A cube is a three-dimensional shape where all three dimensions—width, height, and length—are equal. It has six square faces, and all edges are of the same length and perpendicular to each other. The formula for calculating the volume of a cube is straightforward. Generally, you simply multiply the length × width × height of the cube. Since all edges of a cube are equal in length, another way to express the volume formula is s3, where s represents the length of one side of the cube. See the detailed breakdown of the calculation process in Step 1 below.
Steps
Find the cube root of one side of the cube
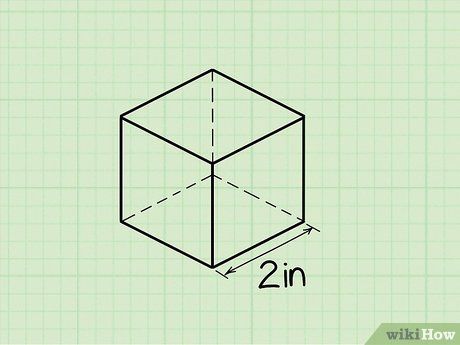
- To better understand the volume calculation, follow each step of the process with the example below. Suppose the length of the side of the cube is 2 cm. We will use this data to find the volume of the cube in the next step.
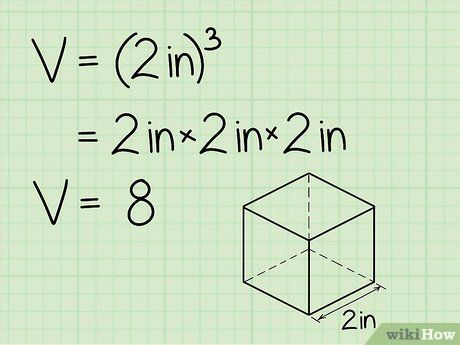
- This process is similar to finding the area of the base, and then multiplying by the height of the cube (or in other words, length × width × height). Since the length, width, and height of a cube are equal, this method can be simplified by cubing the length of any side.
- Let’s proceed with the example above. If the side length of the cube is 2 cm, we can calculate the volume as 2 x 2 x 2 (or 23) = 8.
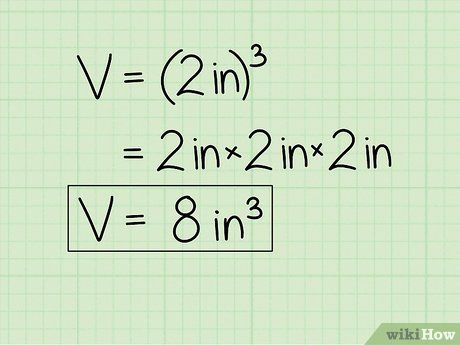
- In our example, since the original measurement is in cm, the final answer should be written in "cubic centimeters" (or cm3). Therefore, our result of 8 will be written as 8 cm3.
- If we had used a different unit of measurement initially, the volume's unit would change accordingly. For example, if our cube had sides of 2 meters, instead of 2 cm, we would use the unit cubic meters (m3).
Calculating Volume from Total Surface Area
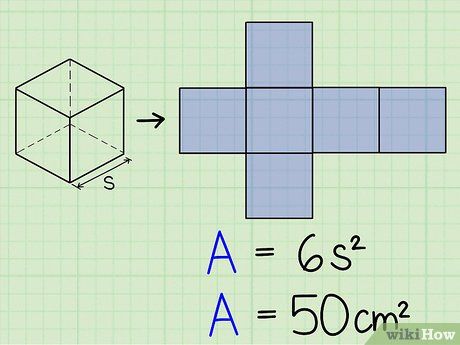
- The total surface area of a cube is calculated with the formula 6s2, where s is the side length of the cube. This formula is essentially the same as calculating the area of each face of the cube (which has six faces) and adding them up. We will use this formula to compute the cube’s volume from its total surface area.
- For example, let’s say we have a cube with a total surface area of 50 cm2, but we don’t yet know the side length. In the following steps, we will use this information to find the cube’s volume.

- In our example, we perform the division 50/6 = 8.33 cm2. Remember, the answer for the area of a face is always in square units (cm2, in2, etc.).
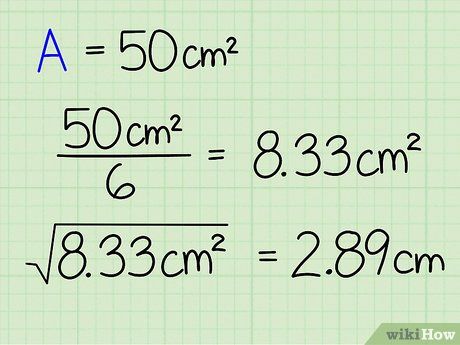
- In our example, √8.33 = 2.89 cm.
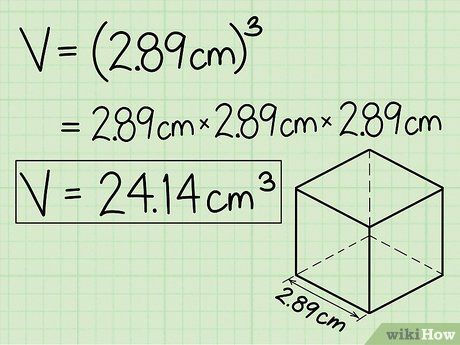
- In our example, 2.89 × 2.89 × 2.89 = 24.14 cm3. Don't forget to note the result in cubic units.
Find the volume from the diagonal
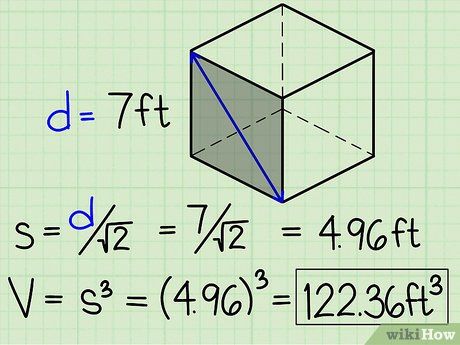
- For example, if a face of the cube has a diagonal of 2.13 meters, we will calculate the side length by dividing 2.13/√2 = 1.51 meters. Now that we know the side length, we can find the volume of the cube by cubing 1.513 = 3.442951 m3.
- Note that, according to the general formula, d2 = 2s2 where d is the diagonal of a face of the cube and s is the side length. This is due to the Pythagorean theorem, where the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Since the diagonal of a face of the cube and the two sides form a right triangle, d2 = s2 + s2 = 2s2.
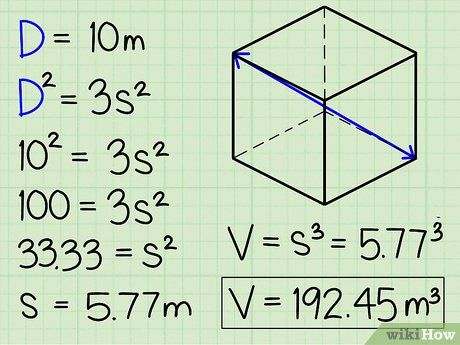
- This formula is derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. D, d, and s form a right triangle with D as the hypotenuse, so we have D2 = d2 + s2. As calculated above, d2 = 2s2, so we get D2 = 2s2 + s2 = 3s2.
- For example, let's say the length of the diagonal from one corner of the cube to the opposite corner on the top face is 10 meters. To calculate the volume, we substitute 10 for "D" in the formula as follows:
- D2 = 3s2.
- 102 = 3s2.
- 100 = 3s2
- 33.33 = s2
- 5.77 m = s. Now, all we need to do to find the volume of the cube is to cube the side length.
- 5.773 = 192.45 m3
