If you're looking to invest in a company or are thinking of selling one, Mytour can guide you on how to calculate its market value, ensuring you can determine its true worth. The market value of a company represents what investors expect in terms of future profits. However, valuing an entire business is not as simple as appraising smaller, more liquid assets like stocks. That said, there are several methods for calculating the market value of a company, enabling you to accurately estimate its true value. A few common techniques include examining the company’s market capitalization (stock value and shares in circulation), comparing it with similar companies, or applying industry multiples to determine its market value.
Steps
Calculating Market Value with Market Capitalization

- Note: This method applies only to publicly traded companies where stock prices are easily determined.
- A downside of this approach is that the company’s value depends on market fluctuations. If the stock market declines due to external factors, the company’s market capitalization will decrease, even if the company’s financial condition remains unchanged.
- Since market capitalization relies on investor confidence, it is a volatile and unreliable method for determining the true value of a company. Many factors can influence the price of each share and, therefore, the company’s market capitalization. As a result, it’s best not to rely solely on this value. However, any potential buyers will likely share similar market expectations and apply comparable pricing for the company’s potential profits.

- By law, all public company balance sheets are published online and are available for free. A simple search will help you find any balance sheet of a public company.

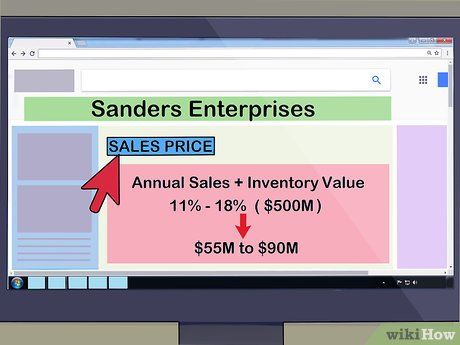
- For example, consider Sanders Enterprises, a publicly traded telecommunications company in the U.S. If the company has 100,000 shares outstanding and each share is trading at $13, the market capitalization of the company would be 100,000 * 13 USD, which equals 1,300,000 USD.
Look at the market value through comparable companies.
- Market capitalization might be considered unrealistic if a company's value is largely based on intangible assets, and investor overconfidence or speculative activity drives the price beyond reasonable limits.
- This method has some limitations. First, it might be hard to find enough data because comparable businesses may have little revenue. Additionally, this valuation method doesn't account for significant differences in the sale price of companies, such as whether the company is forced to sell.
- However, if you're trying to determine the market value of a private company, your options are limited, and this comparative approach is a simple way to get a rough estimate.
- If you want to determine the market value of a private company, you can compare it with publicly traded companies in the same industry and of similar size. This method is easier since you can find the market value of these public companies in just a few minutes by searching for their market capitalization online.
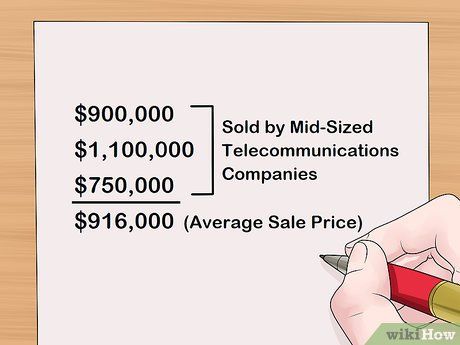
- For instance, let's say three mid-sized telecom companies were recently sold for 900,000 USD, 1,100,000 USD, and 750,000 USD, respectively. The average of these sales would be 916,000 USD. This indicates that the market capitalization of Anderson Enterprises at 1,300,000 USD is likely an overly optimistic estimate.
- You can adjust these values based on the degree of similarity between the company you're estimating and the ones you're comparing it to. For example, if a company shares a very similar size and structure to the one being estimated, you may assign a higher weight to that company's sales price when calculating the average. For further details, you can check out articles on calculating weighted averages.
Determine market value using a multiplier method.


- Revenue or income, along with commissions and inventory expenses, if applicable, are reported in the company's income statement.
- The source of the multiplier will also indicate the relevant financial data to use in your calculation. For instance, total annual income (net income) is a common starting point.

- For example, if the appropriate multiplier for mid-sized accounting firms is estimated to be 1.5 times annual revenue, and Anderson Enterprises has annual revenue of 1,400,000 USD, then using the multiplier method would yield a business value of (1.5 * 1,400,000), which equals 2,100,000 USD.
Advice
- The reason for your valuation will affect the weight you assign to the company's market value. If you're considering investing in a company, what matters most is its compound annual growth rate (CAGR), not the overall size or total value of the company.
- The company's market value may differ significantly from other valuations, such as book value (the net value of tangible assets minus liabilities) and enterprise value (another measure that includes debt), due to fluctuations in debt obligations and other factors.
