When using tampons (tube-shaped sanitary pads), there may be times when you struggle to insert them immediately, leading to discomfort. Difficulty inserting a tampon is a common issue, so learning how to insert one painlessly can help you feel more confident during use.
Steps
Choose the right tampon
Familiarize yourself with vaginal anatomy. To ensure you're inserting a tampon correctly, it's important to understand how it enters the vagina. You might have already felt and inserted a tampon, but not fully grasped how it works. If you're new to tampons or haven't explored their mechanism, take some time to observe your genital area to better understand what happens during use.
- Before using a tampon, use a mirror to examine your vagina and see where the tampon should go and how to position it properly.

Use the appropriate applicator. Tampons often come with various types of applicators. You can choose between plastic, cardboard, or applicator-free tampons. Consider which type works best for you. For most women, plastic applicators are the easiest to use.
- Plastic applicators have a smooth surface, making them easier to insert into the vagina. Cardboard or applicator-free tampons may be harder to insert and can sometimes get stuck or not go in fully.

Select the right tampon size. Since menstrual flow varies among women, tampons come in different sizes and absorbency levels. When choosing a tampon, opt for a smaller size, especially if you experience pain or are new to using them. It’s best to start with a small or regular-sized tampon.
- Each tampon box explains the differences between sizes. Small tampons are the thinnest and least absorbent, requiring more frequent changes if your flow is heavy. Regular tampons are slightly thicker but offer better absorption.
- Super-absorbent tampons are larger and may feel uncomfortable. They are designed to handle heavy menstrual flow.
- Choose a tampon with absorbency that matches your flow. Avoid using high-absorbency tampons unless necessary.
Insert the tampon correctly

Wash your hands and prepare the necessary items. Before inserting a tampon, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry them completely. Next, unwrap the tampon and place it within easy reach, then relax your body.
- To relax, try doing a few Kegel exercises to remind yourself to loosen your muscles. Tighten and then release your vaginal muscles three to four times.
- If the tampon comes with a cardboard applicator, you can lubricate it with Vaseline, water-based lubricant, or mineral oil before use.

Choose a comfortable position. The right position makes it easier to insert the tampon. You can stand with your legs apart or place one foot on a chair, stool, toilet seat, or bathtub edge.
- If these positions are uncomfortable, try lying on your back with your knees bent and legs spread shoulder-width apart.
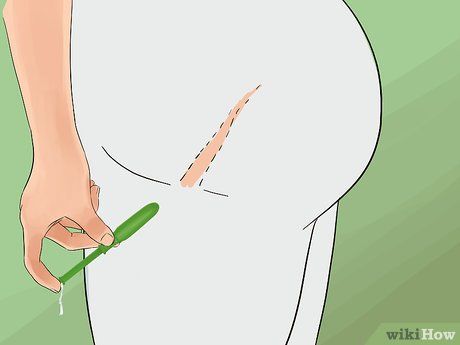
Position the tampon at the vaginal opening. Use your dominant hand to hold the middle of the tampon, where the smaller and larger applicator tubes meet, while your other hand spreads the vaginal lips. Remember to stay relaxed.
- Ensure the string faces outward, as it will remain outside the vagina and is used to remove the tampon later.
- You can use a mirror to observe the process, especially during your first few attempts.

Insert the tampon. Place the applicator tip at the vaginal opening and gently push the tampon inward until it reaches the vagina. The tampon should angle slightly toward your lower back. Use your index finger to push the smaller tube slowly until you feel slight resistance or the smaller tube is fully inside the larger one.
- Use your thumb and middle finger to pull both applicator tubes out without touching the string.
- Avoid touching the string during insertion, as it needs to move freely with the tampon into the vaginal canal.
- Dispose of the applicator and wash your hands after insertion.
- You shouldn’t feel the tampon once it’s properly inserted. If you do, remove it by pulling the string and try again with a new one.
- You can also try pushing the tampon deeper to see if it feels more comfortable. If not, remove it and start over.
Consider medical concerns
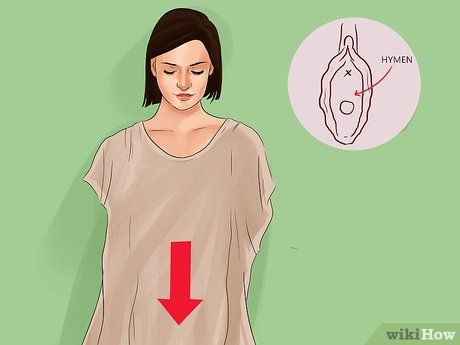
Determine if the hymen is intact. The hymen is a normal, often crescent-shaped membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening. It can tear during sexual activity, physical activities, injury, or illness. An intact hymen may make tampon insertion difficult or painful.
- The hymen may fully or partially cover the vaginal opening. In some cases, it forms a band of tissue across the opening, which can make tampon insertion challenging and painful. Consult a doctor to check and, if necessary, remove this tissue.
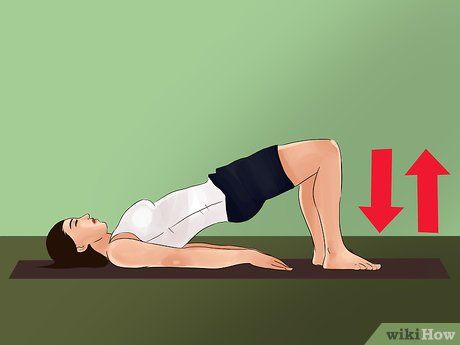
Are you stressed about inserting a tampon? Another common issue many women face is anxiety and tension, especially after a previous failed attempt. Vaginal muscles can tense up, just like muscles in other parts of the body, making tampon insertion uncomfortable or even painful.
- Practicing Kegel exercises has helped many women relieve vaginal muscle tension. Kegels involve tightening and relaxing the vaginal muscles, similar to stopping and starting urination. You can do these exercises anytime, anywhere. Try doing three sets of ten squeezes daily.

Change tampons regularly to avoid Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Replace tampons as needed, typically every 4 to 6 hours while awake, or more frequently depending on your menstrual flow. However, avoid leaving a tampon in overnight. Prolonged use increases the risk of TSS, a rare infection associated with tampon use. Symptoms of TSS include:
- Flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches, joint pain, or headaches
- Sudden high fever
- Dizziness, fainting, or lightheadedness
- Vomiting
- A sunburn-like rash
- Diarrhea

Consult a doctor. If the methods to insert tampons painlessly don’t work, schedule an appointment with your doctor or gynecologist for an examination. For example, the hymen can be perforated or removed to allow easier menstrual flow, making tampon use and sexual activity more comfortable. This minor procedure can be done in a doctor’s office.
- If you experience vaginal muscle tension, learn to control these contractions. Discuss treatment options with your doctor if you need assistance.
- Removing the hymen doesn’t affect virginity. Virginity refers to never having had sexual intercourse, not the presence of a hymen.
- If you experience any TSS symptoms, remove the tampon immediately and seek medical attention. TSS can progress rapidly and is a serious infection requiring urgent treatment.
Tips
- Use tampons only during your menstrual period. Using them on non-menstrual days can make the vagina too dry for comfortable insertion.
- Many women face challenges with tampons after childbirth, but this is usually temporary. If issues persist, consult your doctor.
- If tampons feel uncomfortable, you can always switch to pads! Pads are much easier to use, especially when you’re new to menstruation.
