This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to delete files on your computer using Command Prompt commands.
Steps
Preparing to Delete Files
Locate the file. If you know where the file is stored, simply open the folder containing it. For example, if you want to delete a photo or a text file, navigate to the default "Documents" folder, which is typically where such files are stored.
- If you're unsure of the file's location, type the file name into the Start search bar, then right-click on the file when it appears, and select Open file location to be directed straight to the folder where the file is stored.
Click and drag the file to your computer's desktop. This makes the deletion process easier since you won't need to rename the folder containing the file in Command Prompt.
- There's one exception to this rule: if you're attempting to delete a file from the "System32" folder, which houses Windows system files. In this case, do not move the file.
Right-click the file. A list of options will appear on the screen.
Click on Properties at the bottom of the displayed menu.
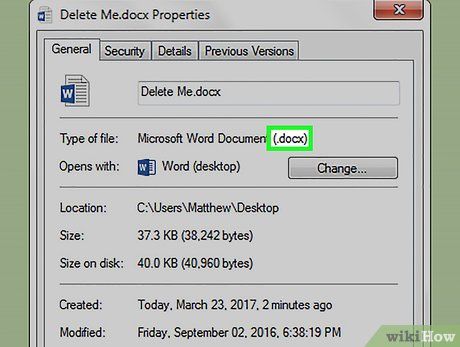
Check the file extension. The file extension appears near the top of the "General" tab in the "Properties" window, to the right of the "Type of file:" line. Knowing the file extension is essential for deleting the file in Command Prompt. Here are some common file extensions:
- .txt - Text file (created in Notepad).
- .docx - Microsoft Word file.
- .jpg or .png - Image file.
- .mov, .wmv, .mp4 - Video file.
- .mp3, .wav - Audio file.
- .exe - Executable file (such as an installation file).
- .lnk - Shortcut file. Deleting a program's shortcut will not uninstall the program from your computer.
Note down the file extension. Once you know the extension, you're ready to open and use Command Prompt.
Deleting Files Using Command Prompt
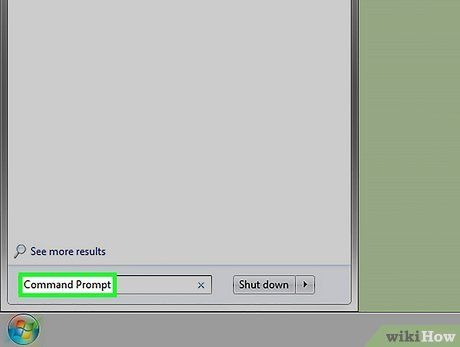
Open Command Prompt. In this case, avoid using the "Administrator" version of Command Prompt unless you intend to delete files in the "System32" folder. You can open Command Prompt in various ways depending on your Windows operating system:
- Hold the ⊞ Win key and press X, then click Command Prompt above the Start button.
- Right-click the Start button in the bottom-left corner of the screen, then select Command Prompt from the menu.
- Type "Command Prompt" into the Start menu search bar (for Windows 8, move your cursor to the top-right corner of the screen and click the magnifying glass icon), then click the "Command Prompt" icon when it appears.
- Open the "Run" app from the Start menu, type "cmd," and click OK.
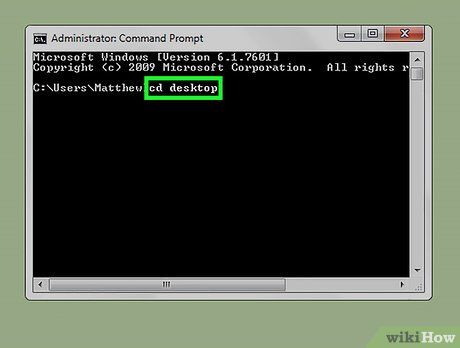
Type cd desktop and press ↵ Enter. This changes the location (or "directory") in Command Prompt to your computer's desktop folder.
- You can use other methods to change directories in Command Prompt if needed.
- Opening Command Prompt in "Administrator" mode will set the directory to the "System32" folder. Therefore, avoid using Administrator mode unless your file is stored in the "System32" folder.
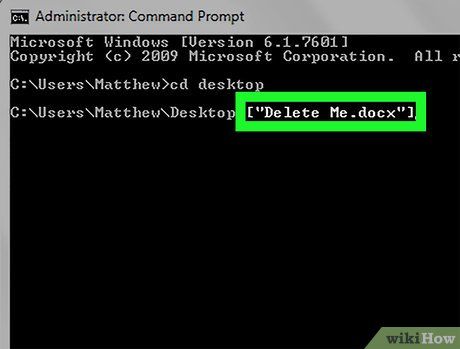
Type del [filename.filetype]. Replace "filename.filetype" with the name and extension of the file you want to delete.
- For example, if the image file is named "icecream," you would type icecream.png; for a text file named "notes," the command would be notes.txt.
- For filenames with spaces, enclose the name in quotes: "I like turtles.jpg" instead of I_like_turtles.jpg.
- To delete all files with the same extension on your desktop (e.g., all text files), type *.filetype, replacing "filetype" with the file extension (e.g., *.txt).
Press ↵ Enter. A new line will appear in Command Prompt, indicating that your file has been deleted.
- Since the "del" command permanently removes the file from your hard drive, you won't need to empty the Recycle Bin afterward.
Tips
- It's recommended to use your system's file management program for deleting files and only resort to Command Prompt when stronger measures are required.
Warnings
- Deleting even a single system file can cause your computer to stop functioning.
- Using Command Prompt to delete files bypasses the Recycle Bin, meaning the files are permanently removed.
