Today, Mytour will show you how to create a column-style probability distribution chart (histogram) in Microsoft Excel. A probability distribution chart is a column graph that displays frequency data, allowing you to calculate metrics like the number of people who achieved a specific score in an exam.
Steps
Enter data

Open Microsoft Excel. The app features a white "X" on a green background. The Excel spreadsheet page will open.
- On a Mac, this step may open a new blank worksheet. If this is the case, simply skip the next step.
Create a new document. Click on Blank workbook in the top-left corner of the window (Windows), or click on File and select New Workbook (Mac).
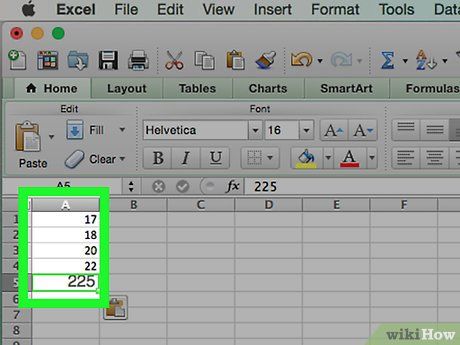
Identify the smallest and largest data points. This is crucial for determining the count in each bin and how many bins are needed.
- For instance, if your data range is from 17 to 225, then the smallest data point is 17, and the largest is 225.
Determine the number of bins you need. Bins are used to group data in a probability distribution chart. The easiest way to calculate the number of bins is to divide the largest data point (in this case, 225) by the number of data points in the chart (for example, 10), then round up or down to the nearest integer. However, it's rare to have fewer than 10 or more than 20 bins. You can use the formula if you're unsure:
- Sturges' formula: K = 1 + 3.322 * log(N) where K is the number of bins, and N is the number of data points. After finding K, round it to the nearest integer. Sturges' formula is best suited for linear or 'clean' datasets.
- Rice's formula: cube root of (data points) * 2 (for a dataset with 200 points, find the cube root of 200, then multiply the result by 2). This formula works best for erratic or inconsistent data.
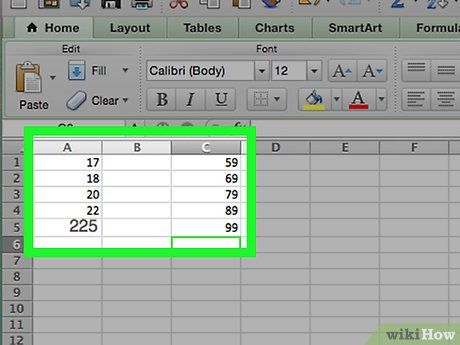
Determine the count in each bin. Now that you've identified the number of bins, you can create the most evenly distributed set of data. The count in each bin includes both the largest and smallest data points, and the range will increase in a linear fashion.
- For example, when creating data for a probability distribution chart showing test scores, you'll almost always use a step of 1 to represent different score ranges (e.g., 5, 6, 7, 8, 9).
- Increasing multiples of 10, 20, or even 100 is a standard practice for counts in each bin.
- If there are outliers, you can place them outside the bin range or adjust the count range to accommodate the outliers.
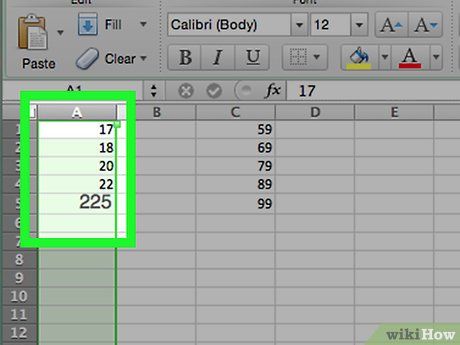
Enter data into the column. Type each data point into a separate cell in column A.
- For example, if you have 40 data points, you can input each corresponding number in cells from A1 to A40.
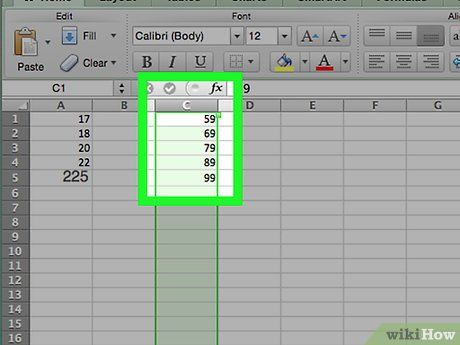
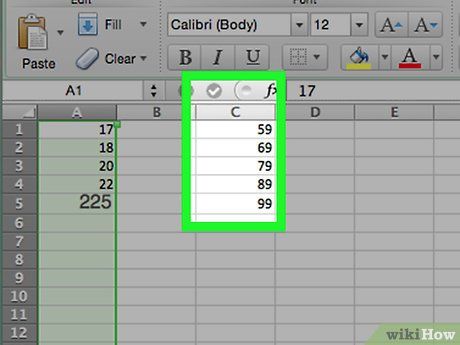
Enter the counts for each bin in column C if you're using a Mac. Starting from cell C1, input each bin's count into its corresponding cell. Once this step is complete, you can proceed with creating the probability distribution chart.
- Skip this step on Windows computers.
Create a chart on Windows
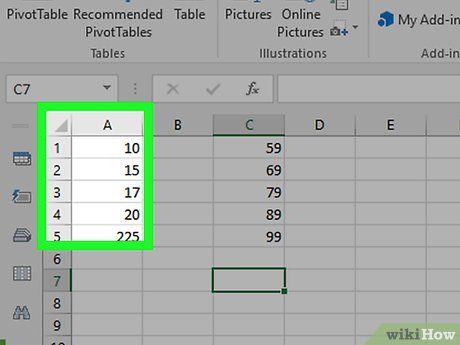
Select the data. Click on the top cell in column A, then hold down the ⇧ Shift key while clicking on the last cell containing data in column A.
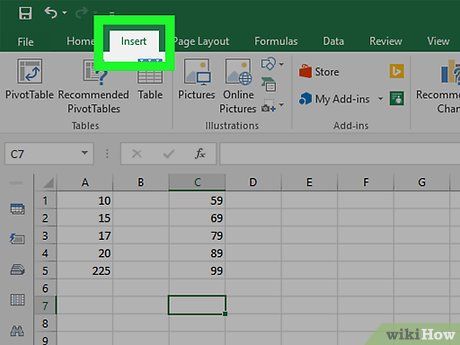
Click on the Insert tab in the green ribbon at the top of the Excel window. The toolbar at the top of the window will switch to display options in the Insert tab.
Click on the Recommended Charts option. This option is located in the "Charts" section of the Insert tab. A window will pop up.
Click on the All Charts tab. This tab is located at the top of the popup window.
Click on the Histogram option on the left side of the window.
Select the Histogram template. Click on the bar chart icon located just to the left to choose the Histogram template (not the Pareto chart), then click OK. A simple probability distribution chart will be generated based on the data you selected.
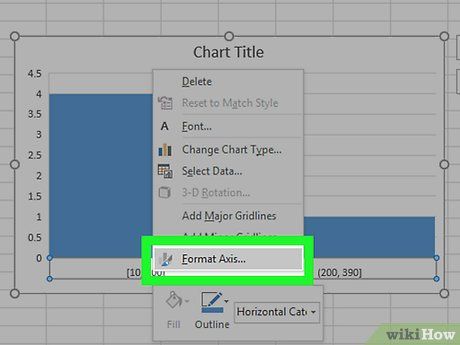
Open the horizontal axis menu. Right-click on the horizontal axis (the axis containing the data ranges), select Format Axis... from the dropdown menu, and choose the bar chart icon from the 'Format Axis' menu that appears on the right side of the window.
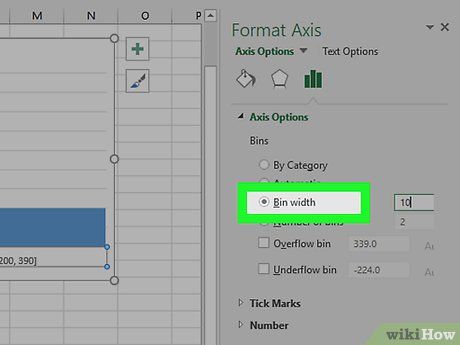
Check the "Bin width" box in the middle of the menu.
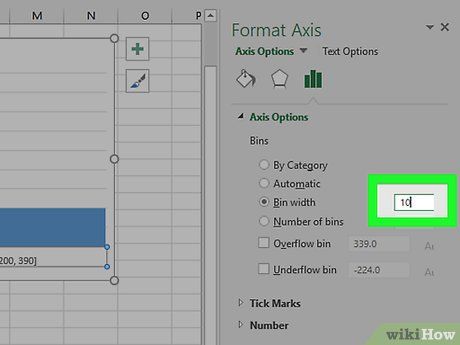
Enter the count interval for each bin. Input the value for the bin width in the 'Bin width' field, then press ↵ Enter. Excel will automatically format the histogram chart to display the appropriate count in each column based on the data.
- For example, if you use bins with an increment of 10, enter 10 here.
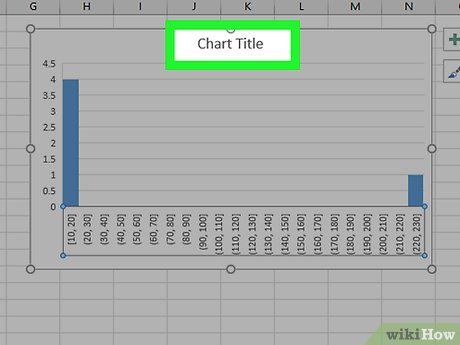
Label the chart. This step is only necessary if you want to add titles to the axes or the entire chart:
- Axis Title - Click the green + sign to the right of the chart, check the 'Axis Titles' box, click on the 'Axis Title' text box on the left or bottom of the chart, then enter your desired title.
- Chart Title - Click on the 'Chart Title' text box at the top of the histogram chart and enter your preferred title.
Save the histogram chart. Press Ctrl+S, choose the save location, enter your desired file name, and click Save.
Create a chart on Mac
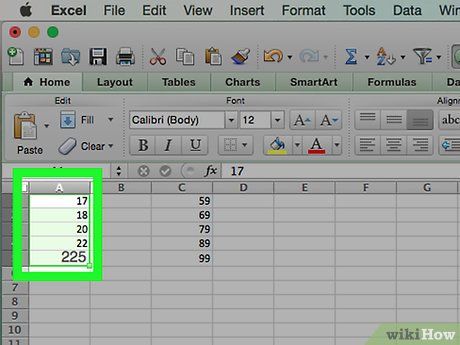
Select the data and bins. Click the top cell in column A to select it, then hold the ⇧ Shift key while clicking the C cell on the same row as A that contains the last value. All corresponding data and count values for each bin will be highlighted.
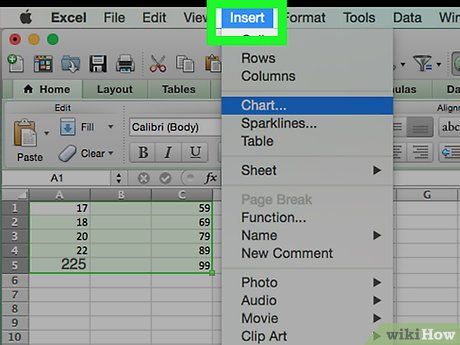
Click on the Insert tab located in the green ribbon at the top of the Excel window.
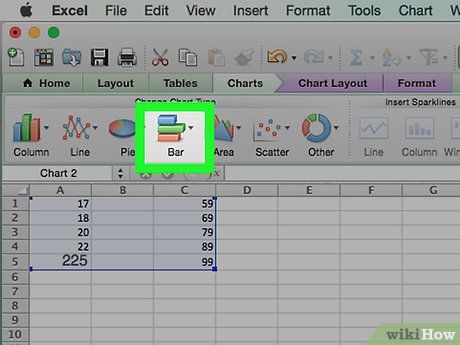
Click on the column chart icon. This option can be found in the 'Charts' section of the Insert toolbar. A window will pop up.
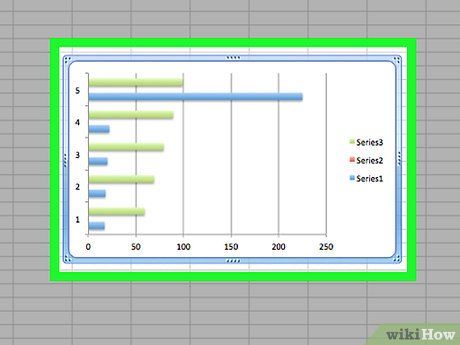
Click on the "Histogram" icon. This group of green columns is located under the "Histogram" title. A probability distribution chart will be created based on the data and the counts in each bin.
- Make sure you don't accidentally click on the "Pareto" icon, which is a set of green columns with an orange line.
Review the probability distribution chart. Before saving, take a moment to ensure that the chart is correct. If not, you may need to adjust the bin counts and recreate the chart.
Save your session. Press ⌘ Command+S, enter the desired file name, choose a location to save (if necessary), and click Save.
Advice
- The bins can be wide or narrow, as long as they match the data and do not exceed a reasonable number of bins for this dataset.
Warning
- Ensure that the histogram is appropriate before drawing any conclusions.
