Today, Mytour will show you how to compile a C program from source code using GNU (which stands for GNU Compiler Collection, abbreviated as GCC) – a compiler for Linux and Minimalist GNU (MinGW) for Windows.
Steps
Using GCC on Unix
Open the Unix Terminal window. This icon is usually dark green with white characters.
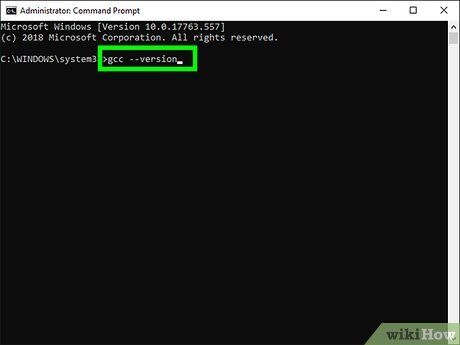
Type gcc --version and press ↵ Enter. This will return the version number of the C compiler. If the command is not found, it may indicate that the GNU compiler is not installed.
- If that’s the case, check your Linux distribution documentation for instructions on installing the appropriate package.
- If you are compiling a C++ program, use “g++” instead of “gcc.”
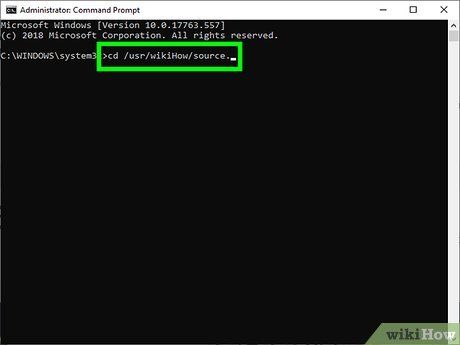
Navigate to the directory where your source code is saved.
- For example, if the source file “main.c” is located at /usr/Mytour/source, enter cd /usr/Mytour/source.
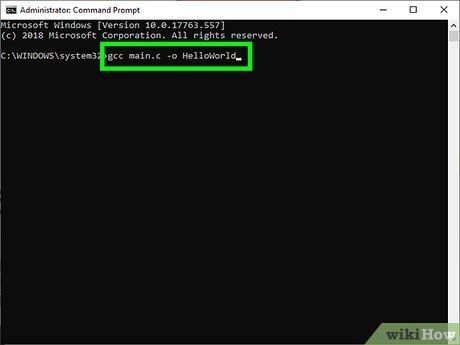
Type the command gcc main.c –o HelloWorld. Replace “main.c” with the name of your source file and “HelloWorld” with the name of the resulting program. The compilation will proceed.
- If you encounter an error message and need more information about the issue, use the command gcc -Wall -o errorlog file1.c. Then, review the contents of the “errorlog” file in your current directory using the command cat errorlog.
- To compile a program from multiple source files, use the command gcc -o outputfile file1.c file2.c file3.c.
- To compile several programs with multiple source files simultaneously, use the command gcc -c file1.c file2.c file3.c.
Launch the program you’ve just compiled. Enter the command &# 46;/HelloWorld, making sure to replace “HelloWorld” with the name of your program.
Using MinGW on Windows

Download Minimalist GNU for Windows (MinGW). This is a very easy-to-install version of GCC for Windows. You can download the installer from https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/.
Run the MinGW installer.
- If the file doesn’t open automatically, double-click on it in your downloads folder and click Install.
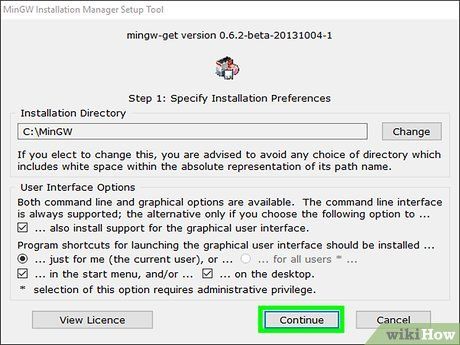
Customize the installation process and click Continue (Continue).
- MinGW recommends that users stick with the default installation directory (C:\MinGW). If you need to change it, avoid using directories with spaces in their names (e.g., “Program Files”).
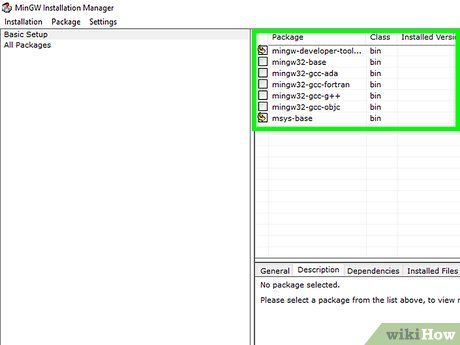
Select the compiler to install.
- For basic needs, you can choose Basic Setup in the left frame and check all the listed compilers in the main right frame.
- Advanced users can opt for All Packages to install additional compilers and tools.
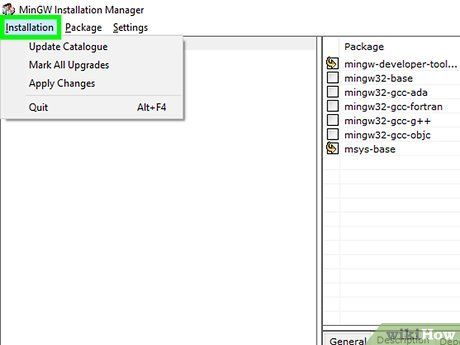
Click on the Installation menu in the top left corner of MinGW.
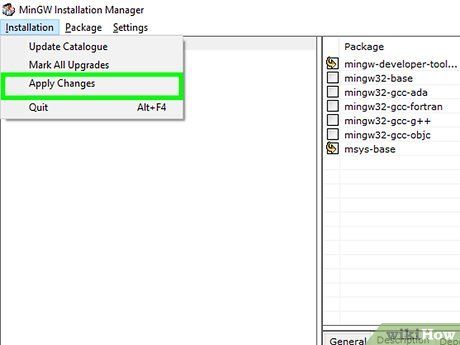
Click on Apply Changes to confirm the changes.
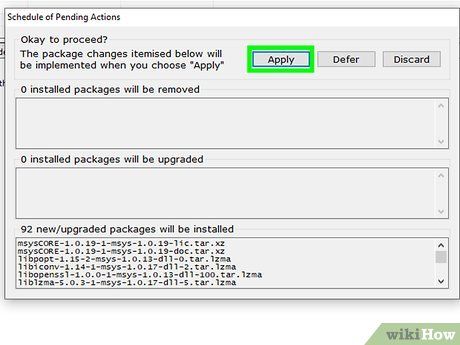
Click on Apply. The installer will begin downloading and installing.
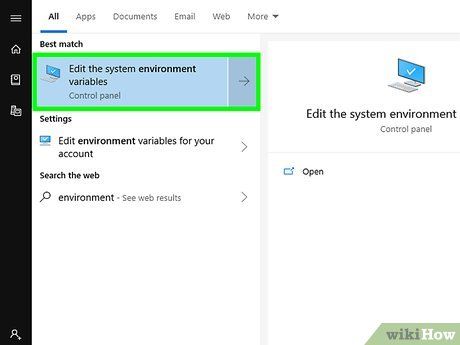
Add the path to MinGW to the system environment variables by:
- Press ⊞ Win+S to open the search bar, then type environment.
- Click on Edit the system environment variables from the search results.
- Click on Environment Variables
- Click Edit below the top section (under “User Variables”)
- Scroll down to the “Variable Value” field.
- Append ;C:\MinGW\bin to the end of the existing text. Note: If MinGW is installed in a different folder, enter ;C:\path-to-that-directory\bin, replacing “path-to-that-directory” with the actual directory path.
- Click OK twice. Then click the final OK to close the window.
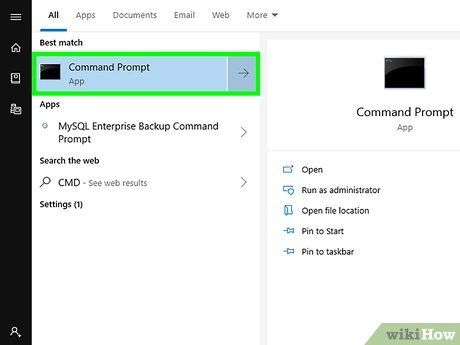
Open Command Prompt with Administrator privileges. To proceed, follow these steps:
- Press ⊞ Win+S and type cmd.
- Right-click on Command Prompt in the search results, then select Run As Administrator.
- Click Yes to allow changes.
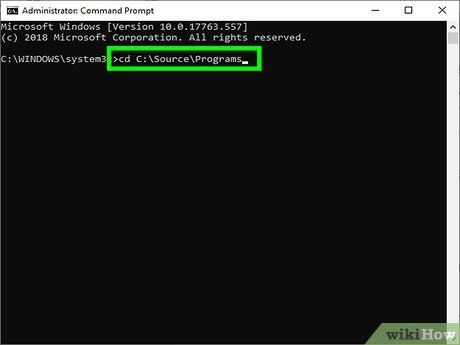
Navigate to the directory where your source code is stored.
- For example, if your source file is named helloworld.c and located in C:\Source\Programs, you would type cd C:\Source\Programs.
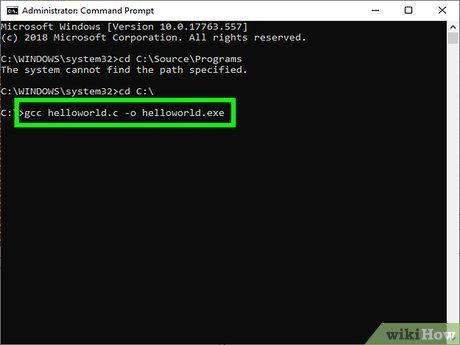
Enter the command gcc helloworld.c –o helloworld.exe. Replace 'helloworld' with your source file and application name. After the program is compiled, you should return to the command prompt without encountering errors.
- Any programming errors must be addressed before proceeding with compilation.
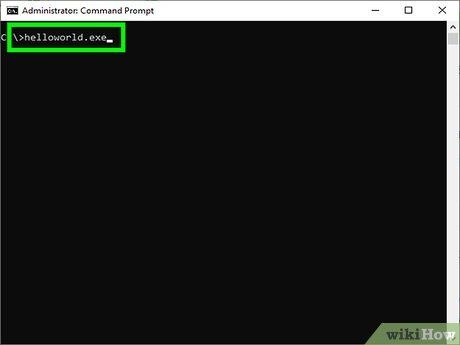
Enter the name of the program to launch. For example, if the program is named helloworld.exe, you must enter this command to start the program.
Advice
- Building code with the -g flag will generate debugging information that can be used by the GDB debugger for better performance.
- A makefile can be created to simplify the compilation of larger programs.
- Be cautious with heavy optimization as it may trade speed for size or even accuracy in the program.
- When compiling C++ programs, you can use G++ just like GCC. Note: C++ files have a .cpp extension instead of .c.
What you need
- A computer running Linux or Windows operating system
- Basic knowledge of GNU/Linux and how to install applications.
- Source code
- A text editor (e.g., Emacs, vi)
