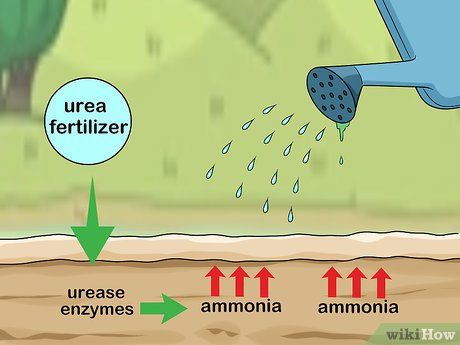
Moisten the soil. Before being converted to nitrates, urea turns into ammonia gas. Since gases can easily escape from the soil, applying fertilizer when the soil is moist helps urea penetrate the ground before the chemical reaction begins. This results in more ammonia being retained in the soil.
- The surface soil layer, approximately 1.3 cm thick, should be wet to retain as much ammonia as possible. You can water the soil, apply urea before it rains, or within 48 hours after snow melts in the field.

Till the soil to mix urea fertilizer into the ground. Tilling the garden or field is an effective way to integrate urea fertilizer into the soil before ammonia gas escapes. Use a plow or hoe to mix the fertilizer into the surface layer of soil.
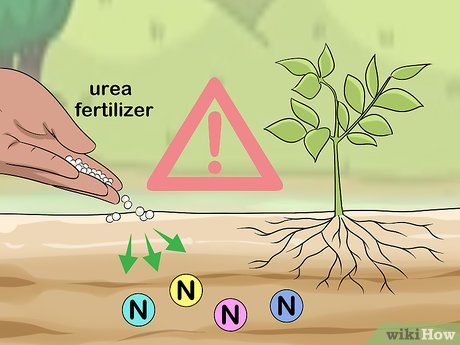
Control nitrogen application for potato crops. Some potato varieties can tolerate higher nitrogen levels, while others cannot. Exercise caution and apply fertilizer uniformly across all potato varieties. Avoid over-applying nitrogen with urea fertilizer.
- You can apply urea fertilizer directly to potato plants or as a solution mixed with other fertilizers, as long as the solution contains 30% nitrogen or less.
- Urea solutions with nitrogen concentrations higher than 30% should only be applied to the soil before planting potatoes.
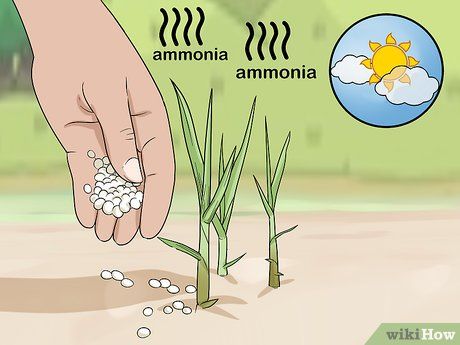
Apply fertilizer to cereal crops on cool days. Urea fertilizer can be applied directly to most cereal crops, but it should be done when temperatures are below 16°C. If applied in warmer conditions, the crops will release an ammonia odor.
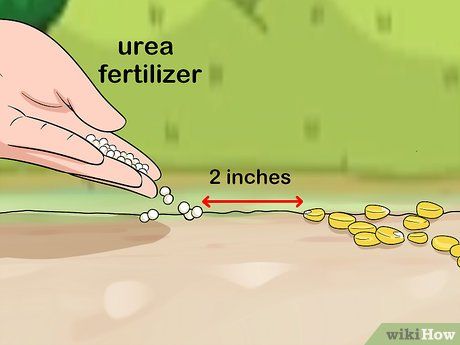
Apply urea fertilizer indirectly to corn seeds. Urea fertilizer should only be applied indirectly to corn by spreading it on the soil surface at least 5 cm away from the corn seeds. Direct contact with urea can be harmful to the seeds and significantly reduce the corn yield.
Combine urea fertilizer with other types of fertilizers.
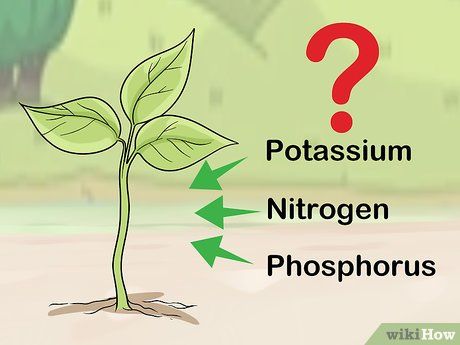
Determine the ideal fertilizer ratio. The fertilizer ratio, also known as the N-P-K number, is a series of three numbers representing the amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the fertilizer mix. If you test the soil, you will be informed of the ideal fertilizer mix ratio to address nutrient deficiencies in the soil.
- Gardeners can often find pre-mixed fertilizers that suit their needs at nurseries or garden centers.
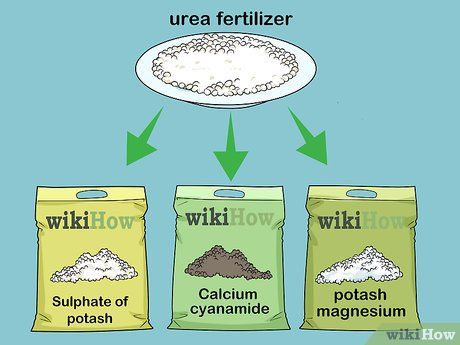
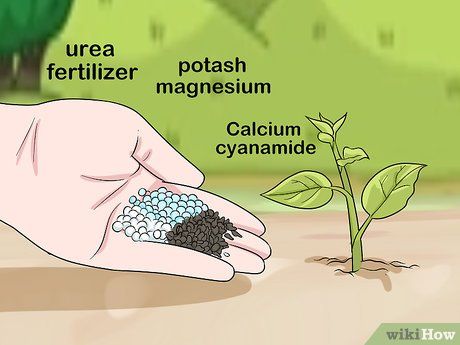
Mix urea with other fertilizers to create a sustainable fertilizer blend. Urea provides nitrogen for crops, but other elements such as phosphorus and potassium are also essential for plant health. Fertilizers that can be safely mixed and stored with urea include:
- Calcium cyanamide
- Potassium sulfate
- Potassium magnesium sulfate
Combine urea with certain fertilizers for immediate application after mixing. Some fertilizers can be mixed with urea, but they lose their effectiveness within 2-3 days due to the chemical reactions between the components. These include:
- Sodium nitrate
- Ammonium sulfate
- Magnesium nitrate
- Diammonium phosphate
- Phosphatic fertilizers obtained from steel production
- Phosphate rock
- Potassium chloride
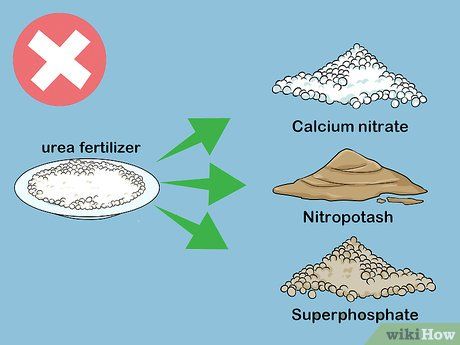
Avoid chemical reactions that could harm your crops. Some fertilizers react with urea, leading to chemical reactions that either evaporate or neutralize the fertilizer mixture. Never mix urea with the following fertilizers:
- Calcium nitrate
- Calcium ammonium nitrate
- Limestone ammonium nitrate
- Ammonium nitrate sulfate
- Nitropotash
- Potash ammonium nitrate
- Superphosphate
- Triple superphosphate
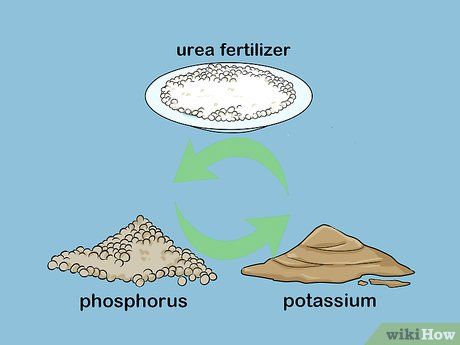
Mix urea with fertilizers rich in potassium and phosphorus to create a balanced fertilizer. Refer to a list of fertilizers that can be mixed effectively or ineffectively with urea. Choose phosphorus and potassium sources to blend into the fertilizer mix. Many of these fertilizers are available at nurseries and garden supply stores.
- Mix the selected fertilizers according to their weight ratio. You can blend them in a large bucket, wheelbarrow, or using a mixing machine.

Spread the urea fertilizer mixture evenly across the field. Applying the urea mixture is similar to applying pure urea: spread it evenly across the soil, then water and till the soil to incorporate the fertilizer.
- Urea fertilizer is lighter than other fertilizers. If using a rotary fertilizer spreader for long distances across the field, ensure the spread width is no more than 15 meters to achieve even coverage.
Tips
- Always follow the instructions provided on the fertilizer product packaging.
- This article discusses fertilizer ratios, which should not be confused with fertilizer percentages. A fertilizer ratio indicates the weight of a specific fertilizer to be mixed into the fertilizer blend. Fertilizer percentages represent the amount of each component in the mix. To calculate a fertilizer ratio using percentages, divide each percentage number by the smallest of the three numbers.
Warning
- Excess nitrates in the soil can cause plant burning. You can prevent plant burning by applying fertilizer to moist soil.
- Always store urea fertilizer separately from ammonium nitrate.
