Superscripts and subscripts allow you to type characters that appear above or below the regular text line. These smaller characters are typically used for footnotes, annotations, and mathematical symbols. You can easily switch between superscripts, subscripts, and normal text in Microsoft Word.
Steps
Superscript
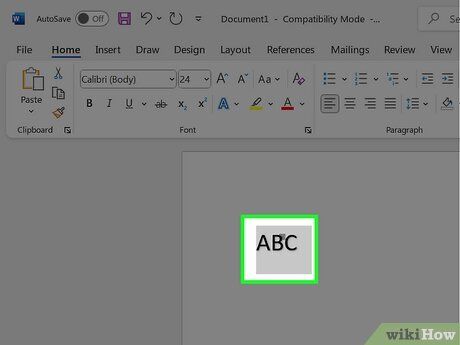
Select the text you want to convert into superscript. Alternatively, place the cursor where you want to begin typing in superscript.
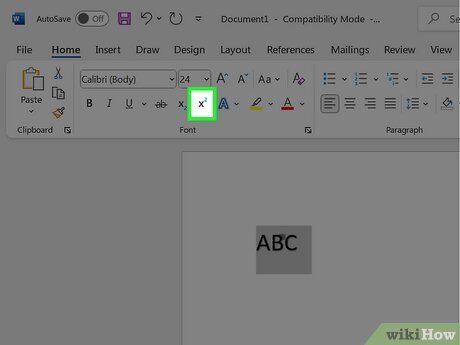
Enable superscript. The highlighted text will be converted into superscript, or you can start typing superscript at the cursor's location. Here are a few ways to activate superscript:
- Click the x² button in the Font section of the Home tab.
- Click the Format menu, select Font, and check the "Superscript" box.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Equals (=) key.
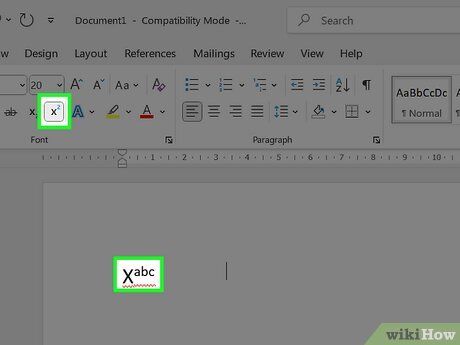
Disable superscript. Once superscript is applied, you can turn it off by following the same steps as for enabling it. This will return the text to its normal formatting.
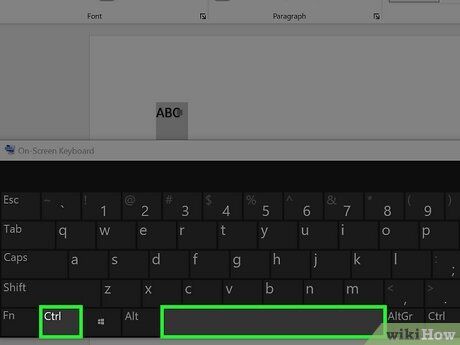
Remove superscript or subscript. You can revert the text to normal formatting by selecting the text and pressing Ctrl + Space.
Subscript
Select the text you want to change to subscript. Alternatively, place the cursor where you want to start typing in subscript.
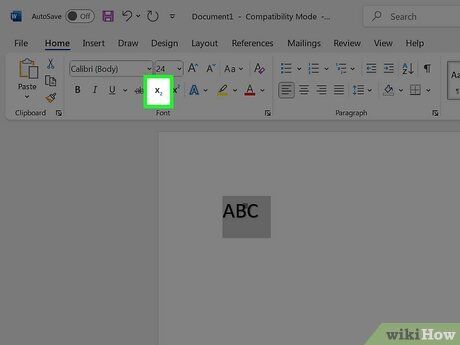
Enable Subscript. The highlighted text will change to subscript, or you can begin typing in subscript at the cursor's location. Here are a few ways to enable subscript:
- Click the x₂ button in the Font options on the Home tab.
- Click the Format menu, select Font, and check the 'Subscript' box.
- Press Ctrl + Equals sign.
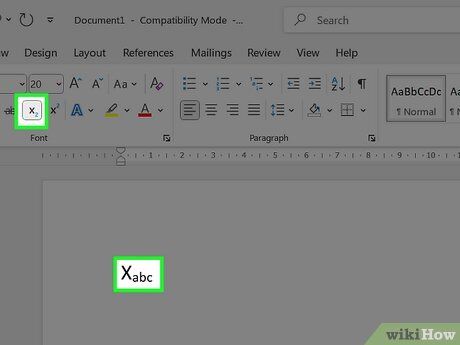
Disable Subscript. After applying subscript, you can disable the feature the same way you enabled it. This will return the text to normal formatting.
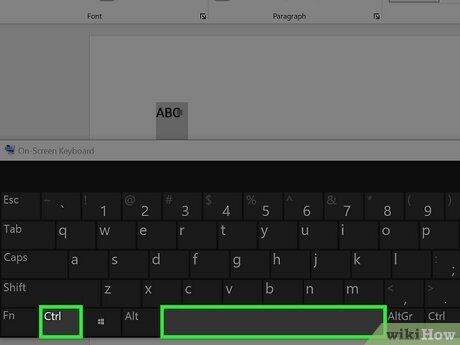
Remove Superscript or Subscript. If you no longer want the text to appear as superscript or subscript, simply select the text and press Ctrl + Space.
